Quebec’s landscapes—from the St. Lawrence shoreline and urban green spaces to boreal forests and freshwater lakes—support rich native life but are increasingly affected by non-native arrivals that change habitats and local livelihoods.
There are 38 Invasive Species in Quebec, ranging from the Asian lady beetle to the Zebra mussel. Each entry includes the Scientific name, Quebec distribution and Status so you can compare where a species occurs and how it’s classified—see the list you’ll find below.
How do I report a sighting of a suspected invasive species in Quebec?
If you spot a possible invasive, take clear photos, note the date and exact location, and submit that information through Quebec’s provincial reporting portal or local conservation authority; many organizations also accept reports by email or phone. Accurate details and images help experts confirm the species and guide any rapid response.
What practical steps can residents take to prevent the spread?
Simple actions work: clean boats and outdoor gear, drain and dry watercraft, avoid releasing pets or plants into the wild, use local firewood, and choose native plants for gardens—plus report unusual sightings. These habits reduce accidental transport of species like zebra mussels and invasive plants.
Invasive Species in Quebec
| Name | Scientific name | Quebec distribution | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese knotweed | Fallopia japonica | Montreal, southern Quebec | spreading |
| Bohemian knotweed | Fallopia x bohemica | southern Quebec urban/riversides | spreading |
| Giant knotweed | Fallopia sachalinensis | southern Quebec sites | spreading |
| Giant hogweed | Heracleum mantegazzianum | Montérégie, Estrie, Laurentians | spreading |
| Phragmites (invasive) | Phragmites australis | coasts, wetlands province-wide | spreading |
| Purple loosestrife | Lythrum salicaria | wetlands across southern Quebec | established |
| Garlic mustard | Alliaria petiolata | southern woodlands and parks | spreading |
| Dog-strangling vine | Vincetoxicum rossicum | southern Quebec, Montreal area | spreading |
| Oriental bittersweet | Celastrus orbiculatus | southern Quebec forests, edges | spreading |
| Common buckthorn | Rhamnus cathartica | southern and central Quebec | established |
| Glossy buckthorn | Frangula alnus | wetlands and edges, southern Quebec | established |
| Norway maple | Acer platanoides | urban forests, Montreal region | established |
| Japanese barberry | Berberis thunbergii | gardens and edges, southern Quebec | spreading |
| Black locust | Robinia pseudoacacia | roadsides, fields, southern Quebec | spreading |
| Eurasian watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum | lakes across southern Quebec | established |
| European frogbit | Hydrocharis morsus-ranae | southern waterways, Montérégie | spreading |
| Common carp | Cyprinus carpio | St. Lawrence, lakes and rivers | established |
| Round goby | Neogobius melanostomus | St. Lawrence River and harbours | established |
| Zebra mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | St. Lawrence, Great Lakes area | established |
| Quagga mussel | Dreissena rostriformis bugensis | lower St. Lawrence, lakes | established |
| European green crab | Carcinus maenas | Gulf and estuaries, St. Lawrence coast | spreading |
| Mute swan | Cygnus olor | southern waterways and islands | spreading |
| European starling | Sturnus vulgaris | urban and rural across Quebec | established |
| House sparrow | Passer domesticus | cities and towns province-wide | established |
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | ports, cities and rural sites | established |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | urban and rural lands | established |
| Emerald ash borer | Agrilus planipennis | Montreal, Outaouais, Estrie | spreading |
| Gypsy moth (spongy moth) | Lymantria dispar dispar | southern forests, recurring outbreaks | spreading |
| Asian longhorned beetle | Anoplophora glabripennis | restricted detections, Montreal region | restricted |
| Brown marmorated stink bug | Halyomorpha halys | houses and crops, southern Quebec | established |
| Japanese beetle | Popillia japonica | Montérégie and southern Quebec | restricted |
| Asian lady beetle | Harmonia axyridis | urban and agricultural areas | established |
| Spiny waterflea | Bythotrephes longimanus | deep lakes in southern Quebec | established |
| Chinese mystery snail | Cipangopaludina chinensis | some lakes and waterways, southern Quebec | established |
| Dutch elm disease | Ophiostoma novo-ulmi | province-wide on elms | established |
| White pine blister rust | Cronartium ribicola | forests across Quebec | established |
| Potato late blight | Phytophthora infestans | province-wide in crops | established |
| Asian tiger mosquito | Aedes albopictus | limited southern Quebec detections | restricted |
Images and Descriptions

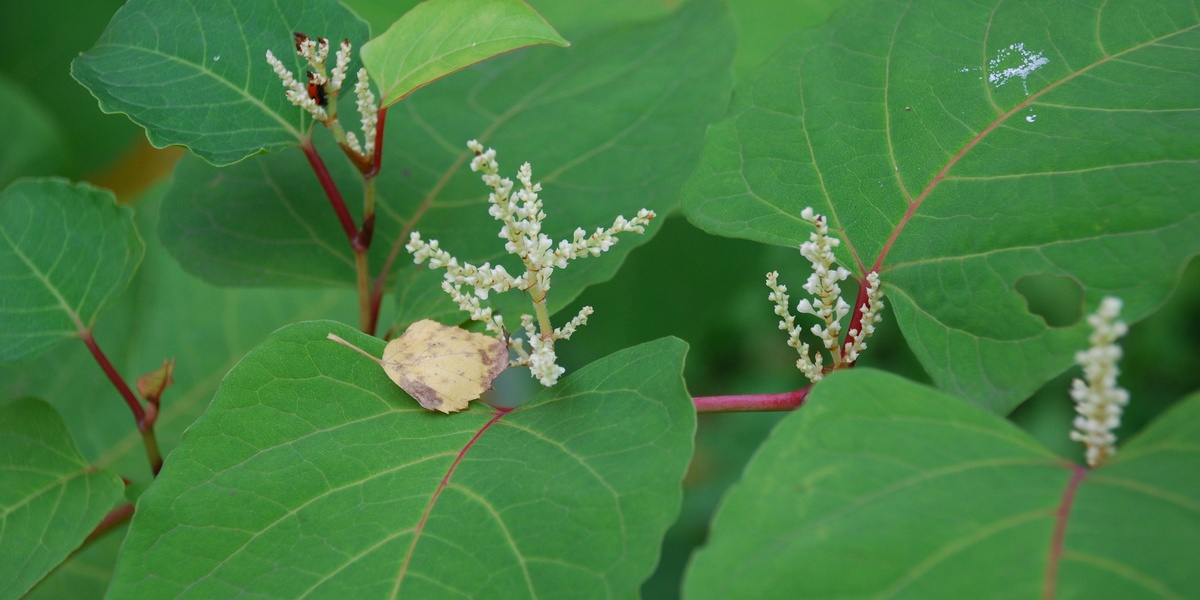
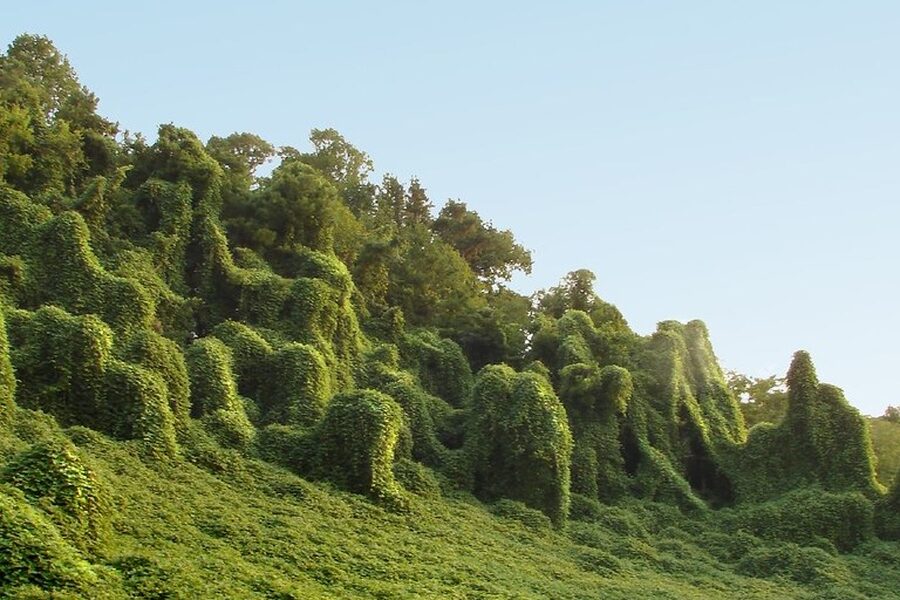
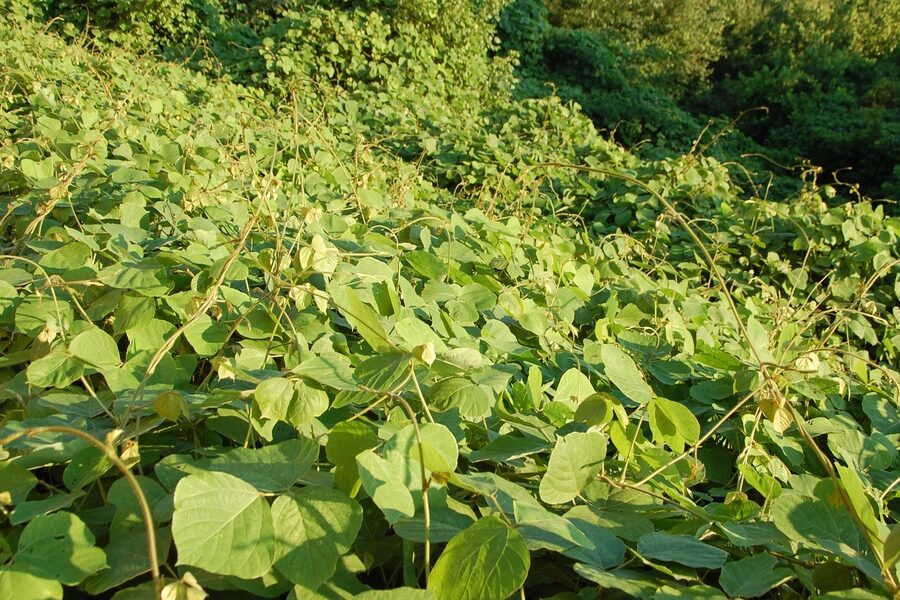
Japanese knotweed
Tough, bamboo-like perennial that forms dense stands along roads, riverbanks and disturbed sites. Breaks apart roots when removed, crowding out native plants. Control by repeated removal or licensed herbicide; report large infestations to municipal authorities.

Bohemian knotweed
Hybrid knotweed common in urban and riparian sites; aggressive root spreaders that damage foundations and outcompete natives. Mechanical removal often fails; long-term herbicide programs and professional removal recommended. Report sightings to local invasive species contacts.

Giant knotweed
Very large knotweed species forming impenetrable stands on riverbanks and disturbed land. Causes erosion and biodiversity loss. Requires persistent control, disposal precautions, and reporting to municipal invasive species programs.

Giant hogweed
Tall plant with sap that causes severe skin burns and scars; found along roadsides, ditches and riverbanks. Wear protection for removal; report to local public health or municipal invasive species contacts for control.

Phragmites (invasive)
Invasive common reed forming dense wetland monocultures that reduce wildlife habitat and clog waterways. Manage with targeted herbicide, mowing or water-level control and report new sites to provincial programs.

Purple loosestrife
Showy wetland plant that replaces native marsh vegetation and alters wetland function. Biological control beetles used in some areas; pulling and disposal effective for small patches. Report emergent infestations to authorities.

Garlic mustard
Shade-tolerant forest herb that smothers spring wildflowers and disrupts soil fungi. Hand-pulling before seed set and bagging is effective. Report spreading populations to local conservation groups.

Dog-strangling vine
Perennial vine that forms dense mats in meadows and forests, reducing biodiversity and forage. Manual removal and herbicide are used; dispose of seeds and report patches to regional programs.

Oriental bittersweet
Woody vine that girdles and topples trees by twining and strangling branches. Cut stems and apply herbicide on cuts; remove seedlings; report heavy stands to municipalities.

Common buckthorn
Aggressive shrub invading woodlands and hedgerows, producing many seeds eaten by birds. Removes native understory. Pull small plants; cut and treat larger ones. Report large infestations to local land managers.

Glossy buckthorn
Invasive wetland shrub that forms dense thickets, shading native plants and altering wetlands. Remove seedlings, cut and treat larger plants; report to conservation authorities.

Norway maple
Non-native maple that produces dense shade and seedlings that outcompete native trees in parks and gardens. Remove seedlings and favor native replacements; report spreading stands to municipal urban forestry programs.

Japanese barberry
Ornamental shrub that escapes cultivation, invades edges and may harbor ticks. Remove and replace with natives; bag and dispose of cuttings, and report expanding populations.

Black locust
Fast-growing tree from the U.S. introduced as an ornamental and for stabilization; resprouts from roots and spreads by seed, shading native species. Control by cutting and treating stumps; report dense thickets.

Eurasian watermilfoil
Submerged aquatic plant forming dense mats that impede boating and harm native plants and fish habitat. Prevent spread by cleaning boats and equipment; hand-pulling, benthic barriers or herbicide used; report new infestations to provincial aquatic invasive programs.

European frogbit
Floating plant resembling small lily pads that forms dense mats on calm waters, reducing oxygen and recreation. Remove mats, clean boats, and report sightings to aquatic invasive hotlines.

Common carp
Large introduced fish that uproots sediment, increases turbidity and harms aquatic plants and native fish. Manage by exclusion or targeted removal in sensitive waters; report unusual population changes to fisheries authorities.

Round goby
Bottom-dwelling fish that competes with native species and consumes eggs; common in ports and rocky shorelines. Prevent spread on boats and report catches to fisheries managers.

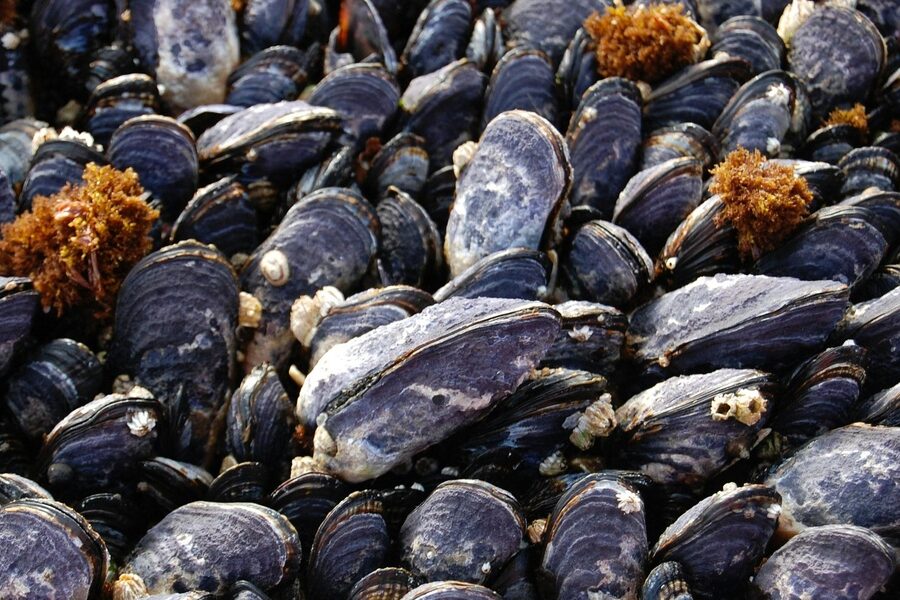
Zebra mussel
Tiny mussel that fouls water intakes, docks and outcompetes natives. Spread via boats and equipment; clean, drain, dry watercraft and report new sightings to provincial invasive species hotlines.

Quagga mussel
Similar to zebra mussel but tolerates deeper waters; clogs infrastructure and alters food webs. Clean boats and gear thoroughly and report sightings to authorities.

European green crab
Aggressive shore crab that predates native shellfish and disrupts eelgrass beds in coastal Quebec. Report coastal sightings, avoid moving bait, and support local trapping programs.

Mute swan
Large ornamental bird that displaces native waterfowl and gardens, and trims aquatic vegetation. Do not feed; report nesting birds to local wildlife authorities for management guidance.

European starling
Introduced bird that competes for nest sites with native species and damages crops. Remove nest boxes, seal cavities and report problem roosts to municipal wildlife programs.

House sparrow
Common introduced bird in urban areas that competes with native species. Manage by reducing food sources and nesting opportunities; report unusual outbreaks.

Norway rat
Non-native rodent that spreads disease, damages property and preys on ground-nesting birds. Prevent by rodent-proofing buildings, secure waste, and report infestations to municipal pest control services.

Feral cat
Free-roaming cats prey heavily on songbirds and small mammals; a major conservation threat. Support trap-neuter-return programs and report colonies to animal services for humane management.

Emerald ash borer
Wood-boring beetle killing ash trees; causes extensive urban and forest loss. Do not move firewood; report sightings and follow municipal removal and replacement programs.

Gypsy moth (spongy moth)
Caterpillar outbreaks defoliate hardwood forests, impacting timber and recreation. Report egg masses, avoid moving firewood, and follow local treatment advisories during outbreaks.

Asian longhorned beetle
Wood-boring beetle that attacks many hardwoods; eradication programs have targeted detected infestations. Report suspect beetles or large exit holes immediately to CFIA or provincial authorities.

Brown marmorated stink bug
Household nuisance and agricultural pest feeding on fruit and crops. Seal buildings, avoid crushing insects, and report new agricultural damage to local extension services.

Japanese beetle
Beetle that skeletonizes leaves and damages turf and ornamentals. Hand-pick, use traps cautiously, and report spreading populations to provincial pest authorities.

Asian lady beetle
Introduced beetle that preys on pests but invades homes in autumn and can outcompete native ladybugs. Seal entry points and report large aggregations to local extension services.
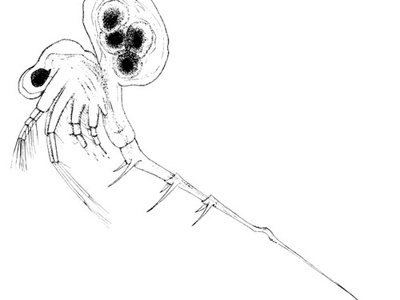
Spiny waterflea
Predatory zooplankton that disrupts food webs and fouls fishing gear. Prevent spread by draining and drying gear between waterbodies and report new lake sightings.

Chinese mystery snail
Escaped aquarium snail that can reach high densities, altering sediments and spreading parasites. Never release aquarium species; report new populations to aquatic invasive programs.

Dutch elm disease
Fungal disease spread by beetles and infected wood, causing elm mortality across Quebec. Do not move elm firewood; report sick trees and follow municipal removal protocols.
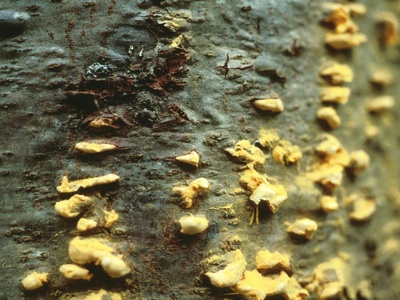
White pine blister rust
Non-native fungus attacking white pines and altering forest composition. Monitor pine health, avoid moving infected material, and report suspect infections to provincial forest health agencies.
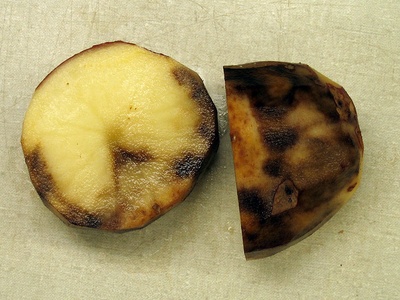
Potato late blight
Fungal-like pathogen causing major potato and tomato crop losses. Use certified seed, crop rotation, resistant varieties and report severe outbreaks to agriculture extension services.
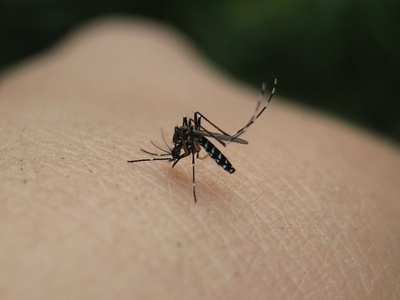
Asian tiger mosquito
Aggressive daytime-biting mosquito and potential disease vector detected in southern Quebec. Remove standing water, use repellents, and report clusters or breeding evidence to public health units.





