The Bahamas’ warm, clear waters host coral reefs, mangroves and seagrass beds that support a rich variety of marine life. Whether you snorkel, dive or fish from a boat, you’ll encounter different shapes, colors and behaviors that make island waters interesting to explore.
There are 74 Fish of the Bahamas, ranging from Almaco jack to Yellowtail snapper. For each species we list Scientific name,Size (length cm),Habitat & range — you’ll find below.
How can I tell an Almaco jack from a Yellowtail snapper?
Almaco jack are deeper-bodied with a more elongated profile and darker, muted colors, while Yellowtail snapper are slimmer, brightly marked with a yellow stripe and tail; size ranges in the Size (length cm) column below help confirm ID, and the Scientific name and Habitat & range fields give context on where each is likely to be seen.
Are any of these species regulated or at conservation risk?
Some of the 74 species have catch limits, size restrictions, or concern listings—check local fisheries rules and the Habitat & range notes for species distributions; consult official sources (local authorities, IUCN) before harvesting or planning conservation actions.
Fish of the Bahamas
| Name | Scientific name | Size (length cm) | Habitat & range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nassau grouper | Epinephelus striatus | 100 | Coral reefs, ledges & spawning aggregation sites (5–40 m) |
| Goliath grouper | Epinephelus itajara | 270 | Reefs, wrecks and shallow ledges (3–50 m) |
| Black grouper | Mycteroperca bonaci | 150 | Rocky reefs and ledges, reef slope (10–80 m) |
| Yellowtail snapper | Ocyurus chrysurus | 45 | Reefs, patch reefs & drop-offs (5–60 m) |
| Mutton snapper | Lutjanus analis | 100 | Reef slopes, wrecks & sand channels (10–100 m) |
| Cubera snapper | Lutjanus cyanopterus | 160 | Deep reefs, rocky ledges & wrecks (20–200 m) |
| Lane snapper | Lutjanus synagris | 40 | Reefs, seagrass edges & sandy bottoms (5–50 m) |
| Dog snapper | Lutjanus jocu | 120 | Reefs, ledges & deep drop-offs (15–100 m) |
| Schoolmaster snapper | Lutjanus apodus | 60 | Shallow reefs and mangrove-fringed flats (1–30 m) |
| Great barracuda | Sphyraena barracuda | 150 | Open reef edges, seagrass beds & blue water (1–100 m) |
| Mahi-mahi | Coryphaena hippurus | 150 | Pelagic, near weedlines and floating debris (surface–100 m) |
| Wahoo | Acanthocybium solandri | 250 | Pelagic, around weedlines & offshore structure (surface–200 m) |
| Yellowfin tuna | Thunnus albacares | 250 | Open ocean, around FADs and schools (surface–500 m) |
| Blue marlin | Makaira nigricans | 300 | Bluewater pelagic, seasonal offshore (surface–1,000 m) |
| White marlin | Kajikia albida | 250 | Pelagic offshore, warm currents and weedlines (surface–600 m) |
| Sailfish | Istiophorus platypterus | 300 | Open ocean, near currents and weedlines (surface–500 m) |
| King mackerel | Scomberomorus cavalla | 200 | Coastal and offshore reefs, channels & wrecks (1–100 m) |
| Greater amberjack | Seriola dumerili | 150 | Reefs, wrecks and deep ledges (20–200 m) |
| Almaco jack | Seriola rivoliana | 130 | Outer reefs and wrecks, pelagic near structure (10–200 m) |
| Jack crevalle | Caranx hippos | 100 | Reefs, beaches and nearshore waters (1–80 m) |
| Horse-eye jack | Caranx latus | 90 | Reef edges, wrecks & channels (5–80 m) |
| Cobia | Rachycentron canadum | 200 | Nearshore structure, wrecks and buoys (surface–100 m) |
| Bonefish | Albula vulpes | 80 | Shallow sandy flats, seagrass beds & tidal channels (0–2 m) |
| Tarpon | Megalops atlanticus | 200 | Flats, mangroves and channels (0–30 m) |
| Permit | Trachinotus falcatus | 100 | Sandy flats, reef edges & wrecks (0–40 m) |
| Yellow goatfish | Mulloidichthys martinicus | 40 | Sandy edges, reef slopes & seagrass (1–40 m) |
| Blue tang | Acanthurus coeruleus | 30 | Shallow reefs, rubble and seagrass edges (1–30 m) |
| Doctorfish | Acanthurus chirurgus | 45 | Reefs and rocky areas, moderate depths (1–40 m) |
| Queen angelfish | Holacanthus ciliaris | 45 | Coral reefs, ledges & drop-offs (5–40 m) |
| French angelfish | Pomacanthus paru | 50 | Reefs, ledges and sponge-rich habitats (5–40 m) |
| Gray angelfish | Pomacanthus arcuatus | 60 | Coral reefs, ledges and mangrove-fringed areas (2–40 m) |
| Stoplight parrotfish | Sparisoma viride | 50 | Coral reefs and reef flats (1–30 m) |
| Blue parrotfish | Scarus coeruleus | 70 | Coral reef slopes and patch reefs (2–40 m) |
| Princess parrotfish | Scarus taeniopterus | 30 | Reef crests and seagrass margins (1–20 m) |
| Redband parrotfish | Sparisoma aurofrenatum | 30 | Shallow reefs and rubble zones (1–25 m) |
| Hogfish | Lachnolaimus maximus | 100 | Reefs, seagrass edges & sand channels (1–50 m) |
| Rainbow runner | Elagatis bipinnulata | 100 | Pelagic & nearshore reefs, around sargassum (surface–200 m) |
| Frigate tuna | Auxis thazard | 75 | Open ocean and nearshore pelagic zones (surface–200 m) |
| Clepticus (rainbow wrasse) | Clepticus parrae | 25 | Shallow reefs and patch reefs (1–30 m) |
| Bluehead wrasse | Thalassoma bifasciatum | 12 | Shallow reefs, tidepools and seagrass edges (0–20 m) |
| Slippery dick | Halichoeres bivittatus | 30 | Reefs and rubble zones (1–30 m) |
| Yellowhead wrasse | Halichoeres garnoti | 25 | Reef slopes, patch reefs and seagrass margins (1–40 m) |
| Sergeant major | Abudefduf saxatilis | 20 | Shallow reefs, rocky shores & harbor areas (0–10 m) |
| Blue chromis | Chromis cyanea | 12 | Patch reefs and shallow ledges (1–30 m) |
| French grunt | Haemulon flavolineatum | 25 | Reefs, ledges and seagrass edges (1–60 m) |
| White grunt | Haemulon plumierii | 40 | Reefs, rock ledges & nearshore waters (1–80 m) |
| Porkfish | Anisotremus virginicus | 30 | Reef slopes, ledges and sandy patches (1–40 m) |
| Tomtate | Haemulon aurolineatum | 20 | Shallow reefs and inner shelf areas (1–30 m) |
| Squirrelfish | Holocentrus adscensionis | 33 | Reef crevices, overhangs & ledges (5–40 m) |
| Blackbar soldierfish | Myripristis jacobus | 35 | Reef caves, overhangs & deeper crevices (5–60 m) |
| Spotted drum | Equetus punctatus | 25 | Reefs, overhangs & coral heads (1–30 m) |
| Fourspot butterflyfish | Chaetodon capistratus | 20 | Coral reefs, lagoons and seagrass edges (1–30 m) |
| Banded butterflyfish | Chaetodon striatus | 18 | Coral reefs and rocky areas (1–40 m) |
| Queen triggerfish | Balistes vetula | 70 | Reef flats, crests and rubble zones (1–40 m) |
| Gray triggerfish | Balistes capriscus | 75 | Deeper reefs, wrecks and ledges (20–200 m) |
| Smooth trunkfish | Lactophrys trigonus | 25 | Shallow reefs, seagrass margins and rubble (1–30 m) |
| Spotted trunkfish | Lactophrys bicaudalis | 25 | Coral reefs and lagoonal areas (1–30 m) |
| Scrawled filefish | Aluterus scriptus | 120 | Reef slopes and open water near structure (5–200 m) |
| Atlantic spadefish | Chaetodipterus faber | 60 | Shallow reefs, wrecks and bays (1–30 m) |
| Spotted moray | Gymnothorax moringa | 150 | Reef crevices, rubble and drop-offs (2–60 m) |
| Green moray | Gymnothorax funebris | 200 | Reef caves, ledges and deep crevices (5–60 m) |
| Caribbean reef shark | Carcharhinus perezi | 250 | Reef slopes, drop-offs and outer reefs (10–200 m) |
| Nurse shark | Ginglymostoma cirratum | 350 | Shallow reefs, ledges and sandy bottoms (1–40 m) |
| Lemon shark | Negaprion brevirostris | 350 | Shallow coastal waters, mangroves & flats (1–40 m) |
| Scalloped hammerhead | Sphyrna lewini | 300 | Offshore reefs, seamounts & pelagic zones (20–500 m) |
| Bull shark | Carcharhinus leucas | 300 | Coastal shallows, channels and mangroves (0–40 m) |
| Southern stingray | Hypanus americanus | 200 | Sandy flats, seagrass beds & lagoon floors (0–30 m) |
| Spotted eagle ray | Aetobatus narinari | 300 | Open reef slopes, bays and sandy flats (5–200 m) |
| Giant manta (oceanic manta) | Mobula birostris | 500 | Offshore pelagic, cleaning stations & seamounts (surface–500 m) |
| Lionfish | Pterois volitans | 38 | Reefs, wrecks and ledges (1–70 m) |
| Atlantic needlefish | Strongylura marina | 100 | Seagrass beds, mangrove creeks & flats (0–10 m) |
| Remora (common) | Remora remora | 60 | Pelagic and reef zones, attached to large hosts (surface–200 m) |
| Golden tilefish | Lopholatilus chamaeleonticeps | 90 | Deep slope habitats and sand-mud bottoms (100–400 m) |
| Blueline tilefish | Caulolatilus microps | 80 | Outer reef slopes and deep ledges (50–300 m) |
Images and Descriptions

Nassau grouper
Large, stocky grouper with mottled brown pattern; prized by anglers and divers. Forms seasonal spawning aggregations on reef edges; cryptic around caves and ledges. Can reach large sizes and is culturally important in Bahamas fisheries.

Goliath grouper
Massive, broad-headed grouper often found sheltering in wrecks and caves. Slow-moving and curious around divers; historic overfishing reduced numbers but individuals still seen. Can weigh several hundred kilograms and is notable for its sheer size.

Black grouper
Powerful predator with dark mottled coloration; common on deeper reef edges and ledges. Ambushes prey like fish and crustaceans. Popular with sport fishers and often solitary except during spawning season.

Yellowtail snapper
Slim, colorful snapper with yellow forked tail and silver body. Often schools near reefs and sandy edges; favorite target for reef anglers and common on fish-cleaning stations. Quick and abundant in Bahamas waters.

Mutton snapper
Pinkish snapper with a black spot on the side and a streamlined body. Moves between reefs and deeper channels; prized by anglers for strong fights and good table quality. Often encounters at dawn and dusk.

Cubera snapper
Large, heavy-bodied snapper with blunt snout and strong jaws. Solitary and nocturnal hunter feeding on fish and crustaceans. Sought by anglers for size and power, often inhabits deeper structure.

Lane snapper
Small, pinkish snapper with prominent lateral stripe and spot on tail. Often in schools over reefs and sand patches; common in shallow water and popular with light-tackle anglers and snorkelers.

Dog snapper
Robust snapper with canine-like teeth and reddish-brown coloration. Solitary or small groups on deep reefs; a wary predator that reaches large sizes and is valued by experienced anglers.

Schoolmaster snapper
Silver-bodied snapper with yellow fins and forked tail; often forms schools near reef edges and mangroves. Common sight for snorkelers and reef anglers, known for schooling behavior and midday activity.

Great barracuda
Long, torpedo-shaped predatory fish with big teeth and silvery body. Ambush hunter often seen cruising alone or in small groups near drop-offs; impressive size makes it familiar to divers and anglers.

Mahi-mahi
Vividly colored, fast pelagic fish with blunt head and long dorsal fin. Found around sargassum mats and debris; prized by sport anglers for spectacular fights and bright green-blue coloration that changes after capture.

Wahoo
Thin, high-speed predator with vertical blue bars; often found with tuna and dolphins around floating objects. Exceptional speed and aggressive strikes make it a prized offshore gamefish in Bahamas waters.

Yellowfin tuna
Powerful, schooling pelagic tuna with yellow fins and torpedo body. Found offshore on deeper blue-water currents; highly prized for sport and commercial catches, offering long runs and strong fights.

Blue marlin
Iconic large billfish with iridescent blue dorsal side and spear-like bill. Sought by big-game anglers during season; typically found in deep blue water and known for spectacular leaps and long runs.

White marlin
Smaller billfish with rounded dorsal fin and silver body. Common in Bahamas blue-water fishing, prized by sport fishers for acrobatic fights and seasonal migrations.

Sailfish
Famous for its high sail and explosive speed; often found in warm Bahamian waters. Extremely fast and acrobatic, making it a top target for catch-and-release sport fishing.

King mackerel
Streamlined pelagic predator with forked tail and silver sides. Often hunted by anglers inshore and offshore; strikes fast on lures and live bait near structure and drop-offs.

Greater amberjack
Large, strong jack with elongated body and dark stripe on side. Found on deep reefs and wrecks; powerful fighter sought by anglers, often feeding on fish and squid around structure.

Almaco jack
Robust jack with rounded profile and amber hue. Often associates with structure and schools of baitfish; prized by anglers for strength and tasty flesh.
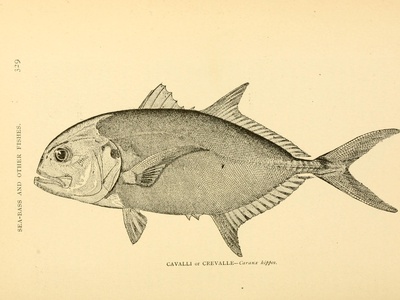
Jack crevalle
Bulky, silvery jack with powerful runs and blunt head. Common around shorelines and reef passes; aggressive predators popular with sport fishers for their hard fights.

Horse-eye jack
Big-eyed, silvery jack that forms large schools. Frequently seen around drop-offs and wrecks; strong runner and common bycatch for anglers in Bahamian waters.

Cobia
Long-bodied, dark-backed fish often seen trailing sharks, rays or boats. Prefers structure and rafted debris; known for stubborn fights and excellent table quality when hooked by anglers.

Bonefish
Classic flats species with silvery, streamlined body. A primary draw for fly and spin anglers in the Bahamas; wary and fast, making sight-fishing exciting in shallow flats and mangrove channels.

Tarpon
Large, powerful acrobatic fish known for spectacular leaps on tackle. Juveniles frequent mangroves and creeks; adults roam flats and nearshore waters. A premier sport fish for sight-casting in Bahamas shallow waters.

Permit
Deep-bodied, silvery gamefish with strong dorsal curvature. Wary and selective eater, making it a challenging target for sight anglers on the flats and near structure.

Yellow goatfish
Small, yellow-barred goatfish often seen rooting in sand with twin barbels. Forms schools and is commonly seen by snorkelers; active during the day and useful for ID on sandy reef edges.

Blue tang
Oval, deep-bodied surgeonfish with bright blue coloration. Common on shallow reefs and patch reefs; grazes algae and is a familiar sight for snorkelers and divers.

Doctorfish
Dark surgeonfish with a distinctive spine near the tail. Grazes algae on reef surfaces; tends to be more robust than blue tang and is commonly encountered by divers on reef walls.

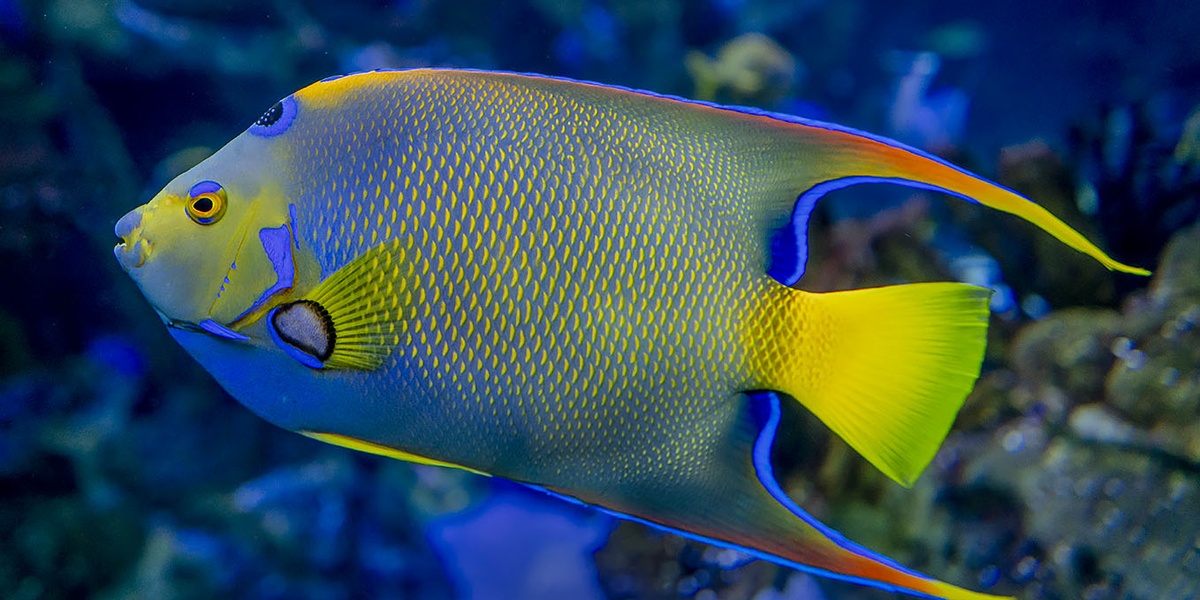
Queen angelfish
Vibrant blue and yellow angelfish with distinctive crown patch. Bold and often seen in pairs near sponges; prized by divers for striking colors and frequent presence on reefs around the Bahamas.

French angelfish
Black body with yellow-rimmed scales and bright face. Often found as pairs and around cleaning stations; distinctive profile makes it easy to identify while diving.

Gray angelfish
Large, greyish angelfish with yellow accents and pale tail. Common along shallow reefs and mangroves; feeds on sponges and invertebrates and is a familiar reef resident for divers.

Stoplight parrotfish
Colorful parrotfish with vivid adult and juvenile phases; uses strong teeth to bite coral and scrape algae. Active during day, creates white sand from bioerosion, and often seen by snorkelers and divers.

Blue parrotfish
Large, elongated parrotfish with blue coloration. Important reef grazer that shapes reef structure through grazing and bioerosion; commonly seen in schools on exposed reef fronts.
Princess parrotfish
Smaller parrotfish species with colorful patterns and distinct juvenile forms. Common on shallow reef crests and sandy patches; active grazer frequently seen by snorkelers and divers.

Redband parrotfish
Small parrotfish with red lateral band; often seen in shallow reef areas and around reef rubble. Browses algae on hard surfaces and is commonly encountered by snorkelers.

Hogfish
Large wrasse-like fish with protruding snout used to root prey from sand. Changes sex from female to male; sought after by anglers and divers recognize them by their long snouts and bold coloration.

Rainbow runner
Slim, fast pelagic fish with blue-green back and yellow stripe. Often near reefs and sargassum mats; valued by anglers for speed and schooling behavior when chasing baitfish.

Frigate tuna
Small, schooling tuna often found near the surface and around floating debris. Common bycatch for offshore anglers and an important forage species for larger predators in Bahamian waters.

Clepticus (rainbow wrasse)
Colorful schooling wrasse with blue and yellow hues. Form large aggregations over reefs and are often among the first fishes noticed by snorkelers due to their abundance and rapid schooling.

Bluehead wrasse
Small, bold wrasse with a blue head and bright body. Common in large numbers on shallow reefs; protogynous hermaphrodite with complex social behavior often observed by divers.

Slippery dick
Small, colorful wrasse with distinct juvenile and adult color phases. Common on reef flats and rubble; feeds on small invertebrates and is frequently seen picking prey among coral and rocks.

Yellowhead wrasse
Small wrasse with yellow head and green body; active cleaner and forager on reefs. Often changes color with age and can be seen darting among coral heads for invertebrates.

Sergeant major
Bold, stripy damselfish common in shallow water and tide pools. Tolerant of swimmers and snorkelers; forms schools and guards nests, making it a familiar sight to casual observers.

Blue chromis
Small, electric-blue schooling damselfish that hovers over reef crests. Forms dense schools that shimmer in sunlight — a common and photogenic sight for divers and snorkelers.

French grunt
Brownish grunt with yellow stripes; nocturnal feeders that shelter in crevices by day. Often form large daytime schools on reefs and move to forage at night, producing audible grunts.
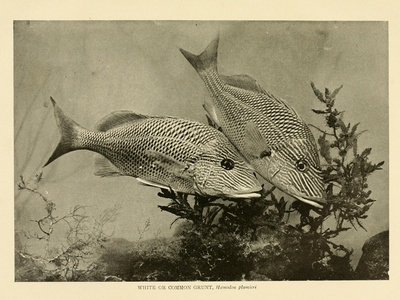
White grunt
Silvery grunt with dark stripes and stout body. Common around reefs and wrecks; active at dusk and night when feeding on crustaceans and small fishes.

Porkfish
Striped, red-and-yellow grunt often seen in pairs or small groups. Noisy forager at dusk and known for distinctive facial markings; popular with divers and small-boat anglers.

Tomtate
Small, slender grunt with yellowish lateral line. Forms schooling aggregations above reefs and seagrass; common bait and reef species easy for snorkelers to observe.

Squirrelfish
Red-bodied, large-eyed nocturnal fish that hides in crevices by day and emerges at night to feed. Distinctive eyes and nocturnal calls make it a recognizable reef resident.

Blackbar soldierfish
Red soldierfish with dark bar markings; secretive and nocturnal, often observed by divers peering from caves. Forms small groups and is active at night hunting small invertebrates.

Spotted drum
Black-and-white vertically striped fish with a long trailing dorsal filament. Often hovers head-down under ledges and in crevices; nocturnal habit and dramatic profile make it a favorite among divers.

Fourspot butterflyfish
Distinctive round butterflyfish with dark eye spot near tail and band through eye. Common on reefs and inshore habitats, often seen in pairs feeding on coral and small invertebrates.

Banded butterflyfish
Vertical black bands on pale body and pointed snout. Frequently seen singly or in pairs, feeding on invertebrates and coral-associated prey; familiar to snorkelers on Bahamian reefs.

Queen triggerfish
Large, laterally compressed fish with bold blue and yellow patterns. Strong jaws for crushing shells; often seen rooting through sand and rubble for crustaceans and mollusks.

Gray triggerfish
Robust triggerfish with gray body and powerful teeth. Found on deeper reefs and structure; known to be territorial and will defend burrows or feeding areas from divers and fishers.

Smooth trunkfish
Box-shaped fish covered in bony plates with mottled spots. Slow-moving and often solitary; ejects toxins when stressed, so divers should admire but not handle it.

Spotted trunkfish
Triangular, boxy fish with white spots on dark background. Common on shallow reefs and seagrass edges; notable for its armored appearance and slow, deliberate swimming.

Scrawled filefish
Long-bodied filefish with distinctive scrawled patterns in adults. Often solitary or in pairs; uses rough skin texture and cryptic colors to blend near reefs and seaweed.

Atlantic spadefish
Deep-bodied, silvery fish with dark vertical bands. Forms big schools over wrecks and nearshore reefs; curious and tolerant of divers, often seen in large aggregations.

Spotted moray
Long, eel-like predator with mottled pattern and habit of hiding in caves. Often pokes head from crevices; cautious but commonly observed by divers on Bahamian reefs.

Green moray
Large, robust moray with greenish coloration from mucus; reclusive during day and active nocturnally. Divers often spot heads protruding from holes on reef slopes and wrecks.

Caribbean reef shark
Common reef-associated shark near drop-offs and wall dives. Medium-sized and often inquisitive around divers; prominent in Bahamas dive sites and an important apex predator on reef systems.

Nurse shark
Docile-looking, broad-bodied shark that often rests on sandy patches and under ledges. Mostly nocturnal and slow-moving; frequently observed by divers on wreck and reef dives.

Lemon shark
Stocky, yellow-brown shark common in shallow Bahamian waters and mangrove nursery areas. Often encounters divers in group sites and is key species for conservation and shark tourism.

Scalloped hammerhead
Distinctive hammer-shaped head and schooling behavior in deeper waters. Seen seasonally around Bahamas offshore features; iconic predator sought by divers and photographers on deep reef excursions.

Bull shark
Powerful, broad-snouted shark tolerant of low salinity and shallow waters. Occurs in Bahamas inshore zones and channels; large and formidable, historically associated with anglers and caveats for swimmers.

Southern stingray
Flat, diamond-shaped ray that burrows in sand and ambushes prey. Common on the flats and a frequent sight for snorkelers; usually docile but equipped with a venomous tail spine if provoked.

Spotted eagle ray
Large, spotted ray with wing-like pectorals and protruding snout. Graceful swimmer often seen in groups cruising above sand or along reef drop-offs; a highlight for divers and snorkelers.
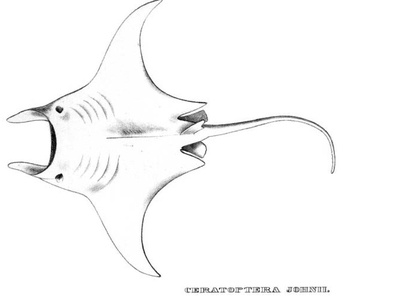
Giant manta (oceanic manta)
Huge, filter-feeding ray with broad wingspan and cephalic lobes. Occurs seasonally around Bahamas cleaning stations and pelagic encounters; awe-inspiring when seen by divers or from boats.

Lionfish
Invasive Indo-Pacific species that has established in Bahamian reefs; distinctive zebra-like stripes and venomous spines. Predatory threat to native reef fauna and a target for removal by divers and fishers.

Atlantic needlefish
Long, slender surface predator with elongated jaws full of sharp teeth. Often seen skimming shallow waters and flats; quick and wary, common nearshore and in estuarine habitats.

Remora (common)
Flat-bodied hitchhiker that attaches to sharks, turtles and boats using a suction disc. Seen around large pelagics and wrecks; harmless and often curious around divers.

Golden tilefish
Deepwater species found on outer shelf slopes and canyons near the Bahamas. Builds burrows in soft substrates and is targeted by deepwater anglers and trawlers for firm white flesh.

Blueline tilefish
Deepwater tilefish often near rocky escarpments and rubble on continental slope. Slower-growing, benthic species prized by deep-droppers and known to occupy burrows or crevice shelters on the slope.





