Algeria, with its diverse landscapes stretching from the Mediterranean coast to the Sahara, boasts a unique array of flora and fauna. However, like many regions globally, its delicate ecosystems face increasing pressure from species introduced from elsewhere, often with detrimental consequences for native biodiversity and local economies.
To shed light on this critical environmental challenge, this resource presents a focused overview. There are exactly 15 Invasive Species in Algeria detailed here, showcasing a broad spectrum from the widespread Asian tiger mosquito to the aggressively colonizing Water hyacinth. For each entry, you’ll find below essential data organized by Scientific Name, Native Region, and Primary Impact.
What is considered an invasive species in Algeria?
An invasive species in Algeria, like anywhere else, is a non-native organism that is introduced to a new environment and causes significant ecological, economic, or human health harm. These species outcompete native plants and animals for resources, disrupt local food webs, and can lead to biodiversity loss if left unchecked.
Why are these invasive species a concern for Algeria’s environment?
The presence of invasive species poses a serious threat to Algeria’s natural heritage. They can degrade habitats, alter natural processes like water flow and nutrient cycling, and reduce the populations of indigenous species, some of which may be endemic to the region. This loss of biodiversity can destabilize entire ecosystems and impact agriculture and fisheries.
Invasive Species in Algeria
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Native Region | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prosopis | Prosopis juliflora | Central and South America | Ecological and economic |
| Prickly pear | Opuntia ficus-indica | Mexico | Ecological and land-use |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Amazon basin, South America | Ecological and economic |
| Mosquitofish | Gambusia holbrooki | Eastern North America | Ecological |
| Red swamp crayfish | Procambarus clarkii | Southern USA and Mexico | Ecological and agricultural |
| Asian tiger mosquito | Aedes albopictus | Southeast Asia | Human health |
| Red palm weevil | Rhynchophorus ferrugineus | Southeast Asia | Economic and ecological |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | South Asia | Economic and human health |
| Brown rat | Rattus norvegicus | Northern China | Economic and human health |
| Nutria | Myocastor coypus | South America | Ecological and economic |
| Nile tilapia | Oreochromis niloticus | Nile basin and East Africa | Ecological and economic |
| Red-eared slider | Trachemys scripta elegans | Central North America | Ecological |
| Australian acacia | Acacia saligna | Southwest Australia | Ecological |
| Blue gum eucalyptus | Eucalyptus globulus | Australia | Ecological and water-resource impacts |
| Silverleaf nightshade | Solanum elaeagnifolium | North and South America | Agricultural and ecological |
Images and Descriptions

Prosopis
Hardy thorny tree introduced for grazing and dune stabilization that forms dense stands across southern Algeria and oases, displacing native plants, reducing pasture for livestock and clogging water points

Prickly pear
Introduced for fruit and hedges, this cactus has become a widespread invasive in Algeria, forming impenetrable thickets that reduce biodiversity, hinder grazing and make land reclamation costly

Water hyacinth
Fast-growing floating plant that clogs Algerian rivers, reservoirs and irrigation canals, reducing oxygen for fish, blocking water flow and increasing maintenance costs

Mosquitofish
Introduced to control mosquitoes, now widespread in Algerian ponds and wetlands where it preys on native fish and amphibians and alters aquatic food webs

Red swamp crayfish
Aggressive freshwater crayfish recorded in Algerian waterways; burrowing damages irrigation banks, it competes with native aquatic species and can impact rice and vegetable crops
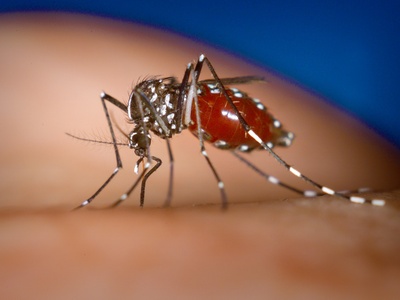
Asian tiger mosquito
Established in northern Algeria, this daytime-biting mosquito increases risk of dengue and chikungunya transmission and causes major nuisance in urban and peri-urban areas

Red palm weevil
Serious pest of date palms across Algeria; larvae bore into trunks and crowns, killing trees that are economically and culturally important and forcing costly control measures

Black rat
Widespread commensal rodent in Algerian towns and farms that damages crops and stored food, spreads disease and preys on native birds and small vertebrates

Brown rat
Common in urban Algeria; contaminates food supplies, damages infrastructure and poses public-health risks through pathogen transmission

Nutria
Semi-aquatic rodent recorded in some Algerian wetlands that feeds on bank vegetation, causing erosion, degrading wetland habitat and damaging crops and irrigation structures

Nile tilapia
Introduced for aquaculture and stocked in Algerian reservoirs; can outcompete native fish, alter aquatic ecosystems and affect small-scale fisheries

Red-eared slider
Released pet turtle now found in Algerian urban ponds and waterways; competes with native turtles, can spread parasites and alters local aquatic communities

Australian acacia
Planted for stabilization and forestry, it has naturalized in parts of Algeria where dense stands outcompete native shrubs, change soil nitrogen levels and increase fire risk

Blue gum eucalyptus
Widely planted in Algeria for wood and erosion control; where it naturalizes it can lower groundwater levels, alter soils and reduce native plant diversity

Silverleaf nightshade
Deep-rooted perennial weed invading Algerian croplands and rangelands, reducing yields, poisoning livestock and requiring expensive control measures





