Mississippi’s rivers, wetlands and coastal areas support rich plant and animal life, but they’re also vulnerable to species introduced from other regions. From clogged waterways to displaced native plants, these nonnative arrivals can change habitats and create new management challenges for landowners and agencies across the state.
There are 40 Invasive Species in Mississippi, ranging from Alligator weed to Zebra mussel. For each entry you’ll find below the information organized as Scientific name,Status,Primary habitat (where found) so you can quickly see identification, current status and where it’s typically encountered — you’ll find below.
How do these invasive species affect Mississippi’s ecosystems?
Invasive species can outcompete natives for space and resources, alter food webs, degrade water quality, and change fire or flood behavior; aquatic invaders like Zebra mussel also damage infrastructure and clog intake pipes, while plants such as Alligator weed can choke waterways and reduce habitat for fish and waterfowl.
What can residents do to help prevent their spread?
Clean boats, trailers and gear, avoid releasing aquarium or garden plants into the wild, dispose of bait and plant material responsibly, learn to identify high-risk species, and report sightings to local extension services or state natural resource agencies to speed response and containment.
Invasive Species in Mississippi
| Name | Scientific name | Status | Primary habitat (where found) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kudzu | Pueraria montana var. lobata | Established, widespread invasive | Forest edges, roadsides, disturbed slopes |
| Chinese privet | Ligustrum sinense | Established, widespread invasive | Forest understory, floodplains, hedgerows |
| Glossy privet | Ligustrum lucidum | Established in parts of Mississippi | Woodland edges, yards, streambanks |
| Japanese honeysuckle | Lonicera japonica | Established, common invasive vine | Forest edges, fences, roadsides |
| Multiflora rose | Rosa multiflora | Established, invasive shrub | Pastures, fencerows, forest edges |
| Autumn olive | Elaeagnus umbellata | Established invasive shrub | Open fields, roadsides, forest margins |
| Tree-of-heaven | Ailanthus altissima | Established invasive tree | Urban lots, roadsides, disturbed areas |
| Chinese wisteria | Wisteria sinensis | Established invasive vine | Fences, woodland edges, disturbed yards |
| Chinese tallow (popcorn tree) | Triadica sebifera | Established, high priority invasive | Wetlands, ditches, pastures, fields |
| Japanese climbing fern | Lygodium japonicum | Established invasive fern | Pine forests, riparian zones, disturbed wetlands |
| Cogongrass | Imperata cylindrica | Noxious/exotic, established | Pine savannas, roadsides, pastures |
| Phragmites (non-native haplotype) | Phragmites australis (non-native) | Established invasive reed | Salt and freshwater marshes, ditches, shorelines |
| Hydrilla | Hydrilla verticillata | Established aquatic invasive plant | Lakes, ponds, slow-moving rivers, reservoirs |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Established aquatic invasive | Backwaters, ponds, slow-moving waters, canals |
| Giant salvinia | Salvinia molesta | Established in some water bodies | Ponds, lakes, slow backwaters |
| Eurasian watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum | Established aquatic invasive | Lakes, reservoirs, slow rivers |
| Alligator weed | Alternanthera philoxeroides | Established aquatic/emergent | Marshes, ditches, shorelines, canals |
| Water lettuce | Pistia stratiotes | Established in warm waters | Ponds, oxbows, canals, backwaters |
| Parrot feather | Myriophyllum aquaticum | Established invasive in southeast | Ponds, canals, shorelines, slow waters |
| Silver carp | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Established, invasive fish | Large rivers, backwaters, reservoirs |
| Bighead carp | Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | Established, invasive fish | Rivers, reservoirs, backwaters |
| Grass carp | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Established feral populations in many waters | Lakes, ponds, rivers, vegetated wetlands |
| Common carp | Cyprinus carpio | Established, widespread invasive fish | Lakes, rivers, wetlands, turbid shallow waters |
| Zebra mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | Established in some Mississippi waters | Rivers, reservoirs, marinas, docks |
| Quagga mussel | Dreissena rostriformis bugensis | Detected/established in regional reservoirs | Lakes, reservoirs, intake structures |
| Asian clam | Corbicula fluminea | Established, widespread invasive | Rivers, lakes, sediments, shallow water |
| Apple snail (island apple snail) | Pomacea maculata | Established invasive aquatic snail | Freshwater marshes, ponds, canals, wetlands |
| Feral hog | Sus scrofa | Established, widespread destructive mammal | Forest, agricultural lands, wetlands |
| Nutria | Myocastor coypus | Historically established, locally managed | Coastal marshes, ditches, wetlands |
| European starling | Sturnus vulgaris | Established, non-native bird | Urban, agricultural lands, woodlands |
| House sparrow | Passer domesticus | Established, non-native bird | Urban areas, farms, buildings |
| Red imported fire ant | Solenopsis invicta | Established, widespread invasive insect | Lawns, pastures, disturbed soils, roadside |
| Formosan subterranean termite | Coptotermes formosanus | Established in coastal and urban areas | Structures, urban trees, wooden debris |
| Asian tiger mosquito | Aedes albopictus | Established, widespread invasive | Urban containers, forest edges, tire piles |
| Japanese beetle | Popillia japonica | Established, present in Mississippi | Lawns, gardens, ornamental plants, turf |
| Emerald ash borer | Agrilus planipennis | Confirmed presence, spreading | Ash trees in urban and forested areas |
| Japanese stiltgrass | Microstegium vimineum | Established invasive grass | Forest floor, shaded disturbed areas, roadsides |
| Brown marmorated stink bug | Halyomorpha halys | Established, agricultural pest | Orchards, crops, homes (overwintering) |
| Chinese mystery snail | Cipangopaludina chinensis | Established in some waterways | Ponds, lakes, slow rivers, wetlands |
| Brown tree snake (not established) | Boiga irregularis | Not established in Mississippi | N/A |
Images and Descriptions

Kudzu
Fast-growing climbing vine that smothers trees and structures, reducing biodiversity and timber value. Control by repeated cutting, herbicide application, or grazing; report large new infestations to county extension or MDAC for assistance.

Chinese privet
Deciduous shrub forming dense thickets that shade native plants and alter wildlife habitat. Pull small plants, cut and apply herbicide to stumps for larger stands; report escapes on natural lands to MSU Extension or local conservation agencies.

Glossy privet
Evergreen shrub/tree that invades riparian and disturbed areas, produces abundant fruit spread by birds. Remove seedlings, cut and treat stumps; replace with native shrubs and report notable invasions to extension services.

Japanese honeysuckle
Vining shrub that outcompetes native groundcover and smothers small trees. Hand-pull seedlings, cut vines and apply herbicide to persistent stems; report large infestations to county extension for management guidance.

Multiflora rose
Thorny shrub forming dense thickets that reduce grazing land and crowd natives. Mechanical removal and targeted herbicide treatments are effective; report new invasions to extension or conservation agencies.

Autumn olive
Nitrogen-fixing shrub that forms dense stands, displacing natives and altering soil. Remove seedlings, cut and treat stumps; monitor for re-sprouts and notify extension or land managers of new patches.

Tree-of-heaven
Rapidly spreading tree producing many wind-dispersed seeds and toxic root chemicals that inhibit other plants. Cut and immediately treat stumps with herbicide; report large infestations to forestry or extension offices.

Chinese wisteria
Ornamental vine that can girdle trees and outcompete natives; it spreads from planting escapes. Remove by cutting and root removal, apply herbicide to roots; discourage planting and report wild populations to extension.

Chinese tallow (popcorn tree)
Fast-spreading tree producing prolific seeds that convert diverse habitats to monocultures. Hand-pull seedlings, cut and stump-treat larger trees; report sightings to Mississippi Department of Agriculture or extension.

Japanese climbing fern
Vining fern that carpets and climbs over native vegetation, changing fire behavior. Remove small patches by hand, apply herbicide to larger infestations; report occurrences to extension or forestry agencies.

Cogongrass
Dense, flammable grass forming monocultures that degrade wildlife habitat and increase wildfire risk. Control requires repeated herbicide and prescribed fire where safe; report new stands to state invasive plant contacts.

Phragmites (non-native haplotype)
Tall reed invading wetlands, displacing native marsh plants and altering hydrology. Control via herbicide and targeted cutting; report expanding patches to coastal resource agencies or extension for coordinated response.

Hydrilla
Submerged aquatic plant forming thick mats that impede boating, fishing, and native plants. Mechanical removal, herbicides, and biological controls used; if you see hydrilla report to MDWFP or local aquatic plant managers.

Water hyacinth
Floating plant forming dense rafts that block waterways, harm wildlife and recreation. Hand removal, mechanical harvesters and herbicides are used; report sightings to MDWFP or local water managers promptly.

Giant salvinia
Free-floating fern forming thick mats that block light and oxygen, devastating fisheries. Rapid reporting is crucial; contact MDWFP or state aquatic nuisance species coordinators for containment and control help.

Eurasian watermilfoil
Submerged aquatic plant that forms dense mats reducing recreation and native biodiversity. Hand-pulling, herbicides and biological controls help; report suspected populations to state aquatic plant managers.

Alligator weed
Aggressive emergent plant that chokes waterways and marshes, displacing natives. Mechanical removal and herbicide application are common controls; report infestations to MDWFP or county extension.

Water lettuce
Floating rosette-forming plant that clogs waterways and reduces oxygen for fish. Remove by hand or mechanical means, use herbicides where allowed; report sightings to state aquatic nuisance contacts.

Parrot feather
Perennial aquatic plant with feathery emergent foliage that forms dense stands, impeding recreation and outcompeting natives. Pull small patches, use herbicide for larger infestations; notify MDWFP or extension.

Silver carp
Filter-feeding carp that leap when startled, harming anglers and competing with native fish. Contact MDWFP for sightings; avoid transporting live fish, and follow local harvest and reporting rules.

Bighead carp
Large filter feeder competing with native fish for plankton, altering ecosystems. Report captures to MDWFP, avoid moving fish between waters, and follow local control guidance.

Grass carp
Introduced for vegetation control, feral grass carp can decimate aquatic plants and disrupt food webs. Report suspect feral populations to fisheries authorities; management includes barriers and targeted removal.

Common carp
Bottom-feeding carp that uproot vegetation and increase water turbidity, harming native species. Reduce spread by not moving live fish, and report heavy infestations to fisheries managers for removal options.

Zebra mussel
Small bivalve that fouls infrastructure, outcompetes natives, and alters food webs. Clean, drain, dry boats and gear; report new detections to USGS/MDWFP and follow decontamination guidance.

Quagga mussel
Similar to zebra mussel, fouls infrastructure and ecosystems. Prevent spread by decontaminating boats, and report any suspected finds to state aquatic invasive species contacts.

Asian clam
Small freshwater clam that competes with natives and clogs screens. Avoid moving bait or substrate between waters; report new infestations to fisheries or invasive species coordinators.

Apple snail (island apple snail)
Large snail that eats aquatic plants and nests prolifically, altering wetland vegetation. Hand removal and habitat management can help; report sightings to MDWFP or extension.

Feral hog
Omnivorous, rooting mammals that damage crops, spread disease, and harm native wildlife. Control via trapping and hunting programs coordinated by MDWFP; report large populations to county wildlife officers.

Nutria
Large semi-aquatic rodent that burrows and destroys marsh vegetation, increasing erosion. Control and monitoring programs exist; report sightings to state wildlife or agricultural agencies for response support.

European starling
Aggressive cavity-nesting bird that displaces native species and damages crops. Limit nesting opportunities on structures, and report unusual outbreaks to wildlife agencies for guidance.

House sparrow
Small bird associated with human structures that competes with native cavity nesters. Reduce nest sites on buildings and report significant impacts to local wildlife extension offices.

Red imported fire ant
Aggressive ant causing painful stings, livestock impacts, and infrastructure damage. Control via baits and mound treatments; report range expansions or unusual impacts to county extension or USDA contacts.

Formosan subterranean termite
Invasive termite causing severe structural damage and high repair costs. Reduce moisture and wood contact with soil, treat infestations with licensed pest control professionals; report detections to extension.
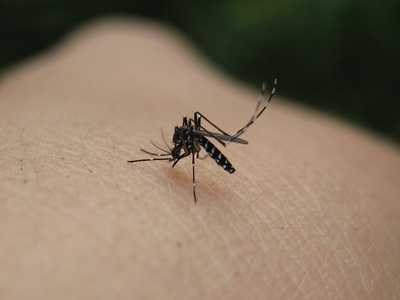
Asian tiger mosquito
Aggressive day-biting mosquito that spreads nuisance and possible disease. Eliminate standing water around homes, use repellents, and report unusual mosquito-borne disease concerns to local health departments.

Japanese beetle
Beetle that skeletonizes foliage and damages flowers and turf. Hand-pick early, use traps cautiously, and consider targeted insecticide or biological controls; report major outbreaks to extension agents.

Emerald ash borer
Wood-boring beetle killing ash trees rapidly, changing forests and urban tree canopy. Do not move firewood, report suspect ash mortality or signs to state forestry/USDA for management and quarantine info.

Japanese stiltgrass
Shade-tolerant invasive grass forming dense mats that suppress native seedlings and alter fire and nutrient cycles. Hand-pull small patches, use herbicide for larger infestations; report to extension for control tips.

Brown marmorated stink bug
Non-native stink bug that damages fruit and crops and invades buildings in fall. Exclude from buildings with sealing, use integrated pest management in crops, report severe outbreaks to county extension.

Chinese mystery snail
Large non-native snail that may compete with natives and spread hitchhiking parasites. Avoid releasing aquarium species into wild, and report new populations to MDWFP or extension.

Brown tree snake (not established)
Excluded: Not established in Mississippi; included here to clarify it is not present. Report any suspect sightings of non-native snakes immediately to state wildlife authorities.





