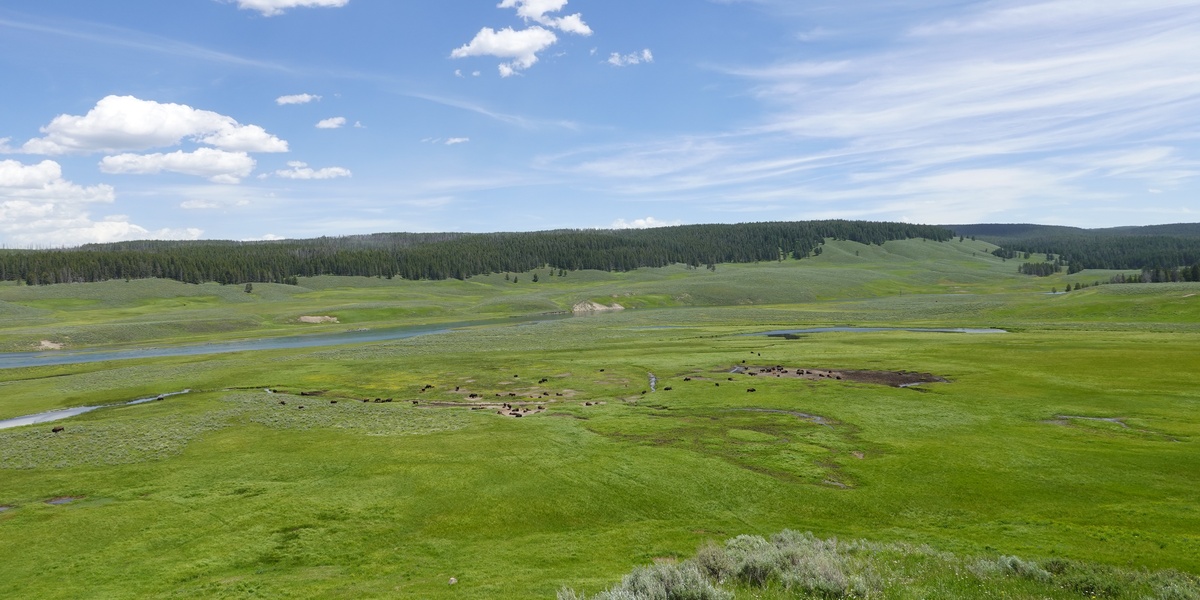
Wide open prairies and rolling steppes support a surprising mix of grazers, predators and birds adapted to seasonal grasses and fire-driven cycles. Temperate grasslands stretch across North America, Eurasia and parts of the Southern Hemisphere, and their animals often reveal how climate and human land use shape ecosystems.
There are 43 Temperate Grasslands Animals, ranging from the American badger to the Western meadowlark. For each species you’ll find below Scientific name,Size (weight kg),Range (regions/countries), making it easy to compare identity, typical weight and geographic distribution — you’ll find below.
Which animals should I expect to see in a temperate grassland?
Expect a mix of ground-dwelling mammals (prairie dogs, badgers), medium-sized grazers (antelopes, bison or their regional equivalents) and a variety of ground- and shrub-nesting birds (larks, meadowlarks, raptors). Seasonal movement, camouflage and burrowing are common adaptations that determine which species are visible at different times of year.
How can the size and range columns help me when I’m identifying species?
Size gives a quick field reference — weight ranges narrow down possibilities when you can estimate an animal’s bulk — while the range column helps rule species in or out by region; combine both with behavior and habitat notes to improve ID accuracy and spot likely locals versus vagrants.
Temperate Grasslands Animals
| Name | Scientific name | Size (weight kg) | Range (regions/countries) |
|---|---|---|---|
| American bison | Bison bison | 400-900 | North American Great Plains (USA, Canada) |
| Pronghorn | Antilocapra americana | 40-55 | Western and Central North American grasslands (USA, Canada) |
| Black-tailed prairie dog | Cynomys ludovicianus | 0.90-1.50 | Central North American prairies (USA, Canada) |
| Gunnison’s prairie dog | Cynomys gunnisoni | 0.90-1.40 | Intermountain grasslands (USA: Colorado, Utah, New Mexico) |
| Black-footed ferret | Mustela nigripes | 1.00-1.50 | Reintroduced in Great Plains grasslands (USA) |
| Swift fox | Vulpes velox | 2.00-4.00 | Shortgrass and mixed-grass prairies (USA, Canada) |
| American badger | Taxidea taxus | 6.00-12.00 | North American prairies and grasslands (USA, Canada) |
| Greater prairie-chicken | Tympanuchus cupido | 0.80-1.60 | Central North American grasslands (USA) |
| Sharp-tailed grouse | Tympanuchus phasianellus | 0.60-1.40 | North American prairies and parklands (USA, Canada) |
| Eastern meadowlark | Sturnella magna | 0.07-0.12 | Eastern and Central North American grasslands (USA, Canada) |
| Western meadowlark | Sturnella neglecta | 0.08-0.13 | Western North American grasslands (USA, Canada) |
| Bobolink | Dolichonyx oryzivorus | 0.04-0.06 | North American grassland breeding grounds (USA, Canada) |
| Grasshopper sparrow | Ammodramus savannarum | 0.02-0.03 | North American prairies and grasslands (USA, Canada) |
| Ferruginous hawk | Buteo regalis | 1.00-2.50 | Western and Central North American grasslands (USA, Canada) |
| Prairie rattlesnake | Crotalus viridis | 0.50-2.00 | North American prairies and shrub-steppe (USA, Canada) |
| Saiga antelope | Saiga tatarica | 20-50 | Eurasian steppe (Kazakhstan, Russia, Mongolia) |
| Mongolian gazelle | Procapra gutturosa | 20-35 | Central Asian steppes (Mongolia, Russia, China) |
| Przewalski’s horse | Equus ferus przewalskii | 250-350 | Mongolian steppe (reintroduced populations) |
| Corsac fox | Vulpes corsac | 2.00-4.00 | Central Asian steppes (Mongolia, Kazakhstan, China) |
| Steppe polecat | Mustela eversmanii | 0.60-1.50 | Eurasian steppes (Russia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia) |
| European ground squirrel | Spermophilus citellus | 0.70-1.40 | Central and Eastern European grasslands (Hungary, Austria, Romania) |
| Bobak (steppe) marmot | Marmota bobak | 3.00-8.00 | Eurasian steppe and meadowlands (Russia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine) |
| Steppe pika | Ochotona pusilla | 0.12-0.25 | Eurasian steppe (Russia, Mongolia, China) |
| Steppe eagle | Aquila nipalensis | 2.00-4.50 | Central Asian steppes (Russia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia) |
| Great bustard | Otis tarda | 7.00-15.00 | Eurasian grasslands and steppes (Spain, Hungary, Russia) |
| Little bustard | Tetrax tetrax | 0.60-1.20 | Mediterranean and Eurasian grasslands (Spain, France, Turkey) |
| European hare | Lepus europaeus | 2.50-5.00 | European grasslands and farmland (Europe, Russia) |
| Meadow vole | Microtus pennsylvanicus | 0.02-0.05 | North American grasslands and meadows (USA, Canada) |
| Plains pocket gopher | Geomys bursarius | 0.30-0.60 | Central North American prairies (USA) |
| Pampas deer | Ozotoceros bezoarticus | 20-30 | South American pampas (Argentina, Uruguay, Brazil) |
| Patagonian mara | Dolichotis patagonum | 8.00-9.00 | Argentine pampas and Patagonian steppe (Argentina) |
| Greater rhea | Rhea americana | 20-27 | South American pampas and grasslands (Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay) |
| Pampas fox | Lycalopex gymnocercus | 3.00-6.00 | Pampas and lowland grasslands (Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay) |
| Pampas cat | Leopardus colocolo | 3.00-6.00 | South American grasslands and shrub-steppe (Argentina, Chile, Bolivia) |
| Guanaco | Lama guanicoe | 80-120 | Patagonian steppe and South American grasslands (Argentina, Chile) |
| Lesser rhea (Darwin’s rhea) | Rhea pennata | 15-20 | Patagonian steppe and Andean grasslands (Argentina, Chile) |
| Emu | Dromaius novaehollandiae | 30-45 | Australian temperate grasslands and open plains (Australia) |
| Eastern grey kangaroo | Macropus giganteus | 30-66 | Eastern Australian grasslands and woodlands (Australia) |
| Blesbok | Damaliscus pygargus phillipsi | 60-80 | South African Highveld grasslands (South Africa) |
| Bontebok | Damaliscus pygargus pygargus | 50-90 | Cape grasslands and fynbos-edge (South Africa) |
| Black wildebeest | Connochaetes gnou | 170-250 | Southern African grasslands and highveld (South Africa, Lesotho) |
| Cape hare | Lepus capensis | 2.50-5.00 | Southern African grasslands and open plains (South Africa, Namibia) |
| Black-tailed godwit | Limosa limosa | 0.25-0.50 | Widespread temperate grasslands wetlands edge (Europe, Asia) |
Images and Descriptions

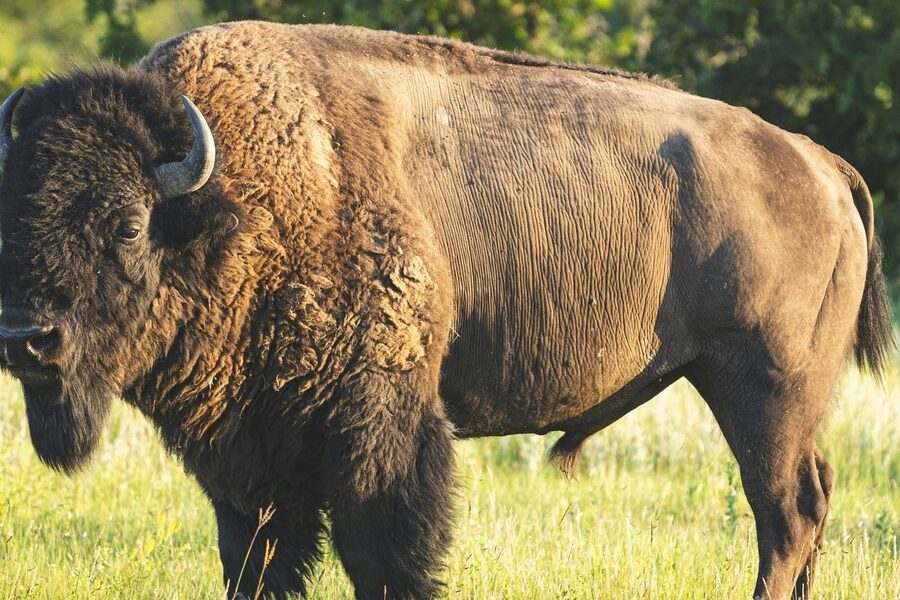
American bison
Massive grazing mammal of prairies; forms herds, shapes grassland by grazing and wallowing, tolerates harsh winters and migratory grassland diets, historically key ecosystem engineer and still found on protected plains and reserves.

Pronghorn
Fast-running antelope of open plains; uses keen vision and endurance to evade predators, grazes and browses sparse grassland vegetation, common in western prairies and badlands.

Black-tailed prairie dog
Social, burrowing rodent that creates extensive colony towns; key soil aerator and prey species, highly adapted to open grasslands with complex communication and sentinel behavior.

Gunnison’s prairie dog
Smaller prairie dog species of mixed-grass high plains; colonial burrower, herbivorous, important for nutrient cycling and as prey for specialized predators.

Black-footed ferret
Specialist carnivore almost entirely dependent on prairie dog colonies; nocturnal, slender, once nearly extinct, now reintroduced where prairie dog populations persist.

Swift fox
Small, nocturnal fox of open plains; uses burrows for shelter, preys on small mammals and insects, adapted to avoid predators with speed and low-profile behavior.

American badger
Fossorial predator specialized for digging; preys on ground squirrels and gophers, well adapted to open soils of grasslands with strong forelimbs and low, powerful build.

Greater prairie-chicken
Lekking grouse of tallgrass and mixed-grass prairies; males display in open arenas, depend on native grasses and forbs for nesting and cover, vulnerable to habitat loss.

Sharp-tailed grouse
Grassland grouse that breeds on leks in open fields; relies on grassland mosaics and early-successional habitats, known for booming displays and camouflage plumage.

Eastern meadowlark
Iconic grassland songbird; nests on ground in grassy fields, feeds on insects and seeds, sings melodious flute-like phrases, indicator of healthy meadow ecosystems.

Western meadowlark
Similar to eastern species but western distribution; ground-nesting passerine of prairies and rangelands, recognizable by bright yellow throat and complex song.

Bobolink
Migratory grassland specialist that breeds in tall hayfields and prairies; males have striking plumage and aerial song, depend on hayland management timing for nesting success.

Grasshopper sparrow
Small, secretive sparrow of shortgrass and mixed prairies; nests on ground, feeds heavily on grasshoppers and insects, adapted to open, sparsely vegetated habitats.

Ferruginous hawk
Large raptor of open plains and semi-arid grasslands; hunts mammals from perches or low flight, adapted to spotting prey across wide-open terrain.

Prairie rattlesnake
Venomous pit viper of grasslands and foothills; ambush predator using camouflaged pattern, tolerates temperature extremes and uses burrows or rocks for shelter.

Saiga antelope
Distinctive bulbous-nosed antelope of open steppe; migratory in some populations, adapted to extreme continental climates with nomadic grazing and herd behavior.

Mongolian gazelle
Formidable long-distance migratory grazer of the steppe; lives in large herds, survives harsh winters and sparse forage, a defining species of Eurasian grasslands.

Przewalski’s horse
Wild horse once extinct in wild, now reintroduced to open steppe; forms small bands, grazes coarse grasses, genetically and ecologically adapted to steppe life.

Corsac fox
Small fox adapted to arid steppes; hunts rodents and insects, uses dens and steppes’ open visibility to detect predators, often forms small family groups.

Steppe polecat
Mustelid predator of grasslands specializing on small mammals; elongated body for entering burrows, opportunistic hunter in open landscapes.

European ground squirrel
Burrowing, colonial rodent of lowland grasslands and pastures; creates colonies that boost biodiversity and serve as prey for raptors and carnivores.

Bobak (steppe) marmot
Large, social marmot of grassland steppes; hibernates long winters, digs extensive burrows, grazes on grasses and forbs and influences soil and plant communities.
Steppe pika
Small lagomorph of dry steppe and semi-desert grasslands; collects haypiles for winter, lives in colonies under sparse vegetation and rocky outcrops.

Steppe eagle
Large raptor that hunts small mammals over open steppe; migratory, long-winged and adapted to thermal soaring above grasslands and low shrub steppe.

Great bustard
Among the heaviest flying birds, inhabits open steppes and farmland; males display on leks, feed on grains and invertebrates, vulnerable to habitat conversion.

Little bustard
Smaller bustard of dry grasslands and cereal steppe; ground‑nesting, cryptic plumage, relies on mosaics of short vegetation for feeding and breeding.

European hare
Fast, long-legged lagomorph of open fields and meadows; largely crepuscular, feeds on grasses and crops, adapted for sprinting from predators in open terrain.

Meadow vole
Common small rodent of wet and dry grasslands; high reproductive rate, creates runways through vegetation, critical prey for many grassland predators.

Plains pocket gopher
Burrowing rodent that shapes prairie soils and plant communities; creates mounds and tunnels, feeds on roots and tubers, prefers deep, friable soils.

Pampas deer
Delicate deer of fertile pampas grasslands; browsers and grazers that avoid dense forests, relies on open plains and seasonal grass availability.

Patagonian mara
Large, long-legged rodent that resembles a small deer; monogamous, runs swiftly across open grasslands, lives in pairs and small groups on arid pampas.

Greater rhea
Large, flightless bird of open grasslands; runs at speed to escape predators, feeds on plants and small animals, nests on ground in loose communal clutches.

Pampas fox
Adaptable canid of South American grasslands; omnivorous diet, uses dens and open cover, plays both scavenger and predator roles in pampas ecosystems.

Pampas cat
Small wild cat of open grasslands and scrub; solitary, hunts rodents and birds, camouflaged coat suits patchy grassland and rocky habitats.

Guanaco
Wild camelid of arid and cold grasslands; forms family groups, grazes tough steppe vegetation, highly adapted to sparse forage and extreme climates.

Lesser rhea (Darwin’s rhea)
Smaller rhea species of southern grasslands and shrub-steppe; flightless, feeds on plants and insects, nests on ground and adapted to cold, windy plains.

Emu
Large, flightless bird of open Australian grasslands; powerful legs for long-distance movement, omnivorous diet, disperses seeds and thrives in variable climates.

Eastern grey kangaroo
Common grazing marsupial of grassy woodlands and pastures; moves by bounding, feeds on grasses, uses sheltering behavior and social groups to survive temperate seasons.

Blesbok
Antelope of rolling sour veld grasslands; forms herds, grazes short grasses, adapted to periodic burns and seasonal grazing pressure.

Bontebok
Grassland antelope once restricted to coastal plains; grazes short grass and salt marsh fringes, historically reduced by hunting but now protected in reserves.

Black wildebeest
Endemic grazing ungulate of open southern grasslands; forms migratory herds, specialized on short grasses, influences plant composition through intense grazing.

Cape hare
Widespread hare of open country and grasslands; nocturnal or crepuscular, browsers and grazers, relies on speed and cryptic coloration in open landscapes.

Black-tailed godwit
Long‑legged wader that breeds in wet meadows and temperate grasslands; nests on damp grassland, migratory but relies on grassland breeding habitat (included due to regular grassland breeding dependence).





