Tropical rainforests brim with flavors and stories: from roadside markets to canopy-foraging, the fruits you’ll meet there shape diets, medicines and local economies. Many are unfamiliar outside their native regions, but they’re central to how people eat and trade in those ecosystems.
There are 39 rainforest fruits, ranging from Ackee to Star apple (Caimito). For each entry you’ll find below the columns Scientific name, Native region, Flavor/uses and Size (cm), so you can quickly compare origin and culinary or practical uses — you’ll find all of this below.
How can I tell which rainforest fruits are safe to eat?
Look for local guidance first — farmers, market sellers and field guides are the best sources. Check color, aroma and texture against reliable references, avoid fruits that are unusually soft or have off smells, and never eat a wild fruit unless you’re confident in its identification and preparation methods.
Can I grow or buy these rainforest fruits outside their native regions?
Some species adapt to container growing or subtropical gardens, but many need specific humidity and temperature; check climate compatibility, import rules and nursery availability. Specialty markets and online traders sometimes offer fresh or preserved specimens if local growing isn’t possible.
Rainforest Fruits
| Name | Scientific name | Native region | Flavor/uses | Size (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durian | Durio zibethinus | Southeast Asia | Rich, custardy, sulfurous; eaten raw, desserts | 15-30 cm |
| Mangosteen | Garcinia mangostana | Southeast Asia | Sweet-tart, floral; eaten fresh, desserts | 4-8 cm |
| Rambutan | Nephelium lappaceum | Southeast Asia | Sweet, juicy, lychee-like; eaten fresh, preserves | 3-6 cm |
| Lychee | Litchi chinensis | Southeast Asia | Floral, sweet; fresh, canned, desserts | 2-4 cm |
| Longan | Dimocarpus longan | Southeast Asia | Musky sweet; eaten fresh, dried | 2-3 cm |
| Jackfruit | Artocarpus heterophyllus | South/Southeast Asia | Sweet when ripe, savory unripe; raw, cooked, vegan meat | 30-90 cm |
| Breadfruit | Artocarpus altilis | Pacific Islands, SE Asia | Starchy, potato-like when cooked; roasted, fried | 10-30 cm |
| Soursop (Guanabana) | Annona muricata | Tropical Americas | Tropical custard, tangy; juices, ice creams | 15-30 cm |
| Custard apple (Bullock’s heart) | Annona reticulata | Tropical Americas | Sweet, creamy; eaten fresh, desserts | 5-10 cm |
| Açaí | Euterpe oleracea | Amazon Basin | Earthy, blackberry-like; smoothies, bowls | 1-2 cm |
| Cupuaçu | Theobroma grandiflorum | Amazon Basin | Tart, chocolate-citrus; sweets, juices | 10-20 cm |
| Cacao | Theobroma cacao | Amazon, Central America | Bitter bean pulp, chocolate; seeds fermented for chocolate | 10-30 cm |
| Camu camu | Myrciaria dubia | Amazon floodplains | Extremely tart, citrusy; juices, vitamin C | 2-3 cm |
| Jabuticaba | Plinia cauliflora | Brazilian Atlantic Forest | Sweet, grape-like; fresh, jams, wine | 2-4 cm |
| Guava | Psidium guajava | Tropical Americas | Sweet-tart; eaten fresh, juices, jellies | 4-12 cm |
| Mango | Mangifera indica | South Asia (tropical forests) | Sweet, aromatic; fresh, chutneys, dried | 5-25 cm |
| Avocado | Persea americana | Central America | Creamy, mild; spreads, salads | 7-20 cm |
| Papaya | Carica papaya | Tropical Americas | Sweet, musky; raw, juices, green cooked | 15-50 cm |
| Pineapple | Ananas comosus | South American tropics | Sweet-tart, tropical; fresh, canned, juices | 10-30 cm |
| Passionfruit | Passiflora edulis | SE Brazil | Tart, aromatic; juices, desserts | 4-8 cm |
| Mamey sapote | Pouteria sapota | Mesoamerica | Sweet, pumpkin-like; eaten raw, smoothies | 6-12 cm |
| Sapodilla | Manilkara zapota | Tropical Americas | Brown-sugar sweet; eaten raw, desserts | 4-8 cm |
| Star apple (Caimito) | Chrysophyllum cainito | Caribbean, Central America | Sweet, custardy; eaten fresh | 6-10 cm |
| Black sapote | Diospyros digyna | Mexico, Central America | Cocoa-like when ripe; eaten fresh, desserts | 5-9 cm |
| Peach palm (Pejibaye) | Bactris gasipaes | Amazon, Central America | Starchy, nutty; boiled, mashed | 2-4 cm |
| Buriti | Mauritia flexuosa | Amazon floodplain and swamp forests | Sweet, oily, beta-carotene rich; juices, oil | 2-4 cm |
| Bacuri | Platonia insignis | Amazon Basin | Sweet-acidic pulp; eaten fresh, sweets | 6-9 cm |
| Ackee | Blighia sapida | West African rainforests; naturalized Caribbean | Buttery, mild when ripe; must be ripened/cooked, toxic unripe | 5-8 cm |
| Miracle fruit | Synsepalum dulcificum | West African rainforest | Makes sour taste sweet; eaten fresh, flavoring | 1-2 cm |
| African plum (Safou) | Dacryodes edulis | West and Central Africa | Rich, buttery; roasted, snack | 3-6 cm |
| African mango (Bush mango) | Irvingia gabonensis | West/Central Africa | Fibrous, slightly acidic; eaten raw, seeds used | 3-4 cm |
| Ambarella (Golden apple) | Spondias dulcis | Indo-Pacific tropical forests | Tart, apple-like; fresh, chutneys, pickles | 4-8 cm |
| Java plum (Jambolan) | Syzygium cumini | Indian subcontinent, SE Asia | Sweet-ashy, astringent; fresh, jams | 2-3 cm |
| Pulasan | Nephelium mutabile | Borneo, Malay Archipelago | Sweeter than rambutan; eaten fresh | 3-6 cm |
| Santol | Sandoricum koetjape | Malesian rainforests | Sweet-sour; eaten raw, preserves | 4-6 cm |
| Langsat (Lanzones) | Lansium parasiticum | Southeast Asian rainforests | Sweet, mildly tart; eaten fresh, candied | 2-4 cm |
| Marang | Artocarpus odoratissimus | Borneo, Philippines | Sweet, custardy, aromatic; fresh, desserts | 10-15 cm |
| Mountain apple | Syzygium malaccense | Southeast Asia, Pacific Islands | Crisp, mildly sweet; eaten fresh | 4-6 cm |
| Rose apple | Syzygium jambos | SE Asia; naturalized Americas | Mild, floral; fresh, local drinks | 3-5 cm |
Images and Descriptions

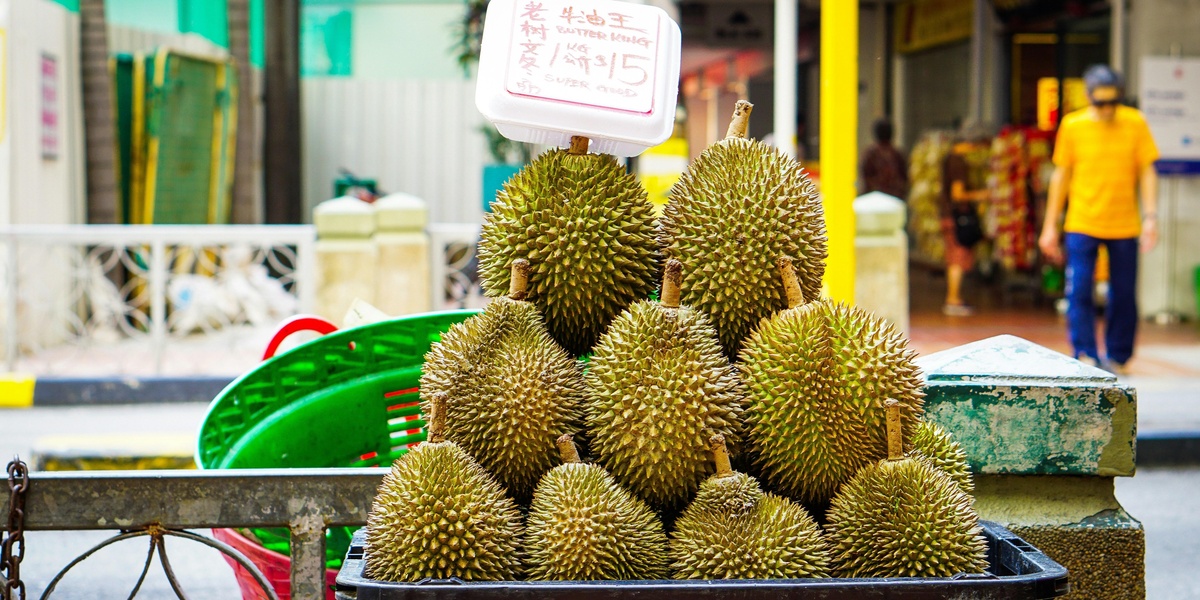
Durian
Iconic Southeast Asian fruit with large spiky rind and custardlike segments. Highly prized for rich flavor but notorious odor; often banned in transit. Ripe flesh is eaten fresh or in sweets; some people find unripe or overripe pulp unpleasant.

Mangosteen
Small purple fruit with snow-white segments and a delicate sweet-tart flavor. Revered in tropical Asia, often eaten fresh or in desserts. The rind is bitter; seeds can be bitter, but edible pulp is prized and safe when ripe.

Rambutan
Hairy red fruit with translucent, firm flesh and a sweet floral taste similar to lychee. Commonly eaten raw, made into jams, or canned. The seed is inedible raw; flesh is safe and popular across tropical forests.

Lychee
Juicy fruit with a bumpy red shell and aromatic, translucent flesh. Eaten fresh or preserved, used in drinks and desserts. Seeds are toxic if chewed raw; always discard seeds and eat ripe flesh.

Longan
Small brown fruit with translucent, juicy flesh and a mildly musky sweetness. Popular fresh, dried, or in desserts and teas. Contains a hard seed; flesh is safe and nutritious when ripe.

Jackfruit
Enormous compound fruit with sweet yellow bulbs when ripe and neutral, fibrous flesh used as vegetable when unripe. Popular across tropical Asia for desserts and savory dishes; ripe fruit is aromatic and eaten fresh.

Breadfruit
Large starchy fruit widely used in Pacific and SE Asian cuisines. Firm when unripe—boiled, roasted or fried like a vegetable—becomes softer and sweeter when ripe. Seeds are edible when cooked; fruit is a staple carbohydrate.

Soursop (Guanabana)
Large spiky green fruit with soft, aromatic white pulp that tastes sweet-tart. Eaten fresh, blended into juices and desserts. Some traditional medicinal uses exist; unprocessed seeds are bitter and should not be eaten.

Custard apple (Bullock’s heart)
Soft, segmented fruit with creamy sweet flesh used straight or in desserts. Seeds are toxic when crushed; pulp is prized for custardlike texture. Grows in lowland tropical areas and is commonly foraged or cultivated locally.

Açaí
Small dark purple palm berry harvested from flooded Amazonian forests. Flavor is mildly earthy and chocolatey; commonly processed into puree for bowls, juices, and oils. Perishable raw; usually consumed processed or frozen.

Cupuaçu
Large oblong pod related to cacao with fragrant, creamy pulp tasting like chocolate and citrus. Widely used in Amazonian sweets, juices and cosmetics. Seeds are processed for fats; pulp eaten raw or in confections.

Cacao
Striped pods contain white sweet pulp around bitter seeds. Pulp is edible; seeds are fermented and processed into cocoa and chocolate. Native understory tree of humid tropical forests and economically vital worldwide.

Camu camu
Bright red-purple berry from Amazonian floodplain shrubs with an intensely tart, citrus flavor. Valued for very high vitamin C content; usually processed into juices, powders or supplements as raw fruit is very sour.

Jabuticaba
Cauliflorous dark berries that grow directly on the trunk. Flesh is sweet and grape-like; often eaten fresh or fermented into jams and wines. Skin is mildly astringent; fruit is a regional specialty.

Guava
Aromatic green to yellow fruit with grainy but juicy flesh and sweet-tart flavor. Widely eaten fresh, made into juices, pastes and preserves. Seeds are edible but often strained from processed products.

Mango
Iconic tropical fruit with juicy, sweet flesh and floral aroma. Native to South Asian rainforests and now widespread. Eaten raw, cooked into chutneys, dried or processed; skin and sap can irritate sensitive skin in some people.

Avocado
Butter-rich berry with creamy flesh used as spread, in salads and cooked dishes. Native to humid tropical forests of Mexico and Central America. High in healthy fats; seeds and skin are inedible.

Papaya
Large melonlike fruit with sweet orange flesh and black seeds. Eaten raw, juiced, or green when unripe for cooking. Contains papain enzyme used as meat tenderizer; seeds are peppery and sometimes consumed in small amounts.

Pineapple
Composite bromeliad fruit with juicy, tart-sweet flesh. Native to lowland tropical Americas and widely cultivated. Eaten fresh, canned, or juiced; core is fibrous but edible, and bromeliad leaves not consumed.

Passionfruit
Round-to-oval purple or yellow fruit with seedy, aromatic pulp. Commonly used for juices, syrups, desserts and cocktails. Seeds are edible and crunchy; pulp is tart and fragrant.

Mamey sapote
Large brown fruit with salmon-orange, sweet, custardy flesh tasting of pumpkin, sweet potato and almond. Eaten raw or blended into shakes and desserts. Seeds are inedible; fruit is a regional staple.

Sapodilla
Round brown fruit with grainy, sweet flesh often compared to brown sugar or pear. Eaten fresh or in desserts. Contains latex in unripe fruit; ripe flesh is soft and delicious.

Star apple (Caimito)
Round fruit with glossy purple or green skin and translucent, juicy flesh arranged in star-shaped segments. Sweet, mildly floral flavor; seeds are not eaten. Popular table fruit in tropical home gardens.

Black sapote
Green fruit that turns soft and dark when ripe with a mild, chocolate-pudding flavor. Eaten fresh or in desserts; unripe fruit is astringent. Related to persimmon; seeds and skin are not eaten.

Peach palm (Pejibaye)
Clusters of orange fruits from peach palm trees yielding starchy, slightly nutty flesh. Typically boiled, peeled and eaten like a vegetable or mashed into dishes. Seeds often discarded or processed.

Buriti
Reddish palm fruit with oily, intensely nutritious pulp rich in beta-carotene. Used for juices, jams and pressed oil; important in Amazonian diets. Fruits collected from palm stands in flooded forests.

Bacuri
Hard-shelled fruit with thick, aromatic pulp that is sweet, slightly acidic and creamy. Popular in Amazonian desserts, juices and ice creams. Seeds are hard; pulp is prized regionally.
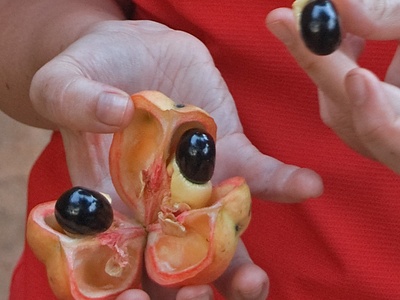
Ackee
West African fruit widely eaten in Caribbean cuisine after proper ripening and cooking. Only properly opened ripe arils are edible; unripe fruit contains hypoglycin toxins causing severe illness if consumed.

Miracle fruit
Tiny red berry whose active glycoprotein temporarily makes sour foods taste sweet. Eaten fresh in West Africa and used experimentally to alter flavor perception. Fruit flesh edible and considered safe; used in “flavor-tripping.”

African plum (Safou)
Also called safou or bush butter; dark purple fruit with oily, buttery pulp often roasted or eaten raw when ripe. Important local food rich in fats; pulp softens with heat and is commonly sold in markets.

African mango (Bush mango)
Small orange fruit with fibrous pulp and a large seed. Pulp eaten fresh or processed; seeds (dika nuts) are valued as a thickener and for oil. Grows in humid African lowland forests.

Ambarella (Golden apple)
Ovoid yellow fruit with crisp, juicy flesh that is tart when firm and sweeter when ripe. Eaten raw, in chutneys, pickles or cooked. Common in Pacific island and Southeast Asian markets.

Java plum (Jambolan)
Dark purple oblong berries with sweet-tart flavor and slight astringency. Eaten fresh, preserved as jams or fermented. Grows in humid tropical regions and is valued locally.

Pulasan
Close relative of rambutan with thicker skin and intensely sweet flesh. Typically eaten fresh; rarer than rambutan and prized in parts of Borneo and the Philippines. Seeds are not eaten.

Santol
Round fruit with thick skin and segmented fibrous pulp that is sweet to mildly sour. Eaten fresh with salt, made into preserves or candies. Seeds are generally discarded.

Langsat (Lanzones)
Clusters of translucent, segmented fruits with a delicate sweet-tart flavor. Popular in Southeast Asia, commonly eaten fresh or preserved. Some varieties have bitter skin; seeds can be slightly bitter.

Marang
Fragrant fruit related to jackfruit with soft, custardy arils that are intensely aromatic and sweet. Eaten fresh or in desserts; perishable and prized locally where it grows in lowland tropical forests.

Mountain apple
Bell-shaped glossy fruit with crisp, watery flesh and subtle sweetness. Consumed fresh or in salads and drinks. Grows in humid tropical forests and island gardens.

Rose apple
Fragrant pale fruit with crisp, mildly sweet flesh and a floral aroma. Eaten fresh or used for local beverages and preserves. Grows well in humid tropical conditions and is often naturalized.





