Wetlands are a patchwork of marshes, swamps and river edges where water shapes the landscape and wildlife. Snakes are a regular part of that mix, playing roles from predator to scavenger and helping keep small animal populations in balance.
There are 67 wetland snakes, ranging from African Rock Python to Yellow-spotted Keelback. For each entry you’ll find below Scientific name,Range/region,Size (cm), so you can scan distribution and typical size at a glance—take a look at the list you’ll find below.
How dangerous are wetland snakes to people?
Danger varies by species and situation: many wetland snakes are non‑venomous and avoid people, while others can be venomous or large enough to injure if provoked. The best approach is prevention—give snakes space, keep pets leashed, and learn which local species are risky—if bitten, seek medical care promptly rather than trying home remedies.
How can I tell a harmless water snake from a venomous one in the field?
There’s no simple rule that works everywhere and appearance can be misleading, so don’t rely on myths. Note behavior (do they flee or act defensive), habitat, and markings, and use a regional field guide or expert photos for comparison. If you need to identify one, photograph it from a safe distance and consult local resources rather than handling it yourself.
Wetland Snakes
| Common name | Scientific name | Range/region | Size (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cottonmouth | Agkistrodon piscivorus | Southeastern United States | 75-120 |
| Green Anaconda | Eunectes murinus | Amazon and Orinoco basins, South America | 300-600 |
| Northern Water Snake | Nerodia sipedon | Eastern and Central North America | 60-110 |
| Grass Snake | Natrix natrix | Europe and parts of Asia and North Africa | 75-120 |
| Red-bellied Black Snake | Pseudechis porphyriacus | Eastern Australia | 125-200 |
| King Cobra | Ophiophagus hannah | South and Southeast Asia | 300-450 |
| Reticulated Python | Malayopython reticulatus | Southeast Asia | 300-700 |
| African Rock Python | Python sebae | Sub-Saharan Africa | 300-500 |
| Banded Water Cobra | Naja annulata | Central Africa | 140-220 |
| Checkered Keelback | Fowlea piscator | South and Southeast Asia | 60-120 |
| Tiger Snake | Notechis scutatus | Southern Australia | 90-120 |
| Mangrove Snake | Boiga dendrophila | Southeast Asia | 180-250 |
| Tentacled Snake | Erpeton tentaculatum | Southeast Asia | 50-90 |
| Elephant Trunk Snake | Acrochordus javanicus | Southeast Asia and northern Australia | 150-250 |
| Yellow Anaconda | Eunectes notaeus | Pantanal region, South America | 200-300 |
| Banded Water Snake | Nerodia fasciata | Southeastern United States | 60-100 |
| Diamond-backed Water Snake | Nerodia rhombifer | Central US and northern Mexico | 75-120 |
| Brown Water Snake | Nerodia taxispilota | Southeastern United States | 90-150 |
| Mud Snake | Farancia abacura | Southeastern United States | 100-140 |
| Rainbow Snake | Farancia erytrogramma | Southeastern United States | 90-120 |
| Queen Snake | Regina septemvittata | Eastern North America | 40-60 |
| Eastern Massasauga | Sistrurus catenatus | North America Great Lakes region | 50-75 |
| Water Cobra | Hydrodynastes gigas | Central South America | 150-250 |
| Viperine Snake | Natrix maura | Southwestern Europe, Northwestern Africa | 60-85 |
| Dice Snake | Natrix tessellata | Southern and Central Europe, Western Asia | 75-100 |
| Puff-faced Water Snake | Homalopsis buccata | Southeast Asia | 80-120 |
| Arafura File Snake | Acrochordus arafurae | Northern Australia and New Guinea | 150-250 |
| Water Python | Liasis fuscus | Northern Australia and New Guinea | 150-250 |
| Salt Marsh Snake | Nerodia clarkii | Southeastern US coast | 40-75 |
| Glossy Crayfish Snake | Liodytes rigida | Southeastern United States | 35-50 |
| Black Swamp Snake | Seminatrix pygaea | Southeastern United States | 25-40 |
| Burmese Python | Python bivittatus | Southeast Asia | 300-500 |
| Banded Krait | Bungarus fasciatus | South and Southeast Asia | 150-200 |
| Forest Cobra | Naja melanoleuca | West and Central Africa | 150-220 |
| Common Garter Snake | Thamnophis sirtalis | North America | 45-65 |
| Eastern Ribbon Snake | Thamnophis saurita | Eastern North America | 45-65 |
| Giant Garter Snake | Thamnophis gigas | California, USA | 80-120 |
| Florida Green Water Snake | Nerodia floridana | Florida and southern Georgia | 75-140 |
| Plain-bellied Water Snake | Nerodia erythrogaster | USA and Mexico | 75-120 |
| Crab-eating Water Snake | Fordonia leucobalia | Coastal Southeast Asia, Northern Australia | 60-100 |
| Dog-faced Water Snake | Cerberus rynchops | Coastal Southeast Asia, Northern Australia | 60-90 |
| Olive Keelback | Atretium schistosum | Indian subcontinent | 50-80 |
| Buff-striped Keelback | Amphiesma stolatum | South and Southeast Asia | 40-60 |
| Javan Mudsnake | Xenodermus javanicus | Southeast Asia | 40-50 |
| Amazon Tree Boa | Corallus hortulanus | Amazon Basin, South America | 150-200 |
| Brazilian Rainbow Boa | Epicrates cenchria | Central and South America | 150-200 |
| Fer-de-Lance | Bothrops atrox | Northern South America | 75-125 |
| Black-necked Garter Snake | Thamnophis cyrtopsis | Southwestern US and Mexico | 40-70 |
| Black-bellied Swamp Snake | Hemiaspis signata | Eastern Australia | 40-50 |
| Keelback | Tropidonophis mairii | Northern and Eastern Australia, New Guinea | 50-75 |
| Bocourt’s Water Snake | Subsessor bocourti | Southeast Asia | 90-120 |
| Rainbow Water Snake | Enhydris enhydris | Southeast Asia | 40-60 |
| Triangle Keelback | Xenochrophis trianguligerus | Southeast Asia | 70-100 |
| Chinese Water Snake | Myrrophis chinensis | China, Vietnam, Taiwan | 40-70 |
| Plumbeous Water Snake | Enhydris plumbea | Southeast Asia | 40-60 |
| Banded Fishing Snake | Sinonatrix annularis | China and Taiwan | 60-90 |
| Mock Viper | Psammodynastes pulverulentus | Southeast Asia | 40-60 |
| South American Bushmaster | Lachesis muta | South America | 200-300 |
| Aquatic Garter Snake | Thamnophis atratus | Western United States | 45-75 |
| Black-banded Water Cobra | Naja christyi | Congo Basin | 120-200 |
| Smith’s Water Snake | Grayia smythii | West and Central Africa | 100-130 |
| Olive Water Snake | Afronatrix anoscopus | West and Central Africa | 50-70 |
| Ornate Water Snake | Grayia ornata | Central Africa | 100-150 |
| Indian Python | Python molurus | Indian subcontinent | 250-400 |
| Striped Keelback | Xenochrophis vittatus | Southeast Asia | 50-70 |
| Yellow-spotted Keelback | Xenochrophis flavipunctatus | Southeast Asia | 50-80 |
| Schneider’s Bockadam | Cerberus schneiderii | Southeast Asia | 50-80 |
Images and Descriptions

Cottonmouth
A stout-bodied pit viper famous for its defensive white mouth display. Venomous: Yes. It inhabits swamps, marshes, and slow-moving waterways, often seen basking on logs or banks. This snake is a top predator in its aquatic environment.

Green Anaconda
One of the world’s heaviest snakes, perfectly adapted for life in slow-moving rivers and swamps. Venomous: No. It is a powerful constrictor that ambushes large prey like capybara and caiman from the water’s edge.

Northern Water Snake
A highly adaptable and common snake found in nearly any freshwater habitat, from rivers to backyard ponds. Venomous: No. Though often mistaken for the venomous cottonmouth, this feisty snake is harmless and preys mainly on fish and amphibians.

Grass Snake
A slender, graceful snake often found near ponds, marshes, and streams where it hunts amphibians. Venomous: No. It is known for its distinctive yellow or white collar and its dramatic defense of playing dead when threatened.

Red-bellied Black Snake
A beautiful, glossy black snake with a striking red or pink belly, commonly found in swamps, forests, and creek beds. Venomous: Yes. It is generally shy but possesses potent venom, preying on frogs, reptiles, and small mammals.

King Cobra
The world’s longest venomous snake, often found near streams and in mangrove swamps within its forested range. Venomous: Yes. Uniquely, its diet consists almost entirely of other snakes, and it is the only snake that builds a nest for its eggs.

Reticulated Python
One of the world’s longest snakes, it is a powerful swimmer often found in rivers, swamps, and even urban canals. Venomous: No. This constrictor is an ambush predator with a beautiful, intricate geometric pattern that provides excellent camouflage.

African Rock Python
Africa’s largest snake, this powerful constrictor is never far from a permanent water source like a river or swamp. Venomous: No. It is known for its aggressive temperament and ability to consume large prey such as antelope or crocodiles.

Banded Water Cobra
A truly aquatic cobra with prominent black bands, perfectly adapted for hunting fish in rivers and lakes. Venomous: Yes. It has a potent neurotoxic venom and is one of the few cobras that spends the majority of its life in water.

Checkered Keelback
An extremely common semi-aquatic snake found in flooded rice paddies, ponds, and rivers across its vast range. Venomous: No. It is named for the checkerboard pattern on its back and is a voracious predator of fish and frogs.

Tiger Snake
A highly venomous elapid often found in wetlands, swamps, and along creeks where its frog prey is abundant. Venomous: Yes. Its coloration and pattern are extremely variable, ranging from olive green to black, often with yellow bands.

Mangrove Snake
A striking black-and-yellow snake that inhabits mangrove swamps and lowland riverine forests, often hunting at night. Venomous: Yes. It has a mild, rear-fanged venom primarily used to subdue prey like birds, bats, and rodents.

Tentacled Snake
A bizarre, fully aquatic snake with two unique tentacles on its snout used to sense vibrations from passing fish. Venomous: Yes. It is mildly venomous, using rear fangs to immobilize its prey with a quick, sideways strike.
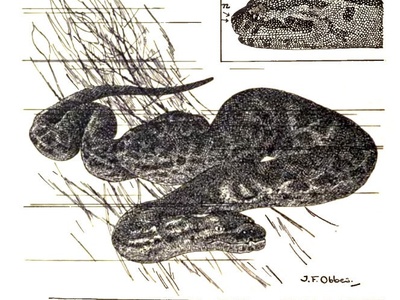
Elephant Trunk Snake
A fully aquatic, non-venomous snake with loose, baggy skin covered in rough, file-like scales for gripping slippery fish. Venomous: No. It is a slow-moving ambush predator that waits on the bottom of muddy rivers and estuaries.

Yellow Anaconda
Smaller than its green cousin, this anaconda has a yellowish-green background with black blotches, ideal for swamp camouflage. Venomous: No. It is a powerful constrictor that thrives in the marshes and slow rivers of the Pantanal wetland.

Banded Water Snake
Characterized by broad, dark bands across its back, this non-venomous snake is a fixture of southern swamps, rivers, and lakes. Venomous: No. It is often active at night, hunting for frogs and fish in shallow water.

Diamond-backed Water Snake
A large, heavy-bodied water snake named for the distinct, chain-like diamond pattern on its back. Venomous: No. It is a powerful swimmer that prefers larger, slow-moving rivers and swamps where it preys almost exclusively on fish.

Brown Water Snake
A very large, semi-aquatic snake with dark brown blotches, often found basking on branches overhanging rivers and swamps. Venomous: No. It is known for dropping into the water from tree limbs when disturbed, earning it the nickname “water-pilot.”

Mud Snake
A large, glossy black snake with a red or pink checkered belly, living in swamps and muddy-bottomed waterways. Venomous: No. This secretive snake is a specialist predator, feeding almost exclusively on giant aquatic salamanders like sirens and amphiumas.

Rainbow Snake
A stunningly iridescent snake with red and yellow stripes, this species is highly aquatic and secretive, living in swamps and rivers. Venomous: No. It is known as the “eel moccasin” because its primary food source is the American eel.

Queen Snake
A small, slender semi-aquatic snake that lives along clean, rocky streams and rivers with abundant crayfish. Venomous: No. It is a dietary specialist, feeding almost exclusively on freshly molted crayfish, which it finds by smell.

Eastern Massasauga
A small rattlesnake with a big reputation, this species inhabits wetlands like fens, bogs, and marshy prairies. Venomous: Yes. It is a shy pit viper that relies on camouflage to ambush small rodents and frogs in its damp habitat.

Water Cobra
A large, bold colubrid snake, also known as the false water cobra, that flattens its neck into a hood when threatened. Venomous: Yes. It has a mild, rear-fanged venom and actively hunts fish, amphibians, and other reptiles in wetlands.

Viperine Snake
This highly aquatic snake strongly resembles a venomous viper with its pattern and defensive behavior, but it is harmless. Venomous: No. It spends most of its time in or near water, hunting fish and frogs with great skill.

Dice Snake
Named for its checkered or spotted pattern, this is a slender, highly aquatic snake that is an expert at catching fish. Venomous: No. When threatened, it can secrete a foul-smelling fluid from its cloaca or play dead.

Puff-faced Water Snake
A common, stout-bodied snake of rice paddies, ponds, and ditches, easily identified by its distinctively patterned head. Venomous: Yes. It possesses a mild, rear-fanged venom effective on its fish and frog prey but not dangerous to humans.

Arafura File Snake
Similar to the Elephant Trunk Snake, this fully aquatic species has loose, granulated skin perfect for gripping slimy fish. Venomous: No. It is an important traditional food source for Indigenous Australian communities in its region.

Water Python
A semi-aquatic python with dark, iridescent skin that gives it a beautiful sheen, perfectly suited for its wetland habitat. Venomous: No. It thrives in floodplains, swamps, and lagoons, where it hunts birds, mammals, and reptiles at the water’s edge.

Salt Marsh Snake
A specialist of coastal salt marshes and mangrove estuaries, this snake is uniquely adapted to brackish water environments. Venomous: No. It has several subspecies with varying stripes and colors, all of which feed on small fish and invertebrates.

Glossy Crayfish Snake
A small, secretive snake that spends most of its life burrowing in the mud of swamps, ditches, and crayfish burrows. Venomous: No. As its name implies, it is a specialist that feeds almost exclusively on crayfish.

Black Swamp Snake
A small, shiny black snake with a bright red belly, this species is highly aquatic and thrives in vegetation-choked wetlands. Venomous: No. It is a shy, gentle snake that feeds on a variety of small aquatic invertebrates like leeches and worms.

Burmese Python
A giant constrictor famous for its role as an invasive species in the Florida Everglades, a massive wetland. Venomous: No. In its native range, it is strongly associated with water, being an excellent swimmer and ambushing prey from riverbanks.

Banded Krait
A large, highly venomous elapid with stark yellow and black bands, often found in wetlands and rice paddies. Venomous: Yes. It is primarily nocturnal and preys on other snakes, including aquatic species, as well as eels and frogs.

Forest Cobra
A large, intelligent, and highly active cobra that is just as comfortable in trees as it is swimming in rivers or swamps. Venomous: Yes. It is not a true water cobra but is an excellent swimmer and frequently hunts fish and frogs.

Common Garter Snake
One of North America’s most common and widespread snakes, it often lives near water sources like ponds and marshes. Venomous: No. While its saliva is mildly toxic to its small prey, it is considered harmless to humans.

Eastern Ribbon Snake
A very slender, semi-aquatic relative of the garter snake with three distinct, bright stripes, usually yellow or white. Venomous: No. It is a graceful swimmer that prefers the vegetated edges of ponds, streams, and marshes to hunt frogs and fish.

Giant Garter Snake
One of the largest garter snakes, this endangered species is highly aquatic, living in marshes and agricultural wetlands. Venomous: No. Its survival is tied directly to the health of its wetland habitat and populations of its primary prey, frogs and tadpoles.

Florida Green Water Snake
A large, stout water snake that can be greenish, brownish, or reddish, but lacks the distinct patterns of its relatives. Venomous: No. It is a dominant predator in the marshes and swamps of Florida, especially the Everglades.

Plain-bellied Water Snake
A large, often patternless snake with a distinct, unmarked reddish or yellowish belly, found in calm bodies of water. Venomous: No. It is a powerful snake that often basks on logs and is known for its defensive disposition when handled.

Crab-eating Water Snake
A specialist of mangrove swamps and tidal mudflats, where it uses its powerful jaws to crush and eat small crabs. Venomous: Yes. It has a mild, rear-fanged venom and is one of the few snakes adapted to hunting hard-shelled crustaceans.

Dog-faced Water Snake
Named for its somewhat canine-like snout, this snake is a common inhabitant of mangrove ecosystems and tidal rivers. Venomous: Yes. It is mildly venomous and an opportunistic nocturnal hunter, preying on fish and crustaceans in the brackish water.

Olive Keelback
A common snake of rice fields, ponds, and marshes, recognized by its uniform olive-brown color and keeled scales. Venomous: No. It is diurnal and actively hunts for frogs, tadpoles, and fish in shallow, slow-moving water.

Buff-striped Keelback
A small, slender, and harmless snake often found in moist grasslands, rice paddies, and near other water bodies. Venomous: No. It is easily identified by two prominent buff or yellow stripes running down its back.

Javan Mudsnake
A bizarre, non-venomous snake with unique, granular scales and prominent dorsal ridges, giving it a dragon-like appearance. Venomous: No. This nocturnal, semi-aquatic snake inhabits wet areas like rice fields and streamsides, feeding on frogs and fish.

Amazon Tree Boa
A highly variable, arboreal boa that is extremely common along the river corridors and flooded forests of the Amazon. Venomous: No. It drapes itself on branches overhanging water, waiting to ambush birds, bats, and other small animals.

Brazilian Rainbow Boa
Famed for its stunning iridescent sheen, this boa lives in humid forests and savannas, often staying close to rivers. Venomous: No. It is a terrestrial constrictor that is also a capable swimmer, hunting rodents and birds at night.

Fer-de-Lance
A highly venomous and adaptable pit viper that is often found in higher concentrations near water sources in forests and fields. Venomous: Yes. Its name means “lancehead” in French, referring to the shape of its head.

Black-necked Garter Snake
A colorful garter snake that prefers rocky canyons and arid environments but almost always lives near permanent streams or pools. Venomous: No. It uses these riparian habitats to hunt for tadpoles, frogs, and small fish.

Black-bellied Swamp Snake
A small, semi-aquatic venomous snake that inhabits swamps, marshes, and rainforest streams, often hiding in dense vegetation. Venomous: Yes. It is active both day and night, specializing in hunting lizards, particularly skinks, and frogs.

Keelback
A non-venomous, semi-aquatic snake common in a wide range of habitats, especially wetlands, streams, and suburban gardens. Venomous: No. Uniquely, it can eat the toxic, invasive Cane Toad without being harmed, making it ecologically important.

Bocourt’s Water Snake
A large, heavily-bodied, and powerful aquatic snake that lives in marshes, swamps, and flooded agricultural areas. Venomous: No. It is a nocturnal ambush predator that preys almost exclusively on fish, including commercially farmed species.

Rainbow Water Snake
A common, semi-aquatic snake of still or slow-moving freshwater bodies like ponds and rice paddies. Venomous: Yes. This mildly venomous, rear-fanged snake is named for the slight iridescence seen on its scales in the sunlight.

Triangle Keelback
A brightly colored water snake with a row of orange to red spots down its side, found in marshes and wet forests. Venomous: No. Despite its harmless nature, it can be quite defensive, flattening its neck and striking when threatened.

Chinese Water Snake
A small, semi-aquatic snake that inhabits rice paddies, ponds, and other wetland environments in its range. Venomous: No. It is a common species that primarily feeds on small fish and amphibians, often hunted for food or traditional medicine.

Plumbeous Water Snake
A very common, small water snake with a dull, lead-colored back and a pale belly, often found in ditches and rice fields. Venomous: Yes. It is a mildly venomous, rear-fanged species that is generally placid and feeds on frogs and fish.

Banded Fishing Snake
A semi-aquatic snake found in a variety of wetland habitats, from mountain streams to rice paddies. Venomous: No. It is a nocturnal hunter that, as its name suggests, is a very capable predator of fish.

Mock Viper
Named for its viper-like head and attitude, this small snake is often found in moist leaf litter near streams in forested areas. Venomous: Yes. It has a mild, rear-fanged venom and preys on frogs and lizards.

South American Bushmaster
The world’s longest pit viper, this formidable snake inhabits humid forests, often choosing its ambush sites near streams. Venomous: Yes. It is a rare, nocturnal predator known for its large venom yield and a tail that ends in a spiny rattle.

Aquatic Garter Snake
A garter snake that is more heavily tied to water than many of its relatives, living along streams and ponds. Venomous: No. It is an active diurnal hunter, feeding on slugs, salamanders, and fish in its riparian habitat.

Black-banded Water Cobra
A close relative of the Banded Water Cobra, this species is also highly aquatic, living in the rivers of the Congo. Venomous: Yes. It is a powerful swimmer with a potent neurotoxic venom, adapted for a life spent hunting fish.

Smith’s Water Snake
A large, fast-moving, and alert snake that actively hunts for fish and frogs during the day in rivers, lakes, and swamps. Venomous: No. Its smooth scales and powerful body make it an extremely efficient swimmer.

Olive Water Snake
A secretive, nocturnal snake that forages in the shallow waters of swamps, rainforest streams, and flooded areas. Venomous: No. It is a gentle species that preys on tadpoles, small frogs, and fish.

Ornate Water Snake
A large, diurnal, and highly active water snake that vigorously pursues its prey of fish in various aquatic habitats. Venomous: No. It is known for its incredible speed, both in the water and on land when moving between water bodies.

Indian Python
A large constrictor that prefers habitats near a permanent water source, such as river valleys, marshes, and grasslands. Venomous: No. It is a slow-moving, nocturnal ambush predator that kills its prey by coiling around and suffocating it.

Striped Keelback
A small, striped snake common in wet, open habitats like rice fields, marshes, and the edges of ponds. Venomous: No. It is diurnal and actively forages for its prey, which consists almost entirely of frogs.

Yellow-spotted Keelback
A semi-aquatic snake recognized by the yellow or orange spots on its upper body, often found in disturbed, wet areas. Venomous: No. It’s an adaptable snake that thrives in human-altered habitats like irrigation canals and fish farms.

Schneider’s Bockadam
A common inhabitant of coastal mudflats, mangrove forests, and tidal estuaries, with eyes positioned high on its head. Venomous: Yes. This mildly venomous, rear-fanged snake is well-adapted for aquatic life, hunting for fish and crustaceans.





