Burkina Faso may be landlocked, but its rivers, floodplains and reservoirs host a surprising variety of freshwater life. Seasonal rains and permanent waterways like the Volta tributaries create habitats where local fish communities persist and support livelihoods, research and local diets.
There are 92 Fish of Burkina Faso, ranging from Adanson’s Labeo to West African Lungfish. For each species you’ll find below the columns Scientific name,Max length (cm),Habitat to help with identification, size expectations and ecological context — all organized so you can scan distributions and compare species quickly; you’ll find below.
Which habitats in Burkina Faso contain the greatest number of species?
Most species concentrate in permanent rivers and larger reservoirs where flow, depth and vegetation provide stable conditions; floodplains and seasonal ponds add temporary breeding and nursery areas after rains. Mapping species to those habitat types helps show where diversity is highest and when seasonal movements occur.
How can I use this list for research, conservation or fishing?
Use the Scientific name column for accurate species matching, Max length (cm) to set size expectations and Habitat to plan surveys or target management actions. Cross-reference with regional guides and IUCN data for conservation status or harvesting regulations.
Fish of Burkina Faso
| Common name | Scientific name | Max length (cm) | Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nile Tilapia | Oreochromis niloticus | 60 | Lakes, rivers, reservoirs nationwide; Volta and Niger basins. |
| Nile Perch | Lates niloticus | 200 | Large rivers and lakes like Lake Kompienga; Volta basin. |
| North African Catfish | Clarias gariepinus | 170 | Widespread in rivers, lakes, floodplains; extremely hardy. |
| Sudan Tigerfish | Hydrocynus brevis | 86 | Open waters of large rivers and lakes in the Volta basin. |
| African Bonytongue | Heterotis niloticus | 100 | Swamps, floodplains, and slow-moving rivers; Volta basin. |
| Giraffe Catfish | Auchenoglanis occidentalis | 70 | Rivers and lakes with soft bottoms; Volta and Niger basins. |
| Peters’s Elephantnose | Gnathonemus petersii | 35 | Slow-moving, vegetated rivers, especially in the Comoé basin. |
| Bayad | Bagrus bajad | 112 | Large rivers and lakes with rocky or sandy bottoms; Volta basin. |
| Kafue Pike | Hepsetus odoe | 70 | Clear, vegetated waters of rivers and lakes; Volta, Niger basins. |
| Electric Catfish | Malapterurus electricus | 122 | Slow-moving rivers and pools, often nocturnal; Volta basin. |
| Senegal Bichir | Polypterus senegalus | 50 | Shallow swamps, marshes, and river edges; Volta, Niger basins. |
| African Carp | Labeo coubie | 80 | Large rivers with strong currents; Volta and Niger basins. |
| West African Lungfish | Protopterus annectens | 100 | Floodplains and swamps that seasonally dry up. |
| African Snakehead | Parachanna obscura | 55 | Marshes, swamps, and slow-moving rivers with dense vegetation. |
| Moonfish | Citharinus citharus | 80 | Large rivers and floodplains, especially in the Volta basin. |
| Bulldog | Marcusenius senegalensis | 32 | Bottom of rivers and floodplains, often in turbid water. |
| True Big-scale Tetra | Brycinus macrolepidotus | 60 | Open waters of rivers and lakes; Volta and Niger basins. |
| Nurse Tetra | Brycinus nurse | 16 | Well-vegetated areas of rivers and lakes throughout the country. |
| Silver Sillago | Schilbe intermedius | 50 | Open waters of lakes and large rivers, widespread. |
| Redbelly Tilapia | Coptodon zillii | 40 | Widespread in rivers, lakes, and irrigation canals. |
| Banded Tilapia | Tilapia sparrmanii | 25 | Heavily vegetated, shallow waters of ponds, streams, and floodplains. |
| Guinean Tilapia | Tilapia guineensis | 30 | Brackish-tolerant; lower reaches of coastal-draining rivers like the Comoé. |
| Managu Tilapia | Sarotherodon galilaeus | 41 | Widespread in lakes and rivers; Volta basin. |
| Guenther’s Mouthbrooder | Chromidotilapia guntheri | 16 | Rivers and streams, often near vegetation or rocks. |
| Jewelfish | Hemichromis fasciatus | 27 | Rivers and streams, prefers areas with cover; widespread. |
| Long-snouted Distichodus | Distichodus rostratus | 80 | Large rivers with sandy or rocky bottoms; Niger and Volta basins. |
| Silver Distichodus | Distichodus brevipinnis | 60 | Rivers and floodplains, often among vegetation. |
| Shield-head Catfish | Synodontis schall | 49 | Widespread in most rivers and lakes; Volta and Niger basins. |
| Gambi Squeaker | Synodontis gambiensis | 39 | Rivers and floodplains, mainly in the Niger and Volta basins. |
| Niger Squeaker | Synodontis sorex | 42 | Niger River basin tributaries and associated floodplains. |
| Cornish Jack | Mormyrops anguilloides | 150 | Large rivers with rocky outcrops or deep pools. |
| Niger Labeo | Labeo senegalensis | 40 | Rivers and floodplains of the Niger and Volta basins. |
| Adanson’s Labeo | Labeo adansonii | 30 | Upper reaches of rivers like the Comoé. |
| African Pike-characin | Hepsetus cuvieri | 30 | Smaller rivers and streams with clear water and vegetation. |
| Volta Eutropius | Schilbe mystus | 40 | Open waters of rivers and lakes; Volta basin. |
| Kissi Chiselmouth | Varicorhinus kissiensis | 22 | Rocky, fast-flowing upper reaches of rivers in the Niger basin. |
| Senegal Trout-barb | Raiamas senegalensis | 19 | Surface waters of clear, fast-flowing rivers and streams. |
| Short-headed Citharinus | Citharinus latus | 50 | Slow-moving rivers and floodplains; Volta and Niger basins. |
| Dwarf Stonebasher | Pollimyrus isidori | 8 | Shallow, heavily vegetated swamps and river margins. |
| African Banded Barb | Enteromius fasciolatus | 8 | Small, clear streams with sandy bottoms and vegetation. |
| Banded Jewel Cichlid | Hemichromis bimaculatus | 10 | Quiet, vegetated waters of streams and rivers. |
| Kribensis | Pelvicachromis pulcher | 10 | Slow-moving, soft, acidic forest streams, Comoé basin. |
| West African Killi | Scriptaphyosemion geryi | 5 | Small, temporary pools and streams in forested savannas. |
| Ocellated Synodontis | Synodontis ocellifer | 49 | Rivers and lakes, particularly the Niger and Volta basins. |
| Upside-down Catfish | Synodontis nigriventris | 10 | Heavily vegetated riverbanks and roots. |
| Volta Labeo | Labeo-barbus voltae | 19 | Lower and middle reaches of rivers in the Volta basin. |
| Threespot Barb | Enteromius trispilos | 11 | Small rivers and streams, often in savanna regions. |
| Niger Fin-eater | Mesoborus crocodilus | 20 | Open waters of the Niger river system. |
| Four-banded Tilapia | Pelmatolapia mariae | 30 | Introduced in some reservoirs for aquaculture and fisheries. |
| Elongate Glass Catfish | Pellonula leonensis | 13 | Open waters of large rivers and lakes; pelagic. |
| Volta Glass Catfish | Parailia pellucida | 15 | Rivers and lakes in the Volta basin, often near the surface. |
| Big-mouth Sleeper | Eleotris daganensis | 19 | Bottom of slow-moving streams and rivers, often near banks. |
| Striped Fin-eater | Ichthyborus quadrilineatus | 17 | Surface waters of rivers; Niger and Volta basins. |
| Niger Thryssa | Thrattidion noctivagus | 4 | Pelagic in large rivers, active at night. |
| Clown Barb | Enteromius ablabes | 10 | Small streams and brooks, often with clear water. |
| Short-bodied Pipefish | Microphis brachyurus | 22 | Estuarine parts of the Comoé river, brackish to freshwater. |
| Four-barbel Catfish | Amphilius platychir | 15 | Fast-flowing, rocky streams in highland or savanna areas. |
| Short-nosed Lyretail | Aphyosemion bitaeniatum | 5 | Shallow pools and swampy parts of streams, Comoé basin. |
| Red-spotted Killi | Fundulopanchax gularis | 6 | Temporary pools and marshes in coastal savanna regions. |
| Niger Distichodus | Distichodus engycephalus | 45 | Main channels of large rivers, especially the Niger. |
| Blunt-toothed Pellonula | Odaxothrissa mento | 17 | Open waters of large rivers; Niger and Volta basins. |
| Slender Lungfish | Protopterus dolloi | 130 | Swampy, deoxygenated waters; possibly in Comoé basin. |
| Horseface Mormyrid | Campylomormyrus tamandua | 45 | Bottom of large rivers with strong currents. |
| Saddle Bichir | Polypterus endlicherii | 75 | Rivers and swamps with ample vegetation for cover. |
| Shortfin Barb | Enteromius brevipinnis | 7 | Tributaries and streams in the Volta basin. |
| Long-finned Barb | Enteromius longifilis | 10 | Small rivers and streams with moderate current. |
| West African Glass Catfish | Schilbe uranoscopus | 45 | Deep, open waters of large rivers and lakes. |
| Ornate Bichir | Polypterus ornatipinnis | 60 | Slow-moving rivers and swamps with dense vegetation. |
| Volta Scraper | Garra waterloti | 9 | Rocky sections of rivers and streams in the Volta basin. |
| Niger Scraper | Garra nigeriensis | 12 | Rapids and fast-flowing sections of the Niger River system. |
| Ropefish | Erpetoichthys calabaricus | 40 | Slow-moving, muddy rivers and swamps; Comoé basin. |
| Striped Anostomid | Anisitsiellina ubanguiensis | 9 | Tributaries of the Niger river system. |
| False Nile Catfish | Clarotes laticeps | 80 | Large rivers and lakes; Volta and Niger basins. |
| Big-eye Labeo | Labeo-barbus macrops | 21 | Rivers of the Volta basin, often in rocky areas. |
| Bar-tailed Citharine | Citharidium ansorgii | 70 | Large, slow-flowing rivers and floodplains. |
| Volta Upside-down Catfish | Synodontis velifer | 20 | Rivers of the Volta basin. |
| African Spiny Eel | Mastacembelus liberiensis | 30 | Bottom of streams and rivers, burrows in sand or mud. |
| Dwarf Mouthbrooder | Pseudocrenilabrus multicolor | 8 | Shallow, heavily vegetated waters like swamps and pools. |
| Niger Jellybean Catfish | Andersonia leptura | 10 | Sandy bottoms of the middle Niger River. |
| Straight-mouthed Citharinus | Citharinops distichodoides | 84 | Large rivers; known from the Niger basin. |
| Red-eyed Labeo | Labeo-barbus intermedius | 50 | Rivers and lakes, originally from Ethiopia but introduced. |
| Fork-tailed Labeo | Labeo annectens | 30 | Rivers in the Volta basin. |
| Fin-backed Catfish | Auchenoglanis biscutatus | 60 | Rivers and lakes in the Volta and Niger basins. |
| Slendertail Mormyrid | Mormyrus tenuirostris | 30 | Rivers in the Volta basin. |
| Volta Stonebasher | Pollimyrus adspersus | 11 | Shallow, vegetated areas of the Volta river system. |
| Niger Long-snout | Mormyrops oudoti | 50 | Deep channels of the Niger River. |
| Niger Striped Barb | Enteromius nigeriensis | 8 | Streams and tributaries of the Niger River. |
| Silver Robber | Alestopetersius smykalai | 8 | Small forest streams in the Comoé basin. |
| Long-nosed Distichodus | Distichodus-altus niloticus | 25 | Vegetated areas of rivers and floodplains. |
| West African Ctenopoma | Ctenopoma petherici | 20 | Swamps, marshes, and heavily vegetated, slow-moving waters. |
| Big-eyed Barb | Enteromius macrops | 10 | Rivers and streams throughout the region. |
| Niger Halfbeak | Hyporhamphus picarti | 20 | Surface of lower rivers, tolerant of brackish water. |
Images and Descriptions

Nile Tilapia
A highly adaptable and crucial food fish, forming the backbone of aquaculture and fisheries. It’s known for its fast growth and maternal mouthbrooding, where females protect their young in their mouths.

Nile Perch
An enormous predatory fish and a prized sport and food fish. It’s a native top predator in Burkina Faso’s larger water bodies, controlling other fish populations and supporting a valuable fishery.

North African Catfish
This air-breathing catfish can survive in poor water and even move over land. It’s a vital, protein-rich food source and a key species in local aquaculture due to its resilience and rapid growth.

Sudan Tigerfish
A powerful, silver-flanked predator famous for its large, interlocking teeth. It’s a popular target for sport anglers due to its aggressive nature and fierce fight, making it an iconic African game fish.

African Bonytongue
Often called the African Arowana, this primitive fish is a filter-feeder with an upturned mouth. It is valued in aquaculture for its rapid growth and is a significant, though bony, food fish in many areas.

Giraffe Catfish
Easily recognized by its elongated snout and giraffe-like spotted pattern, this catfish is a bottom-dweller. It’s a delicious and highly valued food fish, often caught by local fishers using various traditional methods.

Peters’s Elephantnose
Famous for its trunk-like chin appendage used to find food and navigate with weak electric fields. This nocturnal fish is more a curiosity than a major food source, showcasing incredible sensory adaptation.
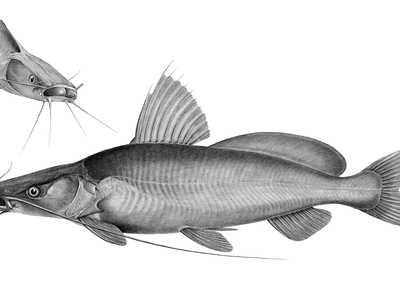
Bayad
A large, predatory catfish with a silvery body and long barbels. The Bayad is a commercially important species, highly sought after for its firm, well-flavored flesh, making it a staple in local markets.

Kafue Pike
Resembling a true pike, this voracious predator has a long body and sharp teeth. It often lies in wait in vegetation to ambush smaller fish, making it an important mid-level predator in its ecosystem.

Electric Catfish
This unique, sausage-shaped catfish can generate a powerful electric shock up to 350 volts to stun prey. It is generally avoided by fishers but is sometimes consumed for its reported medicinal properties.

Senegal Bichir
A living fossil, this ancient-looking fish has lungs to breathe air and armored, diamond-shaped scales. Its snake-like movement and dinosaur-like appearance make it a fascinating species of minor fishery importance.

African Carp
A large, powerful cyprinid with a distinctive fleshy snout used for scraping algae off rocks. It’s a very important commercial species in the Volta and Niger river systems, prized for its size and taste.

West African Lungfish
This incredible fish has both gills and lungs, allowing it to survive droughts by burying itself in a mud cocoon for months. It’s an important evolutionary link and a local, seasonal food source.

African Snakehead
A predatory, air-breathing fish with a long dorsal fin and snake-like head. It’s known for its parental care, with parents aggressively guarding their bright red fry. It is a valued food fish.

Moonfish
A very deep-bodied, silvery fish with a small mouth, resembling a disc or moon. It’s a detritus feeder, sifting through mud for organic matter, and is an important part of commercial catches on floodplains.

Bulldog
A member of the elephantfish family, it has a blunt, down-turned mouth. It uses a weak electric field to navigate and find insect larvae in the mud, playing a key ecological role in bottom habitats.

True Big-scale Tetra
A large, silvery tetra with prominent scales and an adipose fin. It’s a fast-swimming predator of insects and small fish, and it forms an important part of the commercial catch in many large river systems.

Nurse Tetra
A common and widespread small characin, often forming large schools. It is a vital part of the food web, feeding on insects and small organisms while being preyed upon by larger fish like tigerfish and perch.

Silver Sillago
Commonly known as butterfish, this schooling catfish is a key commercial species. It has a silvery, compressed body and is often caught in large numbers, being a staple food that is frequently smoked or dried.

Redbelly Tilapia
A versatile cichlid, recognized by its reddish throat and belly during breeding season. It’s an important food fish and has been used for aquatic weed control due to its diet of plants and algae.

Banded Tilapia
A small but hardy tilapia known for its distinct vertical bands, especially when breeding. While not a primary food fish due to its size, it is widespread and ecologically important as a food source for predators.
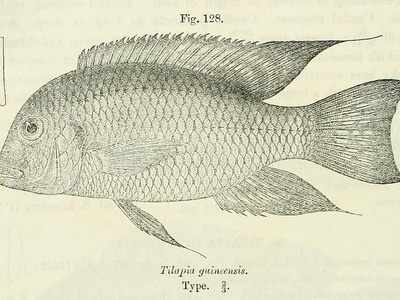
Guinean Tilapia
This cichlid is notable for its tolerance to salty water, unlike many other tilapias. It is a substrate spawner, where parents guard eggs laid on a cleaned surface, and is a locally important food fish.

Managu Tilapia
Known for biparental mouthbrooding, where both male and female incubate eggs in their mouths. This cooperative parenting is unusual and makes them fascinating. They are also a significant food fish.

Guenther’s Mouthbrooder
A colorful cichlid where both parents participate in mouthbrooding to protect their eggs and fry. It’s a fascinating example of biparental care in fish, though less commercially important than tilapia.

Jewelfish
A stunning but aggressive predatory cichlid with a beautiful pattern of iridescent spots and dark blotches. While too small to be a major food fish, it’s a very effective predator of smaller fish and insects.

Long-snouted Distichodus
This large, plant-eating fish has a long, pointed snout used to graze on algae and aquatic plants. Its size and good taste make it a highly valuable commercial species, especially in the Niger River system.

Silver Distichodus
A deep-bodied, silvery fish that feeds primarily on plants and seeds, especially on flooded plains. It is an important food fish, contributing significantly to fisheries’ catches during the high-water season.

Shield-head Catfish
One of the most common squeaker catfishes, recognized by its bony head shield. It’s an omnivore and often travels in groups. An important food fish, often dried or smoked for preservation.

Gambi Squeaker
This squeaker catfish is identified by its spotted pattern and forked tail. It’s a bottom-dweller, feeding on insects and detritus. It is commonly caught and consumed by local communities.

Niger Squeaker
Named for its long, pointed snout, this Synodontis is adapted for foraging in crevices. It’s a nocturnal bottom-feeder and, like other squeakers, can make audible grunting sounds when distressed.

Cornish Jack
A very large, eel-like elephantfish that is a nocturnal predator of other fish. It uses its weak electric sense to hunt in the dark and is one of the largest species in the Mormyridae family.
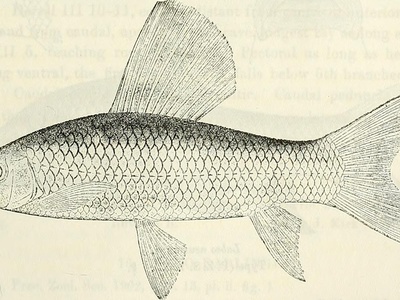
Niger Labeo
This robust cyprinid is an important herbivore, grazing on algae and biofilm from submerged surfaces. It undertakes significant migrations for spawning and is a valued commercial fish.

Adanson’s Labeo
A smaller Labeo species, this fish prefers faster-flowing waters in the upper parts of river systems. It is an important herbivore in these habitats, though less commercially significant than its larger relatives.

African Pike-characin
A smaller relative of the Kafue Pike, this ambush predator also lurks in vegetation to catch small fish and insects. It’s an important predator in smaller aquatic systems where larger fish are absent.

Volta Eutropius
Another commercially important “butterfish” alongside S. intermedius. This schooling predator feeds on small fish and insects. It is highly valued and often caught in large quantities for local consumption.

Kissi Chiselmouth
Adapted to life in rapids, this cyprinid has a sharp, cartilaginous lower jaw for scraping algae from rocks. It’s a specialized grazer, important for the ecology of upland streams.

Senegal Trout-barb
A slender, predatory cyprinid that behaves like a small trout, actively hunting insects at the surface. Its streamlined body and active nature make it a dynamic component of river ecosystems.

Short-headed Citharinus
Similar to the Moonfish but with a slightly different body shape. This species is also a detritivore, playing a crucial role in nutrient cycling by feeding on organic matter at the bottom of floodplains.

Dwarf Stonebasher
A tiny elephantfish that hides among plants and leaf litter. It uses its electric sense to find minuscule insect larvae. Though small, it is abundant and a food source for many predators.

African Banded Barb
A small, attractively striped barb that lives in schools. It is an omnivore, feeding on tiny invertebrates and plant matter, and serves as an important prey item for larger fish and birds.

Banded Jewel Cichlid
Smaller and more common than its larger cousin, this jewel cichlid is known for its brilliant red coloration and parental care. It’s not a food fish but is a feisty and beautiful part of the river fauna.

Kribensis
A popular aquarium fish, the Kribi is a dwarf cichlid known for its vibrant colors and cave-spawning behavior. In the wild, it is a shy but fascinating fish, important to its specific habitat’s biodiversity.

West African Killi
A colorful annual killifish whose eggs can survive the dry season buried in mud, hatching when the rains return. This adaptation to ephemeral habitats makes it a remarkable example of survival.

Ocellated Synodontis
Distinguished by large, dark spots ringed with a lighter color, resembling eyes (ocelli). This attractive pattern makes it stand out among squeaker catfishes. It is both an ornamental and food fish.

Upside-down Catfish
Famous for its habit of swimming and resting upside-down, this small catfish is adapted to feed from the water’s surface or the underside of leaves. Its unique behavior is a fascinating natural wonder.

Volta Labeo
A medium-sized cyprinid that is an important part of the river’s fish community. It feeds on algae and detritus and undertakes spawning migrations, contributing to local fisheries.

Threespot Barb
A small barb identified by three distinct dark spots along its side. It is a common, schooling species that plays a fundamental role in the food chain of smaller water bodies.

Niger Fin-eater
A specialized predator with a sinister name, this fish is a lepidophage, meaning it feeds on the scales and fins of other fishes. This rare feeding strategy makes it an unusual and interesting species.

Four-banded Tilapia
Originally from coastal rivers, this tilapia is recognized by its distinct vertical bands. It is a hardy and adaptable species, sometimes used to supplement fishery stocks in man-made lakes.

Elongate Glass Catfish
A small, translucent, herring-like fish that forms large schools in open water. It is a crucial forage fish, providing a primary food source for larger predators like Nile Perch and Tigerfish.

Volta Glass Catfish
A small, almost transparent catfish that lives in schools. It’s a key part of the pelagic food web, feeding on plankton and tiny insects, and in turn being eaten by larger predatory fish.

Big-mouth Sleeper
A goby-like fish with a large mouth, it is a sedentary ambush predator. It rests on the bottom, camouflaged, waiting for small fish or invertebrates to pass by, representing a unique predatory style.

Striped Fin-eater
Another specialist scale-eater, this fish has a slender body with four dark stripes. It attacks other fish in quick dashes to scrape off scales, a highly specialized and aggressive feeding behavior.

Niger Thryssa
A tiny, anchovy-like fish that is one of the smallest vertebrates in the ecosystem. It forms dense schools and is a critical food source for many fish, despite its minuscule size.

Clown Barb
A common and active small barb with a distinct dark lateral stripe. It is an omnivore and a prolific breeder, making it an abundant and important part of small stream ecosystems.

Short-bodied Pipefish
A freshwater-adapted pipefish, related to seahorses. The male uniquely carries the eggs in a brood pouch on his underside until they hatch. A fascinating example of male parental care.

Four-barbel Catfish
A small, flattened catfish adapted to cling to rocks in strong currents. Its body shape helps it resist being washed away while it forages for aquatic insect larvae in turbulent water.

Short-nosed Lyretail
A beautiful killifish with two prominent horizontal stripes and often colorful fins. It inhabits specific, often challenging environments and is popular among aquarium enthusiasts for its beauty.

Red-spotted Killi
A colorful killifish with bright red spots, adapted to habitats that dry up annually. Its drought-resistant eggs ensure the survival of the species, making it a specialist of ephemeral waters.

Niger Distichodus
This herbivorous fish has a distinctively shaped head and feeds on aquatic plants. It’s an important food fish that helps control plant growth in the river system.

Blunt-toothed Pellonula
A predatory, herring-like fish with strong teeth, unusual for its family. It forms schools and preys on other small pelagic fish, occupying a higher trophic level than its relatives.

Slender Lungfish
A more eel-like lungfish than its cousin, it is also capable of breathing air. Its presence indicates ancient river connections and habitats with low oxygen levels.

Horseface Mormyrid
This bizarre elephantfish has a very long, curved snout resembling a trunk, which it uses to probe for insects in crevices among rocks. Its unique appearance is a remarkable adaptation.

Saddle Bichir
One of the largest bichir species, identified by its prominent dorsal finlets and banded pattern. A nocturnal predator of fish and invertebrates, it is a true living fossil.

Shortfin Barb
A small, silvery barb common in the upper and middle reaches of river systems. It is an important part of the local food web, linking primary production to larger predatory fish.

Long-finned Barb
This barb is named for the elongated dorsal fin ray often seen in breeding males. It is a common species in many river systems, feeding on small insects and algae.

West African Glass Catfish
A predatory catfish that is more active and pelagic than many other catfish species. It is an important commercial species, often caught alongside other Schilbe species.

Ornate Bichir
Considered one of the most attractive bichirs, with a striking pattern of black and yellow markings. This bottom-dwelling predator is a rare and fascinating component of the aquatic fauna.

Volta Scraper
This fish uses a sucker-like mouth to attach to rocks in fast currents and scrape off algae. It is highly adapted to living in rapids, a niche that few other fish can occupy.

Niger Scraper
Similar to its Volta cousin, this species is a specialized algae-eater adapted to turbulent water. Its presence indicates a healthy, fast-flowing river habitat with rocky substrates.

Ropefish
A truly unique, snake-like fish related to bichirs. It has no pelvic fins and can breathe air. It is a nocturnal predator that uses its excellent sense of smell to find worms and crustaceans.

Striped Anostomid
A small, head-standing characin that often swims with its head pointing downwards. This posture is used for picking small invertebrates from the substrate. It is a unique and specialized forager.

False Nile Catfish
Resembling a Bagrus catfish, this large predator has a broad head and well-developed adipose fin. It is a commercially valuable species, often caught by fishers targeting large catfish.

Big-eye Labeo
Characterized by its relatively large eyes, this cyprinid feeds on algae and detritus. It is a moderately common species that contributes to local fisheries and ecosystem health.

Bar-tailed Citharine
A large, deep-bodied fish similar to Citharinus but with a different fin structure. It is a detritivore that plays a vital role in processing organic matter on the river bottom.

Volta Upside-down Catfish
This squeaker is distinguished by its high, sail-like dorsal fin. Like its relatives, it is a hardy bottom-dweller, feeding on a wide variety of foods from insects to algae.

African Spiny Eel
Despite its name, it’s not a true eel. This elongated fish has a series of sharp dorsal spines and a fleshy snout. It is a nocturnal hunter of worms and insect larvae.

Dwarf Mouthbrooder
A small but colorful cichlid where the female broods the eggs in her mouth. Its small size and beautiful colors make it a favorite for aquarists, but it is a wild native of quiet waters.

Niger Jellybean Catfish
A small, slender catfish with a translucent body, adapted for burrowing in sand. Its specialized lifestyle makes it a rarely seen but interesting part of the river’s biodiversity.

Straight-mouthed Citharinus
This very large herbivore/detritivore is distinguished from other citharinids by its mouth structure. It is a highly prized food fish due to its massive size and palatable flesh.

Red-eyed Labeo
This species has been introduced in some areas for fisheries. It is a large cyprinid that feeds on algae and detritus and can adapt to various lacustrine environments.

Fork-tailed Labeo
A medium-sized Labeo species that is an important grazer in its habitat. It is part of the diverse cyprinid community that forms the basis of many riverine food webs.

Fin-backed Catfish
Similar to the Giraffe Catfish but with a higher dorsal fin. It is also a valued food fish, known for its good taste, and is caught using lines and nets by local fishermen.

Slendertail Mormyrid
An elephantfish with a slender, elongated snout. It uses this tool to probe for food in soft substrates. Its presence indicates a healthy river bottom environment.

Volta Stonebasher
A small mormyrid that is common in swamps and floodplains. It is an important link in the food chain, consuming small invertebrates and being preyed upon by larger fish.

Niger Long-snout
A predatory mormyrid with a distinctively long snout. It is a powerful hunter of small fish, using its electric sense to detect them in dark or murky water.

Niger Striped Barb
A small, schooling barb with a prominent horizontal stripe. It is an active forager, feeding on insects, algae, and detritus, and is common in its native habitat.

Silver Robber
A small, predatory tetra that often nips the fins of other fish. Its aggressive behavior and iridescent scales make it a striking inhabitant of clear forest streams.

Long-nosed Distichodus
A smaller Distichodus species that feeds on plants, insects, and small crustaceans. It is an important omnivore in floodplain habitats, contributing to ecosystem balance.

West African Ctenopoma
A labyrinth fish, able to breathe atmospheric air with a special organ. This allows it to thrive in oxygen-poor waters where other fish cannot survive. It is a hardy ambush predator.

Big-eyed Barb
This barb is named for its large eyes, an adaptation for feeding in low light. It is a widespread and common species, forming an important part of the fish biomass in many streams.

Niger Halfbeak
A surface-dwelling fish with a distinctive elongated lower jaw. It feeds on insects and small organisms from the water’s surface, perfectly adapted to its narrow ecological niche.





