Rhode Island’s varied coastline, rivers and freshwater ponds support a lot of native life—and they also create pathways for nonnative species to arrive and spread. Small, mobile organisms can hitch rides on boats, in bait buckets, or with plants moved between water bodies, and their impacts show up in fisheries, wetlands and shoreline recreation.
There are 44 Invasive Species in Rhode Island, ranging from Asian clam to Zebra mussel. Each entry is organized with columns for Scientific name,Category,Where found (RI) so you can quickly see what the species is, what kind of organism it is, and where it has been observed; for details and locations you’ll find below.
How do I report a sighting of an invasive species in Rhode Island?
Note the location, date and identifying features, take clear photos if possible, and report the sighting to the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management or local conservation groups; many agencies also accept reports and photos via email or online forms, and prompt reporting helps managers track and respond to new occurrences.
What practical steps can I take to prevent spreading invasive species between water bodies?
Follow simple biosecurity: Clean and remove all plants, animals and mud from boats, trailers and gear; drain bilges and livewells, dry equipment thoroughly, and never move live bait or aquarium species between waters—these actions greatly reduce accidental introductions.
Invasive Species in Rhode Island
| Name | Scientific name | Category | Where found (RI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common reed (non-native) | Phragmites australis (non-native lineage) | Plant | Coastal marshes, estuaries, roadside wetlands |
| Japanese knotweed | Reynoutria japonica | Plant | Riversides, disturbed soils, urban riparian corridors |
| Purple loosestrife | Lythrum salicaria | Plant | Freshwater marshes, ditches, pond margins |
| Garlic mustard | Alliaria petiolata | Plant | Woodland understories, forest edges, trailsides |
| Multiflora rose | Rosa multiflora | Plant | Fields, forest edges, hedgerows |
| Oriental bittersweet | Celastrus orbiculatus | Plant | Forests, edges, roadsides, coastal woodlands |
| Japanese barberry | Berberis thunbergii | Plant | Woodland understories, hedgerows, yards |
| Burning bush | Euonymus alatus | Plant | Roadsides, wood edges, urban plantings |
| Tree-of-heaven | Ailanthus altissima | Plant | Disturbed sites, urban lots, roadsides |
| Norway maple | Acer platanoides | Plant | Urban parks, yards, forest edges |
| Japanese honeysuckle | Lonicera japonica | Plant | Forests, edges, trails, shrubs |
| Japanese stiltgrass | Microstegium vimineum | Plant | Disturbed forests, floodplains, trailsides |
| Mile-a-minute vine | Persicaria perfoliata | Plant | Sunny edges, wetlands, disturbed sites |
| Water chestnut | Trapa natans | Plant | Lakes, slow rivers, reservoirs |
| Eurasian watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum | Plant | Lakes, ponds, slow rivers |
| Curly-leaf pondweed | Potamogeton crispus | Plant | Lakes, ponds, reservoirs |
| Fanwort (cabomba) | Cabomba caroliniana | Plant | Ponds, warm lakes, slow streams |
| Porcelainberry | Ampelopsis brevipedunculata | Plant | Forest edges, hedgerows, streambanks |
| Autumn olive | Elaeagnus umbellata | Plant | Fields, roadsides, open woods |
| European green crab | Carcinus maenas | Mollusc | Narragansett Bay, rocky shores, estuaries |
| Asian shore crab | Hemigrapsus sanguineus | Mollusc | Rocky intertidal zones, Narragansett Bay |
| Common periwinkle | Littorina littorea | Mollusc | Rocky shores, salt marsh edges |
| Zebra mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | Mollusc | Freshwater ponds, lakes, reservoirs (where detected) |
| Asian clam | Corbicula fluminea | Mollusc | Rivers, warm ponds, slow streams |
| Round goby | Neogobius melanostomus | Fish | Brackish estuaries, rivers, piers |
| Common carp | Cyprinus carpio | Fish | Ponds, lakes, slow rivers, marshes |
| European starling | Sturnus vulgaris | Vertebrate | Urban, agricultural, coastal areas |
| House sparrow | Passer domesticus | Vertebrate | Urban, farms, suburbs |
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | Vertebrate | Urban, ports, wetlands, farms |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | Vertebrate | Urban, rural edges, islands |
| Mute swan | Cygnus olor | Vertebrate | Coastal ponds, estuaries, freshwater lakes |
| Codium (dead man’s fingers) | Codium fragile ssp. tomentosoides | Algae | Rocky subtidal zones, piers, estuaries |
| White-nose syndrome | Pseudogymnoascus destructans | Pathogen | Caves, bat roosts statewide |
| MSX (oyster disease) | Haplosporidium nelsoni | Pathogen | Narragansett Bay and coastal waters |
| Dermo disease | Perkinsus marinus | Pathogen | Salt ponds, estuaries, coastal waters |
| Hemlock woolly adelgid | Adelges tsugae | Insect | Hemlock stands across RI woodlands |
| Spongy moth (gypsy moth) | Lymantria dispar | Insect | Forest edges, oak stands, suburban woods |
| Winter moth | Operophtera brumata | Insect | Deciduous forests, orchards |
| Brown marmorated stink bug | Halyomorpha halys | Insect | Agricultural fields, homes, orchards |
| Japanese beetle | Popillia japonica | Insect | Lawns, gardens, orchards, fields |
| Asian tiger mosquito | Aedes albopictus | Insect | Urban containers, wetlands, stormwater |
| Spotted lanternfly | Lycorma delicatula | Insect | (Included only if detected) |
| Rusty crayfish | Faxonius rusticus | Mollusc | Rivers, streams, lakes (where present) |
| European frog-bit | Hydrocharis morsus-ranae | Plant | Ponds, slow rivers (localized) |
Images and Descriptions

Common reed (non-native)
Tall, dense reed with feathery plumes; outcompetes native marsh plants, reduces habitat diversity. Originated from Eurasia, spread by seed and rhizomes. Management: targeted herbicide, mowing, and hydrologic restoration; non-native lineage controlled in priority sites.

Japanese knotweed
Bamboo-like hollow stems and large heart-shaped leaves; forms dense stands that damage banks and infrastructure. Introduced from East Asia as ornamental. Management: repeated cutting, systemic herbicide, and careful disposal; difficult to eradicate but controllable locally.

Purple loosestrife
Showy magenta flower spikes; displaces native wetland plants and alters hydrology. Introduced from Europe for ornament. Management: hand-pulling small patches, biocontrol beetles, herbicide; prioritized where rare wetland species occur.

Garlic mustard
Low-growing biennial with scalloped leaves and white flowers; releases chemicals that inhibit natives and reduces forest regeneration. Introduced from Europe. Management: pull before seed-set, repeated controls, community removals effective.

Multiflora rose
Arching shrub with clusters of white flowers and fringed stipules; creates impenetrable thickets, outcompetes native shrubs. Introduced for erosion control and rootstock. Management: cut-stump herbicide, repeated mowing, biocontrol research ongoing.

Oriental bittersweet
Twining vine with orange fruit; girdles and topples trees, displaces natives. Introduced as ornamental from East Asia. Management: cut stems, herbicide on stumps, remove females and treat regrowth; vigilant removal prevents spread.

Japanese barberry
Rounded shrub with small red berries and spines; dense shade-tolerant thickets degrade native herb layers and increase tick habitat. Introduced as ornamental. Management: mechanical removal, herbicide for stumps, replace with natives.

Burning bush
Noted for corky ridges and bright fall color; escapes cultivation to shade out natives. Introduced from Asia. Management: discourage planting, remove seedlings, cut-stump herbicide for large shrubs.

Tree-of-heaven
Large fast-growing tree with compound leaves and foul odor; produces innumerable seedlings, displaces natives. Introduced from China. Management: girdling or cut-stump with herbicide, persistent removal of resprouts.

Norway maple
Large maple with dense canopy and milky sap from petiole; shades out native seedlings and alters soils. Introduced as street tree. Management: replace with native trees, remove seedlings, manage seed sources.

Japanese honeysuckle
Vining plant with fragrant tubular flowers; smothers native vegetation and climbs trees. Introduced as ornamental groundcover. Management: pull vines, cut and herbicide, remove seed sources to prevent re-establishment.

Japanese stiltgrass
Thin grassy mat with silvery midrib; displaces native herb layer and alters fire regimes. Introduced as packing material/contaminant from Asia. Management: mow before seeding, hand-pull small patches, coordinated control in invasion fronts.

Mile-a-minute vine
Rapidly climbing vine with triangular leaves and barbed stems, blue fruit; smothers shrubs and young trees. Introduced from Asia. Management: hand-pull small patches, herbicide on large infestations, biological control programs exist.

Water chestnut
Floating rosette plant with spiny nut fruits; forms dense mats that impede recreation and displace native aquatic plants. Introduced from Europe/Asia. Management: hand-pulling, raking boats, early detection and boat-cleaning critical.

Eurasian watermilfoil
Feathery submerged leaves in whorls; forms dense mats reducing oxygen and native plants. Introduced via aquaria and boats. Management: mechanical harvesting, herbicide, spot treatments, boat decontamination to limit spread.

Curly-leaf pondweed
Submerged plant with wavy-edged leaves that dies back mid-summer causing turbid blooms; displaces natives. Introduced from Eurasia. Management: hand-removal, targeted herbicide, prevent spread on boats and gear.

Fanwort (cabomba)
Delicate fan-shaped leaves on submerged stems; forms thick beds that block recreation and smother natives. Likely introduced via aquarium releases. Management: manual removal, herbicide spot treatments, public outreach to prevent dumping.

Porcelainberry
Climbing vine with colorful berries; overtops shrubs and trees, displacing natives. Introduced as ornamental. Management: cut and treat stumps with herbicide, persistent pulling and removal of fruiting vines.

Autumn olive
Silver-leaved shrub with red fruit; fixes nitrogen and invades savannas and prairies, altering soils. Introduced for wildlife planting. Management: cut-stump herbicide, root removal, prioritize open natural areas.

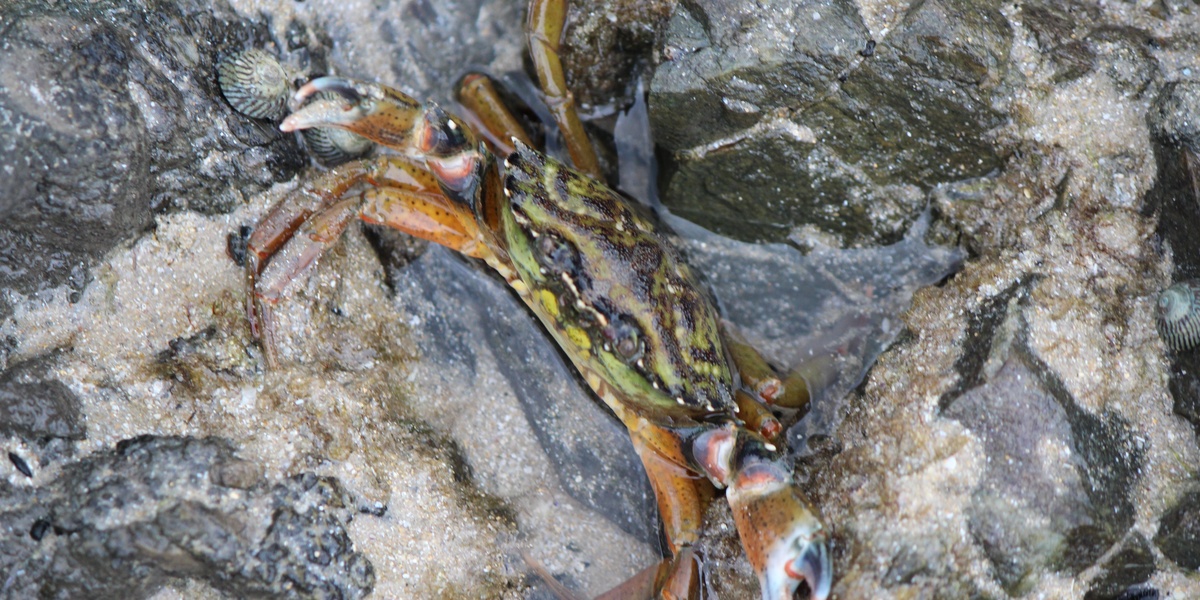
European green crab
Small round crab with greenish shell; preys on shellfish and disrupts eelgrass beds. Introduced via ballast water from Europe. Management focuses on monitoring, harvest trials, and protecting shellfish beds.

Asian shore crab
Small square carapace, banded legs; competes with native crabs and alters intertidal communities. Introduced from Asia in hull/ballast. Management: monitoring and local trapping; widespread control impractical.

Common periwinkle
Conical marine snail introduced from Europe; grazes algae, alters shore ecology and competes with natives. Arrived in 1800s via ballast. Management: limited; monitoring and protection of sensitive shore habitats.

Zebra mussel
D-shaped freshwater mussel with zebra striping; clogs infrastructure, outcompetes natives, alters food webs. Transported on boats. Management: boat-cleaning, surveillance, rapid response where found.

Asian clam
Small ovate clam that filters heavily, can alter sediments and compete with natives. Introduced from Asia via ballast and bait. Management: monitoring, prevent spread by decontaminating equipment.

Round goby
Bottom-dwelling mottled fish with fused pelvic fins; eats native mussels and competes with small fishes. Introduced via ballast water from Europe. Management: monitoring, prevent spread through ballast control.

Common carp
Large, heavy-bodied fish that uproots sediment, increasing turbidity and harming aquatic plants. Introduced from Eurasia for aquaculture. Management: removal, netting, barriers, habitat restoration.

European starling
Glossy black bird with yellow bill; aggressive competitor for nest sites, damages crops and native songbird populations. Introduced in 1800s. Management: nest exclusion, deterrents, legal control in some contexts.

House sparrow
Small brown bird common around buildings; competes with native birds for nest cavities and food. Introduced from Europe. Management: exclusion, nest box modification, local control where impacting natives.

Norway rat
Large brown rodent that spreads disease, predates wildlife and damages infrastructure. Introduced historically via ships. Management: sanitation, trapping, baiting by professionals; ongoing control needed.

Feral cat
Domestic cat populations preying on birds, mammals, and reptiles; major wildlife mortality source. Introduced globally by humans. Management: TNR debated; removal from sensitive habitats encouraged, public education.

Mute swan
Large white swan with orange bill; grazes eelgrass, displaces waterfowl and alters marsh vegetation. Introduced from Europe for ornament. Management: nest/egg control, targeted removal in high-impact areas.

Codium (dead man’s fingers)
Green, spongey branching seaweed that fouls shellfish and covers rocky habitats; outcompetes native algae. Likely arrived on hulls. Management: monitoring, manual removal at small scales, shellfish bed protection.

White-nose syndrome
Fungal pathogen causing high mortality in hibernating bats; white fuzzy growth on muzzles and wings. Introduced from Europe. Management: cave closures, decontamination, research on mitigation and bat recovery.

MSX (oyster disease)
Protozoan parasite causing high oyster mortality and reduced growth; historically introduced from Europe. Management: selective breeding for resistant oysters, monitoring, adaptive shellfish management.

Dermo disease
Protozoan parasite infecting oysters and clams, causing weakness and mortality; expanded northward with warming. Management: monitoring, resistant stock selection, harvest adjustments.

Hemlock woolly adelgid
Tiny white woolly insects at needle bases causing hemlock dieback and mortality. Introduced from Asia. Management: insecticide treatments in high-value trees, biocontrol and monitoring at landscape scale.

Spongy moth (gypsy moth)
Caterpillars with hairy bodies that defoliate oaks and other trees; periodic outbreaks damage forests. Introduced from Europe. Management: monitoring, pheromone traps, Bacillus thuringiensis treatments during outbreaks.

Winter moth
Small caterpillars feed on buds and leaves of maples, oaks, and fruit trees causing defoliation. Introduced from Europe. Management: trunk-band traps, biological controls, targeted sprays.

Brown marmorated stink bug
Shield-shaped bug causing fruit and crop damage and nuisance indoors during cold months. Introduced from East Asia. Management: exclusion, monitoring, targeted insecticide programs in crops.

Japanese beetle
Metallic green beetle with tan edges; skeletonizes leaves and damages turf. Introduced from Japan. Management: traps can worsen local damage; use integrated control and cultural practices.
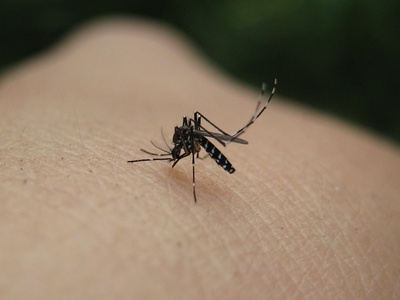
Asian tiger mosquito
Small black-and-white striped mosquito that bites aggressively and can transmit diseases; arrived via tire trade. Management: remove standing water, public outreach, targeted larval control.

Spotted lanternfly
Nymphs and adults feed on sap causing plant stress, hitchhike on vehicles; invasive from Asia. Management: monitor, report sightings, remove egg masses and tree-of-heaven hosts.

Rusty crayfish
Aggressive crayfish that eats plants and small animals, displacing natives. Introduced via bait release from the Midwest. Management: prevent bait release, targeted trapping, public education.

European frog-bit
Floating plant forming mats that shade out natives and hinder boating. Introduced from Europe. Management: hand-pulling, mechanical removal, early detection and local eradication efforts.





