Washington’s rivers, wetlands, forests and shorelines support a huge variety of native life — and they’re also entry points for non-native plants and animals that alter ecosystems, clog waterways, or outcompete local species. Understanding which organisms are present helps landowners, recreationists, and managers prioritize prevention and control.
There are 47 Invasive Species in Washington, ranging from the American bullfrog to the Yellow flag iris. For each entry you’ll find below the Scientific name,Washington status,Primary habitat (WA) so you can quickly scan identification, current threat level, and where it’s most likely to occur.
How do I report a sighting of an invasive species in Washington?
Report sightings to statewide tools like iMapInvasives or your county extension office; include a clear photo, date, exact location (GPS if possible), and habitat notes. Early reports help authorities verify risks and coordinate rapid response or containment.
What practical steps can I take to stop the spread?
Clean gear, boats, and boots between sites, dispose of bait and plant material properly, never release pets or plants into the wild, and favor native species in landscaping. Small, consistent actions reduce transport and establishment of new populations.
Invasive Species in Washington
| Common name | Scientific name | Washington status | Primary habitat (WA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Himalayan blackberry | Rubus armeniacus | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Riparian, urban, forest edges |
| English ivy | Hedera helix | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Urban, forest, riparian |
| Scotch broom | Cytisus scoparius | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Open fields, roadsides, forest edges |
| Gorse | Ulex europaeus | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Coastal, open fields, forest edges |
| Japanese knotweed complex | Reynoutria japonica | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Riparian, roadsides, urban |
| Giant knotweed | Reynoutria sachalinensis | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Riparian, disturbed sites |
| Bohemian knotweed | Reynoutria × bohemica | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Riparian, roadsides, urban |
| Purple loosestrife | Lythrum salicaria | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Wetlands, marshes, ditch banks |
| Yellow flag iris | Iris pseudacorus | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Wetlands, ditches, shorelines |
| Reed canarygrass | Phalaris arundinacea | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Wetlands, riparian, wetlands |
| Garlic mustard | Alliaria petiolata | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Forest understory, trailsides |
| Spotted knapweed | Centaurea stoebe | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Dry grasslands, rangeland |
| Tansy ragwort | Jacobaea vulgaris | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Pasture, roadsides |
| Cheatgrass | Bromus tectorum | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Rangelands, drylands |
| Common tansy | Tanacetum vulgare | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Pasture, riparian, roadsides |
| Eurasian watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum | WA Invasive Species List | Freshwater lakes, ponds |
| Curly-leaf pondweed | Potamogeton crispus | WA Invasive Species List | Freshwater ponds, lakes |
| New Zealand mudsnail | Potamopyrgus antipodarum | WA Invasive Species List | Streams, rivers, freshwater |
| Didymo (rock snot) | Didymosphenia geminata | WA Invasive Species List | Cold streams and rivers |
| Asian clam | Potamocorbula amurensis | WA Invasive Species List | Estuaries, Puget Sound |
| European green crab | Carcinus maenas | WA Invasive Species List | Marine shoreline, estuaries |
| Spartina (cordgrass) | Spartina anglica (hybrid) | WA Regulated invasive; eradication program | Intertidal marshes, estuaries |
| American bullfrog | Lithobates catesbeianus | WA Invasive Species List | Ponds, wetlands, riparian |
| Common carp | Cyprinus carpio | WA Invasive Species List | Freshwater lakes, slow rivers |
| Rusty crayfish | Faxonius rusticus | WA Invasive Species List | Freshwater lakes, streams |
| Spotted wing drosophila | Drosophila suzukii | WSDA/WA invasive pest | Orchards, berry fields, urban gardens |
| Brown marmorated stink bug | Halyomorpha halys | WSDA regulated; invasive pest | Urban, crops, orchards |
| Japanese beetle | Popillia japonica | WSDA regulated; eradication responses | Lawns, turf, ornamentals |
| European starling | Sturnus vulgaris | Established invasive; widespread | Urban, agricultural, riparian |
| House sparrow | Passer domesticus | Established invasive; widespread | Urban, agricultural |
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | Established invasive; public health pest | Urban, ports, agricultural |
| Feral pig | Sus scrofa | WA invasive where present; WDFW concern | Agricultural, forest, riparian |
| European rabbit | Oryctolagus cuniculus | Established invasive on islands/areas; agricultural pest | Grasslands, agricultural |
| Scotch thistle | Onopordum acanthium | WA Noxious Weed List (invasive) | Disturbed sites, rangeland, roadsides |
| White pine blister rust | Cronartium ribicola | WA regulated pathogen | High-elevation forests, white pine stands |
| Phytophthora lateralis | Phytophthora lateralis | WA regulated forest pathogen | Riparian soils, wet forests |
| Sudden oak death (nursery/wild detections) | Phytophthora ramorum | WA regulated; nursery detections and limited wild finds | Nurseries, landscaped areas, some wild hosts |
| West Nile virus | West Nile virus | WA reportable human/wildlife pathogen | Urban, rural, wetlands |
| Eurasian water chestnut | Trapa natans | WA Noxious Weed List; localized invasions | Freshwater lakes, ponds |
| European eelgrass invader (non-native strain) | Zostera spp. (non-native strains) | WA Invasive species concern | Estuaries, eelgrass beds |
| Smallmouth bass (problem populations) | Micropterus dolomieu | WDFW invasive where non-native | Freshwater lakes, streams |
| Northern pike (introduced populations) | Esox lucius | WDFW invasive where introduced | Freshwater lakes |
| Spartina (eastern cordgrass) hybrid management repeat | Spartina alterniflora | WA regulated; eradication program | Estuaries, mudflats |
| Japanese stiltgrass | Microstegium vimineum | Detected in WA; listed invasive in region | Forest edges, disturbed urban |
| Sea squirts (invasive tunicates) | Didemnum vexillum and Botrylloides spp. | WA invasive marine fouling organisms | Marine docks, pilings, shellfish beds |
| Asian shore crab | Hemigrapsus sanguineus | Non-native marine invasive; detections in WA | Rocky intertidal, estuaries |
| Black locust (invasive in parts) | Robinia pseudoacacia | WA invasive in some habitats; prohibited in places | Grasslands, disturbed forests, riparian |
Images and Descriptions

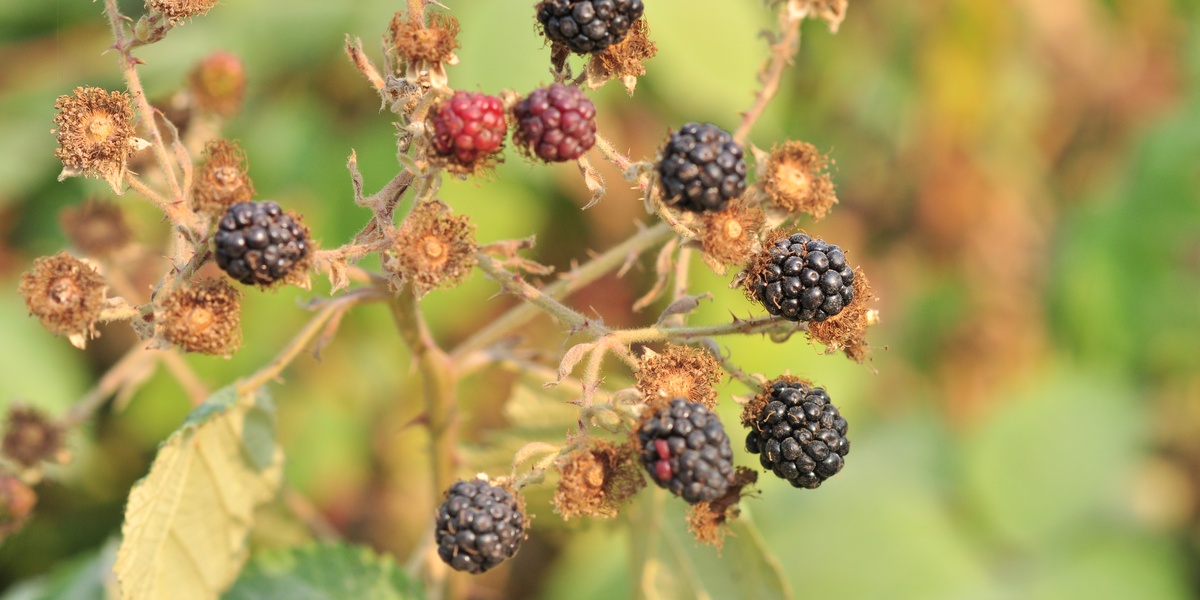
Himalayan blackberry
Thick, thorny bramble forming dense tangles that outcompete native plants. Widespread across western WA, especially roadsides and streambanks. Easy to ID by large compound leaves and arching canes; control by repeated cutting, herbicide or targeted removal.

English ivy
Evergreen vine that climbs trees and buildings, shading native plants and weakening trees. Common in Puget Sound gardens and forests. Distinguishable by lobed glossy leaves and aerial roots. Remove by cutting and pulling, dispose of fragments; long-term control needed.

Scotch broom
Woody shrub with bright yellow pea-flowers that invade grasslands and forests, fixing nitrogen and altering fire regimes. Common across lowland and coastal WA. Pull small plants; herbicide or prescribed burning used for larger infestations.

Gorse
Spiny evergreen shrub with yellow flowers forming impenetrable thickets, high fire risk. Found notably on coastal bluffs and roadsides in western WA. Hard to eradicate; mechanical removal plus herbicide and follow-up seedbank control required.

Japanese knotweed complex
Big bamboo-like clumps of hollow canes from aggressive rhizomes that erode banks and damage infrastructure. Widespread in urban streams and roadsides. Report sightings; control needs persistent excavation or herbicide over years.

Giant knotweed
Large-leaved knotweed variant with similar aggressive rhizomes, causing bank erosion and habitat loss. Occurs with other knotweeds across western WA. Identification and treatment similar to Japanese knotweed; report to local weed boards.

Bohemian knotweed
Hybrid knotweed often more vigorous than parents; forms dense stands along waterways and disturbed ground. Common in Puget Sound lowlands. Persistent control required—mechanical removal and repeated herbicide applications.

Purple loosestrife
Perennial wetland plant with purple spike flowers that replaces native marsh vegetation and harms habitat for waterfowl. Found in lowland wetlands and roadside ditches. Pulling, targeted herbicide and biological control agents are used.

Yellow flag iris
Showy yellow iris that spreads in wetlands to form dense stands, reducing habitat complexity. Common in western Washington water margins and irrigation ditches. Pull small patches; larger infestations need excavation and herbicide.

Reed canarygrass
Aggressive perennial grass forming dense monocultures in wetlands and along streams, displacing native plants and altering hydrology. Found statewide in disturbed wetlands. Control requires mowing, flooding management, and herbicide; long-term effort due to rhizomes and seedbank.

Garlic mustard
Shade-tolerant biennial with scalloped leaves and garlic odor, outcompetes native forest herbs and disrupts mycorrhizae. Patchy but spreading in western WA. Hand-pull before seed set or spot herbicide; report new populations.

Spotted knapweed
Introduced forb forming dense stands that reduce forage and increase erosion. Widespread in eastern WA rangelands and roadsides. Identify by spotted bracts and pink flowers; integrated control with herbicide, grazing management, and revegetation.

Tansy ragwort
Poisonous daisy-family plant toxic to livestock, spreads along roads and pasture edges. Common in Puget Sound and eastern WA. Remove before flowering; biological control agents and herbicide programs exist.

Cheatgrass
Annual invasive grass that changes fire regimes and outcompetes native perennials in sage-steppe and drylands of eastern WA. Creates earlier, more frequent fires. Early detection, grazing management, and reseeding with natives are control options.

Common tansy
Perennial forb with button-like yellow flowers that invades pastures and riparian areas, reducing forage value. Present statewide along disturbed ground. Hand-pull small patches; herbicide recommended for larger infestations.

Eurasian watermilfoil
Submerged aquatic plant with feathery leaves forming dense mats that clog recreation, alter habitat, and displace natives. Found in many Washington lakes. Control via mechanical harvest, benthic barriers, selective herbicide, and boat-cleaning to prevent spread.

Curly-leaf pondweed
Aquatic weed with crinkled leaves that forms early-season mats, impacting recreation and native plants. Detected in several WA lakes. Manage with early-season herbicide, sediment control and preventing boat transfer.

New Zealand mudsnail
Tiny snail that reaches massive densities, competing with native invertebrates and altering food webs. Found in eastern and western WA waters. Very small—clean, drain, dry gear to prevent spread between waterways.

Didymo (rock snot)
Diatom that forms thick mats on streambeds, impacting aquatic insects and trout habitat. Found in cold oligotrophic streams in WA. Prevent spread by decontaminating boots and equipment; report new blooms.

Asian clam
Small, high-density clam that filters estuarine waters altering food webs and sediment. Present in Puget Sound and coastal bays. Hard to control; report finds and follow shellfish sanitation advisories.

European green crab
Aggressive predatory crab damaging shellfish beds, eelgrass and native crabs. Multiple detections in Salish Sea and coastal estuaries with localized eradication and trapping efforts. Report sightings and avoid moving live crabs or bait.

Spartina (cordgrass)
Invasive cordgrass forming dense mats that convert mudflats to marsh, harming shellfish habitat. Extensive eradication efforts in Puget Sound and Willapa Bay; report sightings, do not transplant marsh plants.

American bullfrog
Large frog that preys on native amphibians and spreads disease (chytrid). Established in parts of western Washington. Identify by large size and call; control includes targeted trapping, removal and waterbody management.

Common carp
Large rough fish that uproots vegetation and increases turbidity, degrading wetlands and fisheries. Widespread in many Washington lakes. Management includes netting, barriers, drawdowns and public education to avoid releasing fish.

Rusty crayfish
Aggressive crayfish that eat vegetation and outcompete natives, impacting fish habitat. Detected in some Washington waters. Report sightings; control via trapping and preventing bait-bucket introductions.

Spotted wing drosophila
Small fruit fly that lays eggs in ripening soft fruit, causing economic losses to berries and cherries statewide. Identify by tiny serrated ovipositor scars on fruit. Use monitoring traps, sanitation, harvest timing, and control measures.

Brown marmorated stink bug
Shield-shaped insect that feeds on many crops, causing cosmetic fruit damage and invading homes in fall. Detected and spreading in WA. Report finds; exclude from homes and follow WSDA guidance for management.

Japanese beetle
Leaf- and flower-feeding beetle causing skeletonized foliage on ornamentals and turf. Interceptions and localized infestations in WA with quarantine and eradication efforts. Report sightings, avoid transporting soil/plants, and follow WSDA actions.

European starling
Introduced bird that forms large flocks, competes with native cavity nesters and damages crops. Abundant in Washington towns and farms. Identify by iridescent plumage and chatter; control via exclusion, hazing and habitat modification.

House sparrow
Small introduced bird common in towns and farms that competes with native birds and spreads disease. Widespread across Washington. Control via exclusion and reducing food sources in urban areas.

Norway rat
Large commensal rodent that spreads disease, damages crops and infrastructure. Widespread in Washington cities, ports, and farms. Control via sanitation, trapping, exclusion and professional pest management.

Feral pig
Escaped/feral domestic pigs and wild boar root soils, damage crops and native habitats, and spread disease. Scattered populations in parts of Washington. Report sightings; control via hunting, trapping and coordinated eradication where feasible.

European rabbit
Small introduced rabbit that can cause severe crop and habitat damage locally, especially on islands and agricultural lands. Present in parts of WA. Control via fencing, hunting and habitat management.

Scotch thistle
Spiny biennial thistle forming dense stands that reduce forage and injure livestock. Occurs in eastern and some western Washington sites. Hand-pull rosettes, use herbicide and biological control for larger infestations.

White pine blister rust
Non-native fungal pathogen introduced from Europe that infects and kills five-needle pines, altering forest composition. Present in Washington; monitor seedlings and report infected trees. Management includes resistant stock planting and sanitation.

Phytophthora lateralis
Soilborne pathogen causing Port-Orford-cedar root rot, killing cedar and changing riparian forests. Present in northwest Washington. Prevent spread by cleaning boots/equipment and follow local quarantines.

Sudden oak death (nursery/wild detections)
Invasive water mold causing lethal leaf and stem lesions on oaks and many ornamentals. Detected in WA nurseries and isolated wild sites; strict nursery regulations, reporting and sanitation measures in place.
West Nile virus
Mosquito-borne virus introduced to North America, infecting birds, humans and horses. Present in Washington with seasonal outbreaks. Reduce mosquito habitat, use repellents, report dead birds and follow public health guidance.

Eurasian water chestnut
Floating aquatic plant forming dense mats that hinder recreation and alter ecosystems. Detected in limited Washington waters. Hand-pulling of rosettes and boater awareness important to limit spread.

European eelgrass invader (non-native strain)
Non-native eelgrass strains/hybrids can alter native eelgrass meadows and shellfish habitat. Detected in Puget Sound; management focuses on monitoring, seed control and preventing transplants.

Smallmouth bass (problem populations)
Sport fish introduced into some waters where they predate native salmonids and amphibians. In specific lakes/streams in Washington they are managed as invasive; control measures include removal and angling incentives.

Northern pike (introduced populations)
Top predatory fish introduced into some Washington lakes, severely impacting native fish and salmon. Detected in isolated waters; removal campaigns and angler reporting used for control.

Spartina (eastern cordgrass) hybrid management repeat
Invasive cordgrass species and hybrids create dense marsh habitat replacing mudflats, harming shellfish. Historic large-scale eradication and monitoring in Puget Sound and Willapa Bay; report and avoid moving plants.

Japanese stiltgrass
Shade-tolerant annual grass that forms dense mats in forest understories and roadsides, outcompeting natives. Recently detected in the region; early reporting and removal are crucial to prevent establishment.

Sea squirts (invasive tunicates)
Colonial tunicates that overgrow native invertebrates and shellfish gear, fouling infrastructure in Puget Sound and coastal marinas. Report fouling, clean boats and gear, and follow decontamination guidance.

Asian shore crab
Small aggressive crab impacting native shore crabs and prey; detected in the Salish Sea. Monitor and report sightings; avoid moving intertidal material between sites.

Black locust (invasive in parts)
Fast-growing nitrogen-fixing tree/shrub that invades prairies and disturbed areas, altering soils and outcompeting natives. Present in parts of Washington. Control via cutting, herbicide and preventing seed spread.





