Along coastlines, estuaries and aquaculture ponds, shelled and jointed animals shape habitats and local food webs. From tide pools to commercial shrimp farms, noticing the differences between species helps with identification, conservation and cooking.
There are 20 Crustacean Examples, ranging from Acorn barnacle to Whiteleg shrimp. For each species, the table lists Scientific name,Habitat,Size (cm) so you can compare where they live and how large they grow — you’ll find below.
How can I use the table to identify a crustacean I found?
Start by noting where you found it (shore, mudflat, reef, farm) and its approximate size; then match those details to the Habitat and Size (cm) columns. The Scientific name lets you look up images and region-specific guides for a confident ID, and photos or a local field guide speed the process.
Which of these species are commonly eaten or farmed?
Species like the Whiteleg shrimp are major aquaculture products, while some crabs and larger shrimp are also harvested commercially; many barnacles and tiny intertidal crustaceans are not typical food sources. Always check local regulations and sustainability ratings before harvesting or buying.
Crustacean Examples
| Name | Scientific name | Habitat | Size (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| American lobster | Homarus americanus | Northwest Atlantic rocky cold waters | 65 |
| Spiny lobster | Panulirus argus | Tropical–subtropical reefs and seagrass | 60 |
| Blue crab | Callinectes sapidus | Western Atlantic estuaries and bays | 23 |
| Red king crab | Paralithodes camtschaticus | North Pacific cold benthic zones | 180 |
| Dungeness crab | Metacarcinus magister | Northeast Pacific sandy and muddy bottoms | 25 |
| Fiddler crab | Uca pugnax | Salt marshes and intertidal mudflats | 4 |
| Common shore crab | Carcinus maenas | Temperate rocky shorelines and estuaries | 10 |
| Pistol shrimp | Alpheus heterochaelis | Warm coastal burrows and seagrass beds | 10 |
| Grass shrimp | Palaemonetes pugio | Estuaries, marshes and seagrass beds | 6 |
| Whiteleg shrimp | Litopenaeus vannamei | Tropical to subtropical coastal waters | 23 |
| Peacock mantis shrimp | Odontodactylus scyllarus | Tropical coral reefs and rocky crevices | 18 |
| Red swamp crayfish | Procambarus clarkii | Freshwater rivers, ponds and wetlands | 12 |
| Antarctic krill | Euphausia superba | Southern Ocean pelagic waters | 6 |
| Acorn barnacle | Semibalanus balanoides | Temperate intertidal rocky shores | 2 |
| Goose barnacle | Lepas anatifera | Open ocean attached to floating debris | 10 |
| Calanus copepod | Calanus finmarchicus | North Atlantic planktonic waters | 0.6 |
| Freshwater amphipod | Gammarus pulex | Streams, rivers and freshwater margins | 2 |
| Common woodlouse | Armadillidium vulgare | Humid terrestrial leaf litter and gardens | 2 |
| Mole crab (sand crab) | Emerita analoga | Sandy beaches in surf zone (Pacific coasts) | 4 |
| Hermit crab (Caribbean) | Coenobita clypeatus | Coastal forests and shores, terrestrial near sea | 10 |
Images and Descriptions

American lobster
Large predatory decapod that eats fish, mollusks and carrion; chiefly nocturnal and uses powerful claws to crush prey and compete for shelter. Notable for long lifespan and large size, sometimes living decades and regrowing lost limbs.

Spiny lobster
Omnivore that forages on reefs and seagrass at night; lacks large crushing claws and uses a spiny carapace and long antennae for defense. Famous for long migrations and valuable fisheries across tropical waters.

Blue crab
Active swimmer and opportunistic omnivore eating bivalves, small fish and detritus; males famed for bright blue claws while females have red-tipped claws. They dig and burrow into sediments and are important in estuary fisheries.

Red king crab
Large benthic predator and scavenger feeding on clams, worms and detritus; slow-growing and commercially prized. Notable for enormous leg span and major role in cold North Pacific benthic ecosystems; often harvested at industrial scales.

Dungeness crab
Omnivorous scavenger that feeds on clams, small fish and algae; vigorous swimmer and important Pacific Northwest fishery. Known for sweet-tasting meat and sizable carapace; they dig and hunt along sandy bottoms.

Fiddler crab
Small intertidal crab where males have one oversized waving claw used for courtship and territorial displays; feeds by sifting sediment for microalgae and detritus. Common and conspicuous on mudflats.

Common shore crab
Adaptable omnivore that eats mollusks, worms and algae; tolerates wide salinity ranges and has invaded many global coastlines. Notable invasive status and aggressive foraging, reproducing quickly and often outcompeting native crabs.

Pistol shrimp
Small burrowing shrimp that snaps an enlarged claw to produce a cavitation bubble, stunning prey and making loud snaps; omnivorous and often pairs with goby fish for mutual shelter. Famous for its snapping shock.

Grass shrimp
Small estuarine shrimp that feeds on plankton and detritus; an important forage species for fish and birds. Often found in seagrass beds and marshes, tolerant of varying salinity and playing a key ecological role.

Whiteleg shrimp
Fast-growing penaeid shrimp farmed worldwide; omnivorous scavenger feeding on plankton and detritus. Notable for aquaculture importance and rapid maturation under warm, brackish conditions. They support major seafood industries and global markets.

Peacock mantis shrimp
Carnivorous stomatopod that hunts with hammer-like clubs or spear-like appendages to capture prey; highly vision-specialized with colorful eyes and incredible strike speed. Solitary reef predator that can pulverize shells and aquarium glass.

Red swamp crayfish
Freshwater omnivore eating plants, invertebrates and detritus; burrows and tolerates varied conditions. Known as an invasive species in many regions and valued in cuisine; alters wetland habitats through burrowing activity.

Antarctic krill
Small, planktonic crustacean forming huge swarms, grazing on phytoplankton; cornerstone of Southern Ocean food webs feeding whales, seals, penguins and fish. Notable for massive biomass, seasonal migrations, and commercial krill harvesting.

Acorn barnacle
Sessile filter-feeder attached to rocks in the intertidal, extending cirri to capture plankton. Hardy to wave action and desiccation, it dominates exposed shorelines and is common in temperate seas; used in larval dispersal studies.

Goose barnacle
Pelagic barnacle that drifts attached to floating objects and ship hulls; filter-feeder using long cirri to catch plankton. Noted for planktonic lifestyle and occasional culinary value; useful indicators of ocean currents and debris movement.

Calanus copepod
Copepod that feeds on phytoplankton and small particles, abundant in North Atlantic plankton. Key prey for fish larvae; performs seasonal vertical migrations and is critical in fisheries ecology and oceanic carbon transfer.
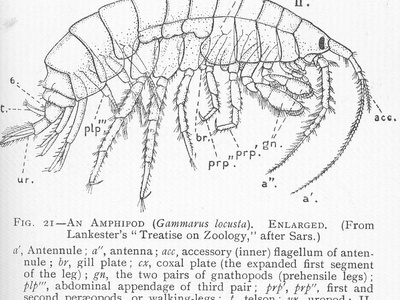
Freshwater amphipod
Freshwater amphipod that scrapes algae and detritus from stones; active swimmer and important link in stream food webs. Sensitive to pollution, widely used as an ecological indicator and to monitor water quality.

Common woodlouse
Terrestrial isopod that feeds on decaying plant material and fungi; rolls into a ball when disturbed. Common in gardens and leaf litter, aiding decomposition and nutrient cycling and preferring humid microhabitats.

Mole crab (sand crab)
Sand-burrowing mole crab that filters plankton by waving feathery antennae while facing waves; common on sandy beaches. Recognizable by quick digging and high mobility; important prey for shorebirds.

Hermit crab (Caribbean)
Terrestrial hermit crab that scavenges fruit, leaf litter and small animals; uses empty shells for protection and often carries water in its shell to keep gills moist. Popular in the pet trade.





