Indianapolis’s parks, river corridors and neighborhood yards are home to a surprising mix of plants and animals — and not all of them belong. Road networks, connected waterways and changing land use make the city especially vulnerable to species that spread quickly, outcompete natives, clog drains or alter habitats.
There are 27 Invasive Species in Indianapolis, ranging from Amur honeysuckle to Zebra mussel; for each you’ll find below the Scientific name,Where found (areas),Impact & prevalence.
How can I report an invasive species I find in Indianapolis?
Take clear photos, note the location (GPS or a nearby address/landmark), and avoid moving the specimen. Submit sightings to iMapInvasives or contact the Indiana DNR or your county extension office; many local conservation groups also accept reports. Quick, accurate reports help prioritize control and tracking.
What should I do if I find Amur honeysuckle or Zebra mussel on my property?
For Amur honeysuckle, remove seedlings by hand and cut larger shrubs before they set seed, disposing of material per local guidance; targeted herbicide follow-up may be needed for re-sprouts. For Zebra mussel, do not move boats or equipment, clean/drain/dry everything, and report detections to state aquatic invasive species contacts to limit spread.
Invasive Species in Indianapolis
| Name | Scientific name | Where found (areas) | Impact & prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Garlic mustard | Alliaria petiolata | Urban woodlands, Riverside trails, Eagle Creek Park | Outcompetes natives; common in forest understory |
| Amur honeysuckle | Lonicera maackii | Edge habitats, parks, vacant lots, White River corridors | Dense understory, displaces natives; very common |
| Multiflora rose | Rosa multiflora | Roadsides, parks, rail corridors, vacant lots | Aggressive thickets, habitat loss; common in disturbed areas |
| Japanese knotweed | Reynoutria japonica | Streambanks, riparian corridors, construction sites | Erodes banks, resprouts from fragments; locally common |
| Japanese stiltgrass | Microstegium vimineum | Forest edges, trailsides, wetlands near White River | Quick-spreading annual grass; common and increasing |
| Common reed (invasive Phragmites) | Phragmites australis (non-native genotype) | Marshes, drainage ditches, wetlands (Eagle Creek area) | Dense monocultures, loss of wetland diversity; locally present |
| Purple loosestrife | Lythrum salicaria | Wetlands, pond edges, White River backwaters | Reduces wetland habitat diversity; present in local wetlands |
| Norway maple | Acer platanoides | Streets, yards, urban forests, Meridian-Kessler areas | Invades parklands, shades natives; common street tree escapee |
| Callery pear (Bradford pear) | Pyrus calleryana | Street trees, suburban yards, Garfield Park vicinity | Breaks, spreads via seedlings; common nuisance |
| Tree-of-heaven | Ailanthus altissima | Vacant lots, railways, riverfronts, northside industrial areas | Rapid colonizer, damages infrastructure; common in disturbed sites |
| Oriental bittersweet | Celastrus orbiculatus | Forest edges, parks, canopy of older trees | Strangles trees, climbs to canopy; common and damaging |
| English ivy | Hedera helix | Older neighborhoods, park trees, scree slopes | Smothers groundlayer and climbs trees; common ornamental escape |
| Eurasian watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum | Eagle Creek Reservoir, small ponds, canal systems | Chokes waterways, impedes recreation; locally reported in reservoirs |
| Curly-leaf pondweed | Potamogeton crispus | City ponds, small lakes, reservoirs | Early-season blooms, alters ponds; present in urban lakes |
| Common carp | Cyprinus carpio | White River, Eagle Creek Reservoir, city lakes | Disturbs sediments, reduces water quality; abundant in waterways |
| Rusty crayfish | Faxonius rusticus | Streams, ponds connected to White River | Displaces native crayfish, eats vegetation; scattered but present |
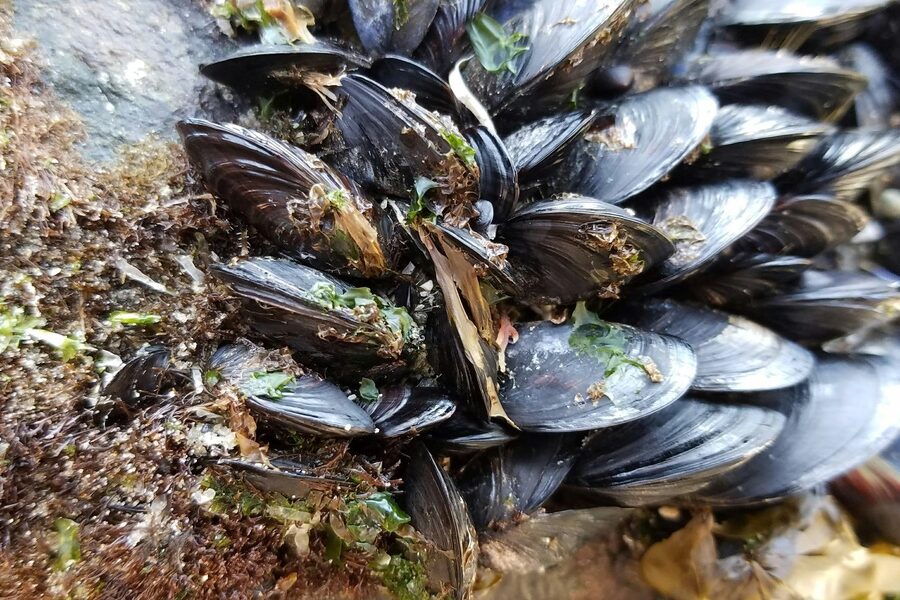
| Zebra mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | Reservoirs and connected waters near Indy | Clogs infrastructure, alters food webs; reported regionally |
| Emerald ash borer | Agrilus planipennis | Citywide in ash trees, parks, street trees | Kills ash trees rapidly; widespread and devastating |
| Gypsy moth | Lymantria dispar dispar | Wooded neighborhoods, park trees, suburban canopy | Defoliates oaks and maples; periodic outbreaks recorded |
| Brown marmorated stink bug | Halyomorpha halys | Homes, gardens, orchards, warehouses | Annoying house pest, agricultural damage; established in Marion County |
| Asian tiger mosquito | Aedes albopictus | Urban yards, tire dumps, rain barrels, standing water | Bites day and night; common container breeder |
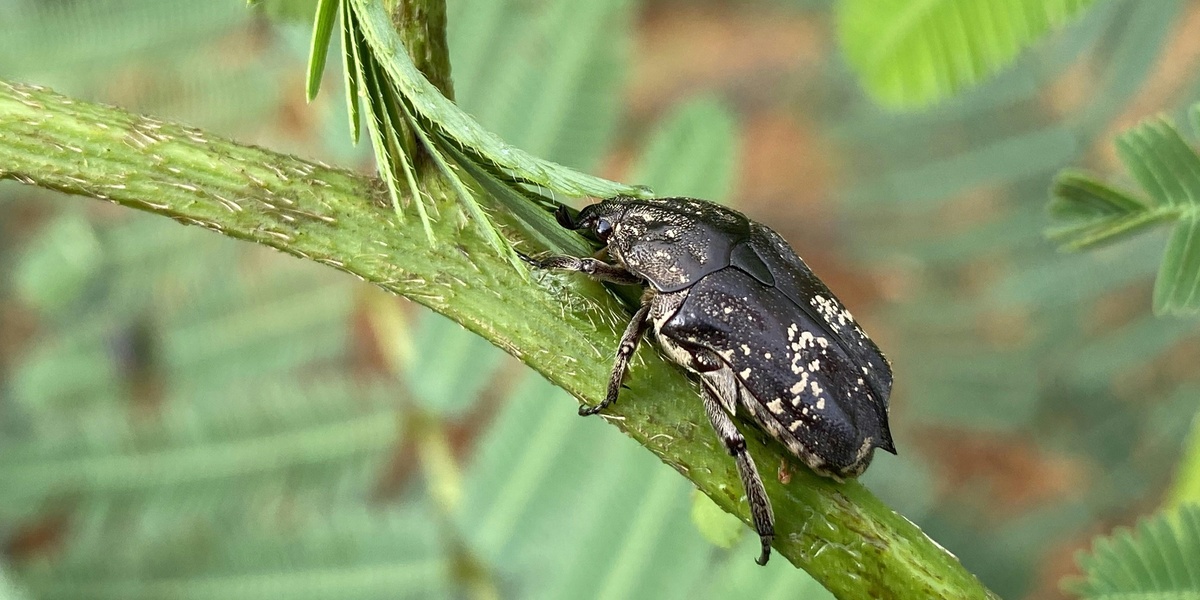
| Japanese beetle | Popillia japonica | Lawns, gardens, parks, golf courses | Defoliates ornamentals and turf; locally common summer pest |
| European starling | Sturnus vulgaris | Downtown, industrial, park rooftops | Outcompetes native birds, nuisance roosts; very common |
| House sparrow | Passer domesticus | City neighborhoods, urban centers, barns | Competes for nesting, common around people |
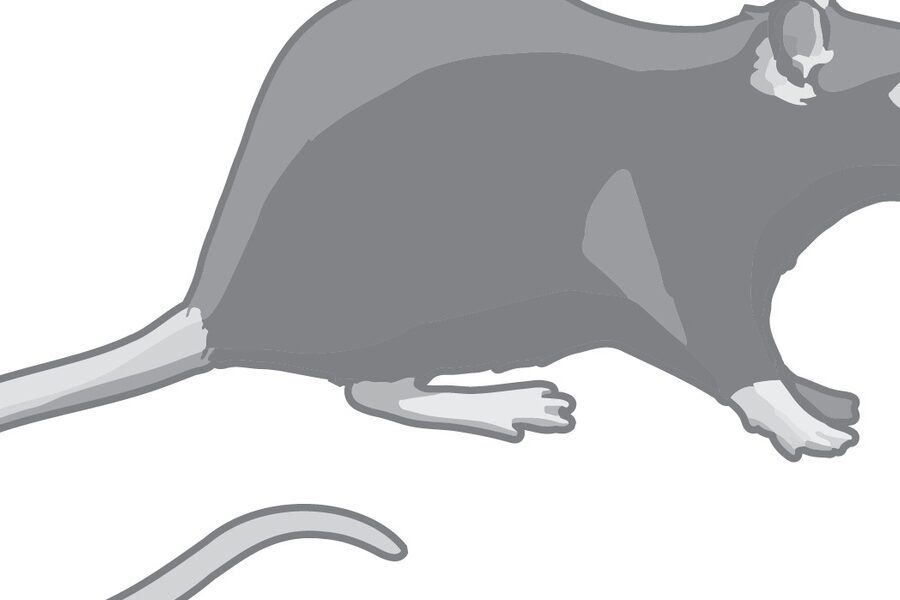
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | Alleys, sewers, commercial districts | Public-health pest, common in urban areas |
| Rock pigeon | Columba livia | Downtown, bridges, train stations, stadiums | Fouling, structural damage, very common |
| Non-native earthworms | Lumbricus spp. and others | Forest floors, park soils citywide | Alters leaf litter, harms native seedlings; widespread |
Images and Descriptions

Garlic mustard
Shade-tolerant biennial from Europe; identifiable by scalloped leaves and white flowers. Invades forest floors, reducing native wildflowers. Hand-pull before seed set or spot-treat with herbicide; dispose of seed plants. Report big infestations to Indy Parks volunteer crews.

Amur honeysuckle
Shrubby Asian honeysuckle with early white/yellow flowers; forms dense thickets that shade out native plants. Remove seedlings, cut stump and apply herbicide, or pull small plants. Restoration planting recommended after removal.

Multiflora rose
Arching shrub with clusters of small white flowers and dense thorny canes; introduced for erosion control. Crowds out native shrubs. Mechanical cutting plus repeated herbicide or repeated mowing needed; remove roots to prevent resprouts.

Japanese knotweed
Tall bamboo-like stems and large heart-shaped leaves; from East Asia. Forms dense stands that destabilize banks and outcompete natives. Control with repeated cutting plus systemic herbicide; avoid moving soil or rhizomes.

Japanese stiltgrass
Shade-tolerant invasive grass with silvery midrib; forms dense mats that suppress native seedlings. Hand-pull small patches in fall; use prescribed burns or herbicide for larger infestations and clean boots to prevent spread.

Common reed (invasive Phragmites)
Tall perennial reed forming dense stands in wetlands; European genotype displaces native marsh plants. Identify by dense tan plumes. Control with targeted herbicide, mowing, or water-level management and follow local permitting.

Purple loosestrife
Showy purple flower spikes from Eurasia; spreads by seed in water. Crowds out native wetland plants and wildlife habitat. Pull small patches before seeding; biological controls and herbicide used in larger infestations—coordinate with resource managers.

Norway maple
Large maple with broad canopy and milky sap; ornamental from Europe. Produces dense shade and dense seedlings that displace natives. Prefer removal of young trees, girdling or stump treatments for large trees, and replace with native species.

Callery pear (Bradford pear)
Ornamental pear with white spring flowers and round fruit; escapes cultivation and forms dense thickets. Roots spread and seed birds disperse. Remove young volunteers, avoid planting cultivars, and replace mature trees when possible.

Tree-of-heaven
A tall tree from China with pinnate leaves and foul smell; prolific seed and root suckering allows fast spread. Cut and apply systemic herbicide to stumps; persistent re-sprouts require repeated treatments.

Oriental bittersweet
Woody vine with orange fruit that climbs and girdles trees; introduced from East Asia. Pull vines from canopy when possible, cut stems and treat resprouts, and remove root crowns to prevent regrowth.

English ivy
Evergreen vine that creates dense mats and climbs trunks, harming tree bark. Hand-pull small patches, cut vines high on tree and remove roots; avoid heavy chemical use in sensitive areas.

Eurasian watermilfoil
Feathery underwater plant forming dense mats, from Eurasia. Hampers boating and displaces native aquatic plants. Control with mechanical harvest, benthic barriers, or approved aquatic herbicides; clean boats to prevent spread.

Curly-leaf pondweed
Submerged plant with ruffled leaves appearing early spring; tolerates cold and disrupts native plant cycles. Control with drawdowns, mechanical removal, and targeted herbicide; clean equipment between waters.

Common carp
Large Old World fish that uproots vegetation and increases turbidity, harming fish and plant communities. Control by harvest or exclusion in small systems; manage nutrient inputs and support native predators where feasible.

Rusty crayfish
Aggressive North American-translocated crayfish with rust-colored spots; reduces aquatic plants and native crayfish. Prevent spread by not moving bait or water; report sightings to DNR and avoid releasing live bait.

Zebra mussel
Small striped bivalve that encrusts boats and infrastructure; filters plankton and alters ecosystems. Clean, drain, dry boats and gear; report suspect populations to state agencies.

Emerald ash borer
Metallic green beetle larvae bore into ash, introduced from Asia. Causes rapid canopy loss and urban tree mortality. Report infestations, cut and treat high-value trees, and follow municipal removal programs.

Gypsy moth
Caterpillar with hairy bodies causing heavy defoliation; from Eurasia. Monitor for egg masses, scrape and destroy, use pheromone traps or contact authorities during outbreaks; encourage native predators.

Brown marmorated stink bug
Shield-shaped bug from Asia that invades buildings and feeds on fruit. Seal entry points, remove by vacuuming, and report agriculturally damaging outbreaks to Purdue Extension.
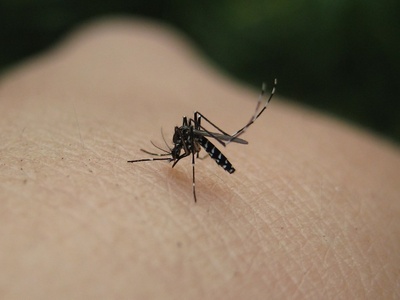
Asian tiger mosquito
Black-and-white striped mosquito spreading from Asia; breeds in small containers and is a nuisance vector. Eliminate standing water, screen windows, use repellents, and report concerns to local health department.

Japanese beetle
Metallic green beetle that skeletonizes leaves and damages turf. Hand-pick into soapy water, use traps sparingly, and treat with targeted insecticides or biological controls for heavy infestations.

European starling
Introduced bird forming large roosts that displace native cavity nesters. Deter with netting, exclusion devices, and habitat modifications; report large roosts to municipal services for safe management.

House sparrow
Small non-native bird closely associated with humans that displaces some native species. Block nest access, remove unused nest material, and maintain predator-friendly habitat to limit populations.

Norway rat
Large rodent introduced from Eurasia; carries disease and damages property. Sanitation, secure garbage, seal building entry points, and use licensed pest professionals for control.

Rock pigeon
Urban dove ancestor of domestic pigeons left feral; causes droppings and building damage. Use exclusion netting, spikes, and deterrents; avoid feeding to prevent population growth.

Non-native earthworms
European and Asian earthworms change soil structure and deplete leaf litter, harming forest regeneration. Prevent spread by avoiding dumping garden soil or bait; support intact leaf litter and native-plant restoration.





