Tennessee’s landscape is a vibrant tapestry, from the majestic Great Smoky Mountains to the rich lowlands along the Mississippi. This incredible biodiversity is a source of pride, yet it faces constant threats from external forces, particularly those that disrupt its delicate balance.
To help shed light on one of these critical challenges, we’ve compiled a definitive resource. Below, you’ll find a list detailing 86 Invasive Species in Tennessee, showcasing a wide range from the pervasive Air Potato to the aquatic Zebra Mussel. For each, we’ve organized essential information by its Scientific Name, Type, Primary Impact, and Origin, offering a comprehensive look at these ecological disruptors.
What exactly is an invasive species?
An invasive species is defined as a non-native organism (animal, plant, or microorganism) that, when introduced to a new ecosystem, causes or is likely to cause economic or environmental harm or harm to human health. Unlike simply non-native species, invasives aggressively outcompete local flora and fauna, disrupt food webs, and can drastically alter habitats, threatening biodiversity.
Why is it important to monitor invasive species in Tennessee?
Monitoring Invasive Species in Tennessee is critical for protecting the state’s unique ecosystems and economic interests. Early detection allows for more effective control and eradication efforts, preventing widespread ecological damage, preserving native wildlife and plant populations, and safeguarding industries like agriculture, forestry, and tourism, which can be severely impacted by these intruders.
Invasive Species in Tennessee
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Type | Primary Impact | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kudzu | Pueraria montana | Plant | Smothers and kills native trees and vegetation by blocking all sunlight. | East Asia |
| Emerald Ash Borer | Agrilus planipennis | Insect | Larvae feed under bark, killing nearly all North American ash tree species. | Northeastern Asia |
| Feral Hog | Sus scrofa | Mammal | Destroys crops and native habitats with destructive rooting behavior; can spread disease. | Eurasia |
| Silver Carp | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Fish | Outcompetes native fish for plankton and poses a physical danger by leaping from water. | China |
| Zebra Mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | Mollusk | Clogs water intake pipes and outcompetes native mussels for food and habitat. | Eastern Europe (Caspian Sea region) |
| Bush Honeysuckle | Lonicera maackii | Plant | Forms dense thickets that shade out native wildflowers and prevent forest regeneration. | East Asia |
| Spotted Lanternfly | Lycorma delicatula | Insect | Damages crops and trees by feeding on sap; secretes sticky “honeydew” promoting mold. | China |
| Tree-of-Heaven | Ailanthus altissima | Plant | Releases chemicals that inhibit other plants; is the preferred host for Spotted Lanternfly. | China |
| Chinese Privet | Ligustrum sinense | Plant | Forms impenetrable thickets in forest understories, displacing nearly all native vegetation. | China |
| Hemlock Woolly Adelgid | Adelges tsugae | Insect | Sucks sap from hemlock trees, leading to needle loss and eventual tree death. | East Asia (Japan) |
| Garlic Mustard | Alliaria petiolata | Plant | Releases chemicals that disrupt soil fungi essential for native tree seedling survival. | Europe |
| Japanese Stiltgrass | Microstegium vimineum | Plant | Forms dense mats in shaded areas, smothering native plants and inhibiting tree regeneration. | East Asia |
| Brown Marmorated Stink Bug | Halyomorpha halys | Insect | Feeds on a wide variety of agricultural crops; becomes a major household nuisance. | East Asia |
| Bighead Carp | Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | Fish | A massive filter feeder that strips the food web of plankton, starving native fish. | China |
| Northern Snakehead | Channa argus | Fish | A voracious top predator that can displace native fish species and alter ecosystems. | East Asia |
| Red Imported Fire Ant | Solenopsis invicta | Insect | Delivers painful, venomous stings and builds large mounds that damage equipment. | South America |
| Mimosa Tree | Albizia julibrissin | Plant | Invades roadsides and riverbanks, forming dense stands that displace native vegetation. | Asia (Iran to Japan) |
| Bradford Pear | Pyrus calleryana ‘Bradford’ | Plant | Cross-pollinates with other varieties, creating thorny, invasive thickets that choke out native species. | China, Vietnam |
| Multiflora Rose | Rosa multiflora | Plant | Creates dense, impenetrable thorny thickets that degrade pastureland and wildlife habitat. | Japan, Korea, China |
| Japanese Honeysuckle | Lonicera japonica | Plant | A climbing vine that smothers and strangles small trees and native understory plants. | East Asia |
| Chestnut Blight | Cryphonectria parasitica | Fungus | Functionally eliminated the American chestnut, a keystone tree species, from eastern forests. | Asia |
| Round Goby | Neogobius melanostomus | Fish | Aggressively competes with native bottom-dwelling fish for food and spawning sites. | Black and Caspian Seas |
| English Ivy | Hedera helix | Plant | Forms a dense “ivy desert” on forest floors and smothers trees. | Europe, Western Asia |
| Wintercreeper | Euonymus fortunei | Plant | Forms a dense groundcover that eliminates native wildflowers; can climb and smother trees. | East Asia |
| Princess Tree | Paulownia tomentosa | Plant | Extremely fast-growing tree that colonizes disturbed areas, displacing native pioneer species. | China |
| Didymo (Rock Snot) | Didymosphenia geminata | Algae | Forms thick, disgusting brown mats on river bottoms, smothering habitat for aquatic insects. | Northern Hemisphere (invasive strains) |
| Chinese Yam | Dioscorea oppositifolia | Plant | Vines climb high into trees, weighing them down and blocking sunlight from the forest floor. | China |
| Japanese Knotweed | Reynoutria japonica | Plant | Forms dense monocultures with a root system that can damage pavement and foundations. | East Asia |
| Spongy Moth | Lymantria dispar | Insect | Caterpillars can defoliate and kill hundreds of species of hardwood trees and shrubs. | Eurasia |
| Autumn Olive | Elaeagnus umbellata | Plant | Outcompetes native plants by fixing nitrogen, altering soil chemistry for its own benefit. | East Asia |
| Sericea Lespedeza | Lespedeza cuneata | Plant | Forms dense stands in open areas, displacing native grasses and forbs. | East Asia |
| Cogongrass | Imperata cylindrica | Plant | Forms dense, circular stands that exclude all other vegetation and are highly flammable. | Southeast Asia |
| Porcelain Berry | Ampelopsis brevipedunculata | Plant | A vigorous vine that smothers shrubs and small trees under a dense blanket of leaves. | Northeast Asia |
| Oriental Bittersweet | Celastrus orbiculatus | Plant | Twines tightly around trees, girdling their trunks and weighing down canopies. | East Asia |
| New Zealand Mud Snail | Potamopyrgus antipodarum | Mollusk | Reaches enormous densities, outcompeting native snails and insects for food. | New Zealand |
| Rusty Crayfish | Faxonius rusticus | Crustacean | Aggressively displaces native crayfish and destroys aquatic plant beds with its foraging. | Ohio River Basin (invasive in TN streams) |
| Nutria | Myocastor coypus | Mammal | Destroys wetland habitats and riverbanks by eating native plants and burrowing. | South America |
| Dogwood Anthracnose | Discula destructiva | Fungus | Causes leaf spots, stem cankers, and dieback in flowering dogwood trees, a state symbol. | Origin uncertain, likely Asia |
| Thousand Cankers Disease | Geosmithia morbida | Fungus | A fungal disease spread by the Walnut Twig Beetle that is lethal to black walnut trees. | Western United States |
| Common Reed | Phragmites australis | Plant | Forms massive, dense stands in wetlands, crowding out native vegetation like cattails. | Eurasia (invasive subspecies) |
| Amur Corktree | Phellodendron amurense | Plant | Spreads into forests, creating dense shade that inhibits the growth of native seedlings. | Eastern Asia |
| Japanese Spirea | Spiraea japonica | Plant | Forms dense stands along streams and forest edges, displacing native shrubs and herbs. | Japan, China, Korea |
| Periwinkle | Vinca minor | Plant | Forms a dense, evergreen mat on the forest floor, completely smothering native wildflowers. | Europe, Southwest Asia |
| Asian Longhorned Beetle | Anoplophora glabripennis | Insect | Larvae tunnel deep into hardwood trees, eventually killing them. Prefers maples. | East Asia |
| Spiny Water Flea | Bythotrephes longimanus | Crustacean | A predatory zooplankton that alters food webs and fouls fishing lines with its long tail spine. | Northern Europe, Asia |
| Asian Tiger Mosquito | Aedes albopictus | Insect | An aggressive daytime biter that can transmit numerous diseases like West Nile virus. | Southeast Asia |
| Callery Pear | Pyrus calleryana | Plant | The species name for ornamental pears like ‘Bradford’ that create invasive thickets. | China, Vietnam |
| Hydrilla | Hydrilla verticillata | Plant | Forms dense underwater mats that choke waterways, block sunlight, and impede recreation. | Asia |
| Parrot Feather | Myriophyllum aquaticum | Plant | An aquatic plant that forms dense mats, clogging waterways and shading out native aquatic plants. | Amazon River Basin |
| Yellow Flag Iris | Iris pseudacorus | Plant | Forms dense colonies in wetlands and along shorelines, displacing native wetland vegetation. | Europe, Western Asia, North Africa |
| Eurasian Watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum | Plant | Forms dense underwater canopies, crowding out native plants and hindering recreational activities. | Europe, Asia, North Africa |
| Curly Pondweed | Potamogeton crispus | Plant | Grows early in the season, forming dense mats that die back, causing oxygen depletion. | Eurasia |
| Purple Loosestrife | Lythrum salicaria | Plant | Dominates wetlands, marshes, and stream banks, replacing native vegetation. | Eurasia |
| Beefsteak Plant | Perilla frutescens | Plant | Invades shady, moist bottomlands and stream banks, displacing native herbaceous plants. | East Asia |
| Japanese Hops | Humulus japonicus | Plant | A fast-growing vine that smothers low-growing vegetation and small trees along riverbanks. | East Asia |
| Mile-a-Minute Weed | Persicaria perfoliata | Plant | Grows incredibly fast, smothering young trees, native plants, and reforestation projects. | India, East Asia |
| Russian Olive | Elaeagnus angustifolia | Plant | Outcompetes native vegetation along rivers and streams, forming dense, thorny thickets. | Europe and Asia |
| Saltcedar | Tamarix spp. | Plant | Consumes large amounts of water, dries up soils, and deposits salt on the surface. | Eurasia |
| Sweet Autumn Clematis | Clematis terniflora | Plant | A vigorous vine that can completely cover and smother native trees and shrubs. | Japan, China |
| Norway Maple | Acer platanoides | Plant | Creates dense shade that is too dark for native maple seedlings and wildflowers to grow. | Europe |
| Siberian Elm | Ulmus pumila | Plant | Invades prairies and open lands, outcompeting native grasses and shrubs. | Eastern Asia |
| White Mulberry | Morus alba | Plant | Hybridizes with the native Red Mulberry, threatening the genetic integrity of the native species. | China |
| Japanese Barberry | Berberis thunbergii | Plant | Forms dense, spiny thickets in forests and creates ideal habitat for ticks. | Japan |
| Burning Bush | Euonymus alatus | Plant | Invades forests and fields, forming dense thickets that shade out native plants. | Northeast Asia |
| Chocolate Vine | Akebia quinata | Plant | A fast-growing vine that smothers and kills shrubs and trees. | East Asia |
| Liriope (Monkey Grass) | Liriope muscari / spicata | Plant | Spreads from gardens into forests, forming a dense monoculture that displaces native flora. | East Asia |
| Golden Bamboo | Phyllostachys aurea | Plant | An extremely aggressive running bamboo that forms dense, impenetrable groves. | Southeast China |
| Daphne Spurge | Daphne laureola | Plant | An evergreen shrub that invades forests, forming dense stands. All parts are highly toxic. | Europe, North Africa |
| Chinese Silvergrass | Miscanthus sinensis | Plant | Forms large, dense clumps that displace native vegetation and create a fire hazard. | East Asia |
| Air Potato | Dioscorea bulbifera | Plant | A highly aggressive vine that smothers native vegetation, including mature trees. | Asia, Africa |
| Goldfish | Carassius auratus | Fish | Can disrupt aquatic ecosystems by stirring up sediment and preying on native invertebrates. | East Asia |
| Rock Bass (Shadow Bass) | Ambloplites rupestris | Fish | Invasive outside its native TN range, it outcompetes and preys on native fish. | Native to East TN, invasive in Central/West |
| White Perch | Morone americana | Fish | A prolific fish that can outcompete native species and impact sportfish populations. | Atlantic Coast of North America |
| Alewife | Alosa pseudoharengus | Fish | Can outcompete young native fish for zooplankton and cause thiamine deficiency in predators. | Atlantic Coast of North America |
| Whirling Disease | Myxobolus cerebralis | Parasite | A microscopic parasite that deforms and kills young trout and salmon. | Eurasia |
| Dutch Elm Disease | Ophiostoma ulmi / novo-ulmi | Fungus | A fungal disease spread by bark beetles that has devastated American elm populations. | Asia |
| Laurel Wilt | Raffaelea lauricola | Fungus | A deadly disease of plants in the laurel family, spread by the redbay ambrosia beetle. | Asia |
| Sirex Woodwasp | Sirex noctilio | Insect | Females inject a toxic mucus and fungus while laying eggs, killing pine trees. | Europe, Asia, North Africa |
| Sudden Oak Death | Phytophthora ramorum | Pathogen | A water mold (oomycete) that causes lethal cankers on oaks and blights on other plants. | Origin Unknown |
| Viburnum Leaf Beetle | Pyrrhalta viburni | Insect | Larvae and adults skeletonize the leaves of viburnum shrubs, eventually killing them. | Europe |
| Beech Bark Disease | Nectria coccinea faginata | Disease Complex | An insect-fungus complex that kills mature American beech trees, altering forest composition. | Europe |
| Asian Needle Ant | Brachyponera chinensis | Insect | A venomous, stinging ant that displaces native ants and can cause allergic reactions. | East Asia |
| Common House Sparrow | Passer domesticus | Bird | Aggressively displaces native cavity-nesting birds like bluebirds and swallows from nest sites. | Eurasia |
| European Starling | Sturnus vulgaris | Bird | Outcompetes native birds for nest cavities and forms massive, noisy, and messy roosts. | Eurasia |
| Rock Pigeon | Columba livia | Bird | Their droppings can damage buildings and pose a health risk in urban areas. | Europe, North Africa, Middle East |
| Mute Swan | Cygnus olor | Bird | Aggressively defends territory, displacing native waterfowl. Overgrazes aquatic vegetation. | Eurasia |
Images and Descriptions

Kudzu
A notoriously fast-growing vine with large, three-lobed leaves. It can grow up to a foot a day, completely blanketing trees, buildings, and utility poles in a dense green carpet.

Emerald Ash Borer
A small, jewel-like metallic green beetle. While the adults cause little damage, their D-shaped exit holes are a key sign of a deadly infestation by their destructive larvae.

Feral Hog
A highly intelligent and adaptable wild pig with coarse hair and sharp tusks. They travel in groups called sounders and can cause immense agricultural and ecological damage overnight.

Silver Carp
A large, deep-bodied fish known for its startling habit of jumping high out of the water when disturbed by boat motors. They are voracious filter feeders that disrupt aquatic food webs.

Zebra Mussel
A tiny, D-shaped freshwater mussel with alternating light and dark stripes. They attach to hard surfaces in massive, dense colonies, causing major biofouling problems for infrastructure.

Bush Honeysuckle
A large, multi-stemmed shrub with arching branches and fragrant, white-to-yellow flowers. Its early leaf-out and late leaf-drop give it a competitive advantage over native plants.

Spotted Lanternfly
A visually striking planthopper with gray, spotted forewings and vibrant red hindwings. Despite its beauty, it’s a major pest of grapevines, fruit trees, and hardwoods like maple.

Tree-of-Heaven
A fast-growing tree with large, compound leaves that resemble sumac. It has a strong, unpleasant odor often compared to rancid peanut butter and spreads aggressively through suckers.

Chinese Privet
A semi-evergreen shrub with small, dark green leaves and clusters of small white flowers. It is one of the most problematic invasive plants in Tennessee’s forests and bottomlands.

Hemlock Woolly Adelgid
A tiny, aphid-like insect that covers itself with a white, waxy “wool” for protection. This pest is responsible for the widespread decline of Eastern and Carolina hemlocks.

Garlic Mustard
A biennial herb that dominates forest floors. In its first year, it’s a low rosette; in its second, it bolts up with white flowers. Crushed leaves smell strongly of garlic.

Japanese Stiltgrass
A sprawling, shade-tolerant annual grass with a distinctive silvery, off-center stripe down its pale green leaves. It rapidly colonizes disturbed areas, trails, and forest floors.

Brown Marmorated Stink Bug
A shield-shaped insect with a mottled brownish-gray color. It is known for its ability to damage fruit and for invading homes in large numbers during the fall to overwinter.

Bighead Carp
Similar to Silver Carp but even larger, with a distinctly large head and downward-facing eyes. They are a primary component of the “Asian Carp” threat to Tennessee’s large river systems.

Northern Snakehead
A long-bodied, predatory fish with sharp teeth and a snake-like pattern. It can breathe air, allowing it to survive on land for short periods and move between water bodies.

Red Imported Fire Ant
An aggressive reddish-brown ant that swarms to attack any disturbance to its mound. Its sting causes a painful pustule and can be dangerous to humans, pets, and wildlife.

Mimosa Tree
A small, umbrella-shaped tree prized for its feathery, fern-like leaves and fragrant, pink, pom-pom-like flowers. It spreads prolifically via long-lived seeds.

Bradford Pear
A once-popular ornamental tree with weak branches and showy white spring blossoms. Its offspring revert to a wild, thorny form that creates impenetrable and ecologically sterile stands.

Multiflora Rose
A vigorous, climbing shrub that can form massive mounds. It features clusters of small, fragrant white flowers and is armed with sharp, curved thorns, making it difficult to control.

Japanese Honeysuckle
A common, sweet-smelling vine with paired, oval leaves and tubular white-to-yellow flowers. It grows aggressively, twining around other plants and forming dense groundcover that eliminates native species.

Chestnut Blight
A devastating fungal pathogen that enters wounds in the bark of chestnut trees. It creates cankers that girdle and kill the tree, forever changing the composition of Appalachian forests.

Round Goby
A small, mottled brown fish with a large head and a unique, single pelvic fin shaped like a suction cup. It is a prolific breeder and can survive in poor water quality.

English Ivy
A popular evergreen climbing vine with waxy, dark green leaves. When it escapes cultivation, it smothers ground vegetation and can weigh down and kill mature trees by blocking sunlight.

Wintercreeper
An evergreen vine or shrub with glossy, dark green leaves, often used as an ornamental groundcover. It spreads relentlessly, carpeting forest floors and strangling trees it climbs.

Princess Tree
A medium-sized tree with very large, heart-shaped leaves and showy, pale violet flowers in spring. Its rapid growth and prolific seeding allow it to quickly dominate open areas.

Didymo (Rock Snot)
A microscopic diatom (algae) that can bloom into massive growths that look like wet wool or toilet paper. It thrives in cold, clear water and degrades fish habitat.

Chinese Yam
A fast-growing vine with distinctive heart-shaped leaves and small, bulb-like tubers (bulbils) on its stems. These bulbils fall to the ground and start new plants, allowing it to spread quickly.

Japanese Knotweed
A tall, bamboo-like perennial plant with hollow stems and large, spade-shaped leaves. It spreads through a powerful rhizome system, making it incredibly difficult to eradicate once established.

Spongy Moth
Formerly known as the Gypsy Moth, its voracious caterpillars feed in massive groups. During outbreak years, they can strip entire forests of their leaves, stressing and killing trees.

Autumn Olive
A large shrub with silvery-green leaves and small, tart red berries. Though its berries are eaten by birds, it aggressively colonizes open areas and meadows, shading out native plants.

Sericea Lespedeza
An upright perennial forb with slender stems and small, three-part leaves. It was once planted for erosion control but is now a major pest in pastures, prairies, and natural meadows.

Cogongrass
A perennial grass known for its fluffy, white, plume-like seed heads and off-center midrib. It creates a serious fire hazard and displaces native plants in open habitats.

Porcelain Berry
A deciduous, woody vine related to grapes. It is easily identified in the fall by its distinctive, multicolored berries that shift from pale lilac to bright turquoise and blue.

Oriental Bittersweet
A woody vine that can be distinguished from its native counterpart by its yellow fruit capsules. It grows into the tops of trees, shading them out and making them susceptible to wind damage.

New Zealand Mud Snail
A tiny aquatic snail, often no larger than a grain of rice. It reproduces asexually, allowing a single snail to start a new population that can number in the hundreds of thousands per square meter.

Rusty Crayfish
A large, aggressive crayfish identified by two rusty-colored spots on its carapace. It negatively impacts fish populations by eating their eggs and destroying the vegetation they use for cover.

Nutria
A large, semi-aquatic rodent often mistaken for a beaver, but with a round, rat-like tail. Their intensive feeding on marsh vegetation can convert healthy wetlands into open water.

Dogwood Anthracnose
A fungal disease that severely impacts dogwoods, especially those in cool, moist, shaded locations. It can kill trees and has caused significant mortality in mountain forests.

Thousand Cankers Disease
This disease results from the combined activity of a tiny beetle and the fungus it carries. The fungus creates numerous small cankers under the bark, eventually killing valuable black walnut trees.

Common Reed
A tall, perennial grass that can reach 15 feet in height and grows in dense stands along shorelines and in marshes. Its invasive form creates monocultures with little value for local wildlife.

Amur Corktree
A deciduous tree with deeply furrowed, corky bark and compound leaves. It is a prolific seed producer, and the berries are spread by birds, allowing it to invade forest edges and interiors.

Japanese Spirea
A small, deciduous shrub with clusters of small pink flowers. It is a popular landscaping plant that has escaped cultivation to form dense thickets in natural areas.

Periwinkle
A trailing, vine-like plant with glossy dark green leaves and small purple-blue flowers. Often used as an ornamental groundcover, it escapes into forests where it chokes out all other low-growing plants.

Asian Longhorned Beetle
A large, shiny black beetle with white spots and long, banded antennae. Its large, circular exit holes are a key sign of infestation. It poses a major threat to urban and forested maple trees.

Spiny Water Flea
A tiny crustacean with a very long, barbed tail spine. They eat smaller, native zooplankton, competing with young fish for food. Their spines clump up on fishing gear, causing problems for anglers.
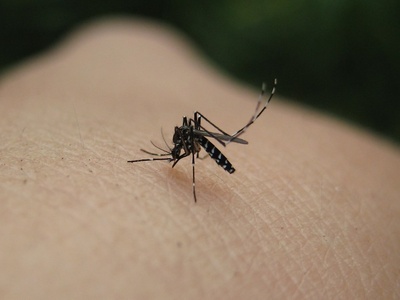
Asian Tiger Mosquito
A small black mosquito with distinctive white stripes on its legs and body. It breeds in small containers of standing water and has become a major pest in residential areas across the state.

Callery Pear
This is the parent species of the infamous Bradford pear. Various cultivars cross-pollinate, producing offspring with large thorns that form impenetrable, ecologically damaging stands in old fields and forest edges.

Hydrilla
An aquatic plant that is considered one of the worst invasive species in the world. It can grow an inch a day, completely filling the water column and altering water chemistry.

Parrot Feather
This plant has bright green, feathery leaves that emerge from the water. It can clog drainage ditches and recreational waterways, and provides poor habitat for native wildlife.

Yellow Flag Iris
A large, attractive iris with bright yellow flowers. It spreads via rhizomes and seeds, creating dense stands that can alter hydrology and reduce habitat for waterfowl and fish.

Eurasian Watermilfoil
An aquatic plant with feathery, submerged leaves. It spreads easily through fragmentation, where small pieces broken off by boats or animals can start new colonies, choking out lakes and rivers.

Curly Pondweed
An aquatic plant with distinctive, lasagna-noodle-like leaves. Its early-season growth and mid-summer decay cycle can lead to algal blooms and fish kills from low oxygen levels.

Purple Loosestrife
A tall, attractive wetland plant with a spike of bright purple flowers. A single plant can produce over 2 million seeds, allowing it to rapidly create dense, single-species stands.

Beefsteak Plant
An annual herb in the mint family with a distinct odor. It has purplish, square stems and serrated leaves. It often forms dense stands in disturbed, shady areas of forests.

Japanese Hops
An annual climbing vine with rough, sandpapery stems and five-lobed leaves. Unlike its valuable relative used for beer, this species grows in smothering, tangled masses in sunny, moist areas.

Mile-a-Minute Weed
An annual vine named for its rapid growth. It has triangular leaves, barbed stems that help it climb, and iridescent blue berries. It quickly overtakes open and disturbed areas.

Russian Olive
A shrub or small tree similar to Autumn Olive but with narrower, silvery leaves. It tolerates poor conditions and aggressively colonizes riparian zones, altering the natural plant community.

Saltcedar
A shrub or tree with small, scale-like leaves and pink or white flowers. It is a major problem in the western U.S. and has established populations in Tennessee, threatening riverbanks and wetlands.

Sweet Autumn Clematis
A climbing vine that becomes extremely noticeable in late summer when it is covered in masses of small, fragrant white flowers. It escapes gardens and can quickly overwhelm native vegetation.

Norway Maple
A common street and landscape tree that looks similar to sugar maple. Its seeds readily sprout in nearby forests, where the saplings’ dense canopy outcompetes native flora on the forest floor.

Siberian Elm
A fast-growing, drought-tolerant tree that can thrive in harsh conditions where native trees cannot. It spreads aggressively by seed and can form dense, low-value stands.

White Mulberry
Originally imported to support the silk industry. This tree is now widespread and poses a significant threat to the less common native Red Mulberry through hybridization and competition.

Japanese Barberry
A popular landscaping shrub with small leaves that can be green, yellow, or red, and small, red, oval berries. It alters soil chemistry and has been linked to higher rates of Lyme disease.

Burning Bush
A popular ornamental shrub known for its brilliant red fall foliage and winged stems. Birds eat its berries and spread the seeds into natural areas, where it can become a dominant shrub.

Chocolate Vine
A semi-evergreen woody vine with distinctive five-lobed leaves and maroon, spicy-scented flowers. It grows extremely fast, forming a thick blanket over other plants, blocking all sunlight.

Liriope (Monkey Grass)
A popular evergreen groundcover with grass-like leaves. The spreading variety, *L. spicata*, is particularly aggressive, escaping into forests where it carpets the ground and prevents native plant growth.

Golden Bamboo
This is a large, fast-spreading bamboo with golden-green canes. It escapes cultivation and can quickly take over yards, forest edges, and stream banks, displacing all other plants with its dense root mat.

Daphne Spurge
A shade-tolerant evergreen shrub with whorled, glossy green leaves. It can create dense stands in the forest understory, and its toxic nature makes it unpalatable to browsing animals.

Chinese Silvergrass
A large, popular ornamental grass with tall, feathery plumes. It readily escapes cultivation, establishing in fields and roadsides where its dense growth and dry winter foliage increase fire risk.

Air Potato
This vine is named for the potato-like growths (bulbils) on its stems. It can grow up to eight inches a day, quickly climbing to the tops of trees and forming a dense shade that kills plants below.

Goldfish
The common pet goldfish, when released into the wild, can grow quite large. They root along the bottom, which clouds the water, and compete with native fish for food resources.

Rock Bass (Shadow Bass)
A sunfish species that, when moved outside its native Tennessee River drainage, can outcompete other native sunfish and bass species for food and habitat in smaller streams.

White Perch
Not a true perch, this species is related to striped bass. They reproduce rapidly and can dominate a water body, preying on the eggs and young of more desirable game fish like walleye.

Alewife
A species of river herring that can become invasive in landlocked reservoirs. They can experience massive die-offs that foul shorelines and alter the food web for sportfish like trout and salmon.
Whirling Disease
This parasite infects the cartilage of young fish, causing them to swim in a characteristic “whirling” pattern. It can have a devastating impact on wild trout populations in affected streams.

Dutch Elm Disease
This disease is responsible for the death of millions of American elm trees across North America. The fungus clogs the tree’s vascular tissue, causing it to wilt and die.

Laurel Wilt
This fungal pathogen is a major threat to sassafras and spicebush in Tennessee. The disease causes a rapid wilting and death of the host tree once the fungus is introduced by the beetle.

Sirex Woodwasp
A large, dark-colored wasp that attacks pine trees. It is a major pest in pine plantations, as the combination of its toxic saliva and a symbiotic fungus can overwhelm and kill healthy trees.

Sudden Oak Death
While not yet widespread in Tennessee’s forests, this pathogen is under strict quarantine. It has caused widespread mortality of oak trees on the West Coast and is a major threat.

Viburnum Leaf Beetle
A small beetle that can completely defoliate native and ornamental viburnum species. Repeated defoliation over several years can weaken and ultimately kill these important native shrubs.

Beech Bark Disease
This disease begins when the beech scale insect feeds on the tree’s bark, creating wounds that are then infected by a Nectria fungus. The resulting cankers can girdle and kill the tree.

Asian Needle Ant
A slender, dark-colored ant that often lives in forested areas. Unlike many ants, it forages individually. Its sting is painful and it is a threat to native ant biodiversity.

Common House Sparrow
A small, stocky bird common in urban and agricultural areas. They are known for their aggressive behavior, often taking over nest boxes and killing the eggs and young of native birds.

European Starling
A glossy, dark bird with a speckled appearance. Introduced in the 1890s, they have spread across the continent, displacing native woodpeckers, bluebirds, and other cavity-nesters.

Rock Pigeon
The common city pigeon. While familiar, they are a non-native species. In large numbers, their acidic droppings can deface and accelerate the deterioration of stonework and historic buildings.

Mute Swan
A large, all-white swan with an S-curved neck and a bright orange bill. Despite their graceful appearance, they can be extremely aggressive towards people and other birds during nesting season.





