Belize’s coastlines, cayes and inland forests host rich biodiversity but are increasingly vulnerable to non-native plants and animals that can alter habitats and damage livelihoods. Understanding which species are present helps land managers, boaters, fishers and residents spot problems early and reduce spread.
There are 13 Invasive Species in Belize, ranging from Australian pine to Yellow fever mosquito. For each entry, information is organized with Scientific name,Status in Belize,Distribution and habitat (Belize) so you can quickly see where a species occurs and how established it is — you’ll find below.
How do I report a sighting of an invasive species in Belize?
Take clear photos, note the exact location (GPS if possible), date and any nearby habitat, and contact Belize’s relevant authorities or local conservation NGOs—such as the Forestry Department, Fisheries, or the Belize Audubon Society—or submit records to community science platforms; avoid moving or handling unknown organisms yourself.
Which of these invasive species pose the biggest local threats?
Risk depends on species and place: some plants like Australian pine outcompete native vegetation and alter shorelines, while species like the Yellow fever mosquito are public‑health concerns; check the Status in Belize and Distribution and habitat (Belize) columns below to prioritize monitoring and response.
Invasive Species in Belize
| Name | Scientific name | Status in Belize | Distribution and habitat (Belize) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lionfish | Pterois volitans / Pterois miles complex | Established, invasive | Caribbean coast, coral reefs, mangroves |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Established, invasive | Rivers, lagoons, inland wetlands, slow-moving freshwater |
| Water lettuce | Pistia stratiotes | Established, invasive | Freshwater ponds, lagoons, slow rivers and wetlands |
| Giant Salvinia | Salvinia molesta | Established, invasive | Ponds, canals and slow freshwater margins |
| Nile tilapia | Oreochromis niloticus | Established, invasive | Rivers, reservoirs, aquaculture ponds |
| Mozambique tilapia | Oreochromis mossambicus | Established, invasive | Brackish lagoons, rivers, ponds and disturbed freshwater |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | Established, invasive | Islands, coastal settlements, farms and forests |
| Brown rat | Rattus norvegicus | Established, invasive | Ports, urban areas, farms and storage sites |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Established, invasive | Buildings, granaries, farms and disturbed sites |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | Established, invasive | Urban edges, islands, farms, forests near settlements |
| Australian pine | Casuarina equisetifolia | Established, invasive | Coastal cayes, beaches, coastal scrub and dunes |
| Brazilian pepper | Schinus terebinthifolius | Established, invasive | Coastal scrub, wetlands and disturbed inland sites |
| Yellow fever mosquito | Aedes aegypti | Established, invasive (public health pest) | Urban and peri‑urban domestic habitats, water containers |
Images and Descriptions

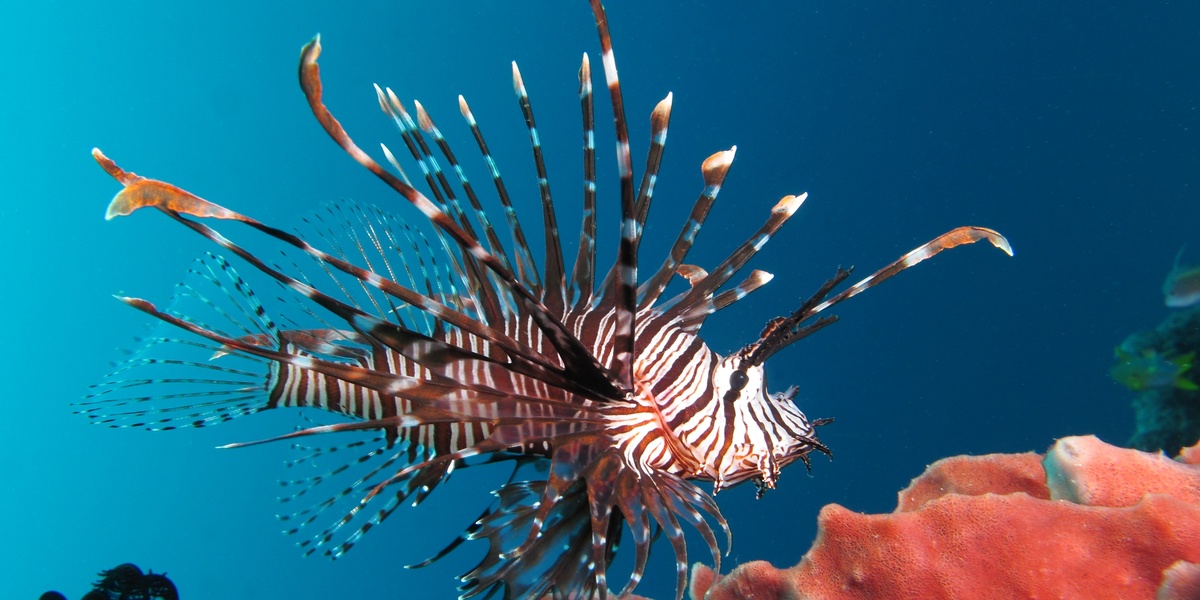
Lionfish
Indo‑Pacific predatory fish introduced via aquarium releases/larval spread; voraciously eats juvenile reef fish and reduces reef resilience and fisheries. Managed by targeted removals, spearfish derbies and market use; report sightings to Belize Fisheries Department or local NGOs.

Water hyacinth
Floating plant from South America that forms dense mats, blocks waterways, lowers oxygen and harms native aquatic life. Spread by fragments and boats after ornamental escapes; controlled by mechanical/manual removal and local cleanup; report large infestations to Forestry or Fisheries.

Water lettuce
Free‑floating aquatic plant from South America that forms thick mats, shading and deoxygenating waterways and hindering navigation. Often arrived via ornamental trade; managed by manual removal and regular monitoring; report to Forestry Department or local conservation groups.

Giant Salvinia
Highly invasive floating fern from South America that rapidly blankets water surfaces, smothering native plants and reducing oxygen. Usually spread via aquarium/boat movement; control via removal and in some areas biological control; notify Forest Department on detection.

Nile tilapia
African cichlid introduced for aquaculture and fisheries; competes with and can hybridize with native fishes, alters habitats after escapes. Arrived via stocking and farm escapes; management focuses on farm biosecurity, stocking controls and reporting escapes to Fisheries.

Mozambique tilapia
African tilapia used in local aquaculture that becomes feral, outcompeting native fish and altering ecosystems. Spread from fish farms and releases; control through regulation of aquaculture, removal and reporting to Fisheries Department.

Black rat
Commensal rodent arriving historically via ships; predates seabird eggs, damages crops and spreads disease. Managed by trapping, baiting and strict biosecurity on cayes; report colony or seabird declines to Forestry or Belize Audubon Society.

Brown rat
Shipborne rodent that damages stored food, transmits disease and impacts native fauna. Common in ports and towns; controlled by integrated pest management, sanitation and baiting; notify public health or Forestry if infestations affect wildlife or farms.

House mouse
Small commensal rodent introduced with humans; damages stored food and can transmit pathogens, and harms small native fauna on islands. Arrived via shipping and trade; manage with sanitation, traps and exclusion; report to agricultural extension or Forestry.

Feral cat
Domestic cat turned feral; preys on native birds, reptiles (including hatchling turtles) and small mammals, causing biodiversity loss. Spread via feral colonies; recommended control includes trapping/removal in sensitive areas, TNR programs and reporting to Belize Audubon Society or Forest Department.

Australian pine
Tree from Australasia planted for windbreaks that forms dense stands on cayes and shores, displacing mangroves and native dunes plants and altering sediments. Spread from plantings and drift; managed by mechanical removal and native replanting; report to Forest Department.

Brazilian pepper
Shrub/tree from South America that forms impenetrable thickets, outcompeting native flora and changing habitats. Introduced as an ornamental; control via mechanical removal and herbicide, plus restoration with natives; report to Forestry or Belize Audubon.
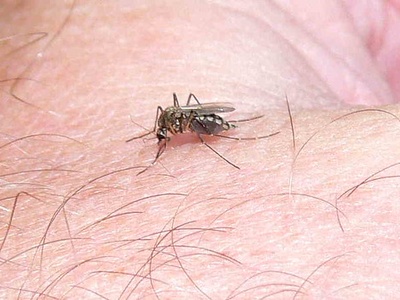
Yellow fever mosquito
Originally African, spread globally via shipping; breeds in artificial containers and transmits dengue, Zika and chikungunya. Managed by household source reduction, municipal control and public‑health surveillance; report outbreaks to Belize Ministry of Health and local vector control teams.





