Japan’s islands host a wide mix of climates and habitats, from subarctic forests to subtropical coasts, which makes the country both biodiverse and vulnerable to outsiders that arrive by ship, trade or accidental transport. Understanding which non-native organisms have become established is important for gardeners, fishers, park managers and anyone who enjoys Japan’s natural spaces.
There are 95 Invasive Species in Japan, ranging from (Correction for above: Emerald Ash Borer) to Zebra Mussel. For each entry you’ll find below the Scientific name, Taxon, Native range so you can quickly scan origins and organism type before diving into details you’ll find below.
How were the species chosen for this list?
The list compiles species recorded as established or repeatedly observed in Japan from government and scientific sources, prioritizing organisms with documented ecological, economic or human-health impacts; entries were included when there was verifiable evidence of presence and impact rather than single accidental detections.
What should I do if I find one of these invasive species in the wild?
Take photos, note the exact location and habitat, avoid moving the organism or material that might spread it, and report the sighting to local authorities or the prefectural environmental office (and national reporting channels where available) so professionals can confirm the ID and advise containment steps.
Invasive Species in Japan
| Name | Scientific name | Taxon | Native range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raccoon | Procyon lotor | Mammal | North America |
| Largemouth Bass | Micropterus salmoides | Freshwater Fish | North America |
| American Bullfrog | Lithobates catesbeianus | Amphibian | Eastern North America |
| Red-eared Slider | Trachemys scripta elegans | Reptile (Turtle) | Southern United States |
| Javan Mongoose | Herpestes javanicus | Mammal | Southeast Asia, Middle East |
| Bluegill | Lepomis macrochirus | Freshwater Fish | North America |
| Nutria | Myocastor coypus | Mammal (Rodent) | South America |
| Canada Goldenrod | Solidago canadensis | Plant | North America |
| Argentine Ant | Linepithema humile | Insect (Ant) | South America |
| Red Swamp Crayfish | Procambarus clarkii | Crustacean | Southeastern United States |
| Masked Palm Civet | Paguma larvata | Mammal | Southeast Asia, China |
| Snapping Turtle | Chelydra serpentina | Reptile (Turtle) | North America |
| Tall Goldenrod | Solidago altissima | Plant | North America |
| Water Hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Aquatic Plant | Amazon Basin, South America |
| Bur-cucumber | Sicyos angulatus | Plant (Vine) | North America |
| Common Ragweed | Ambrosia artemisiifolia | Plant | North America |
| Signal Crayfish | Pacifastacus leniusculus | Crustacean | Western North America |
| Alligator Weed | Alternanthera philoxeroides | Aquatic Plant | South America |
| Channel Catfish | Ictalurus punctatus | Freshwater Fish | North America |
| Rose-ringed Parakeet | Psittacula krameri | Bird | Africa, South Asia |
| Common Myna | Acridotheres tristis | Bird | South Asia |
| Bermuda Grass | Cynodon dactylon | Plant (Grass) | Africa, Asia, Australia |
| Hairy Fleabane | Conyza bonariensis | Plant | South America |
| Redback Spider | Latrodectus hasselti | Insect (Arachnid) | Australia |
| Western Mosquitofish | Gambusia affinis | Freshwater Fish | Southeastern United States |
| Japanese White-eye | Zosterops japonicus | Bird | East Asia (subspecies vary) |
| Feral Goat | Capra hircus | Mammal | Domesticated origin (West Asia) |
| Feral Cat | Felis catus | Mammal | Domesticated origin |
| Green Anole | Anolis carolinensis | Reptile (Lizard) | Southeastern United States |
| Guppy | Poecilia reticulata | Freshwater Fish | South America, Caribbean |
| Red Imported Fire Ant | Solenopsis invicta | Insect (Ant) | South America |
| Brown Trout | Salmo trutta | Freshwater Fish | Europe, Western Asia |
| Rainbow Trout | Oncorhynchus mykiss | Freshwater Fish | North America (Pacific coast) |
| Common Carp | Cyprinus carpio | Freshwater Fish | Eurasia (introduced strains) |
| Muskrat | Ondatra zibethicus | Mammal (Rodent) | North America |
| Italian Ryegrass | Lolium multiflorum | Plant (Grass) | Europe, SW Asia, NW Africa |
| Black Locust | Robinia pseudoacacia | Plant (Tree) | Southeastern United States |
| Smooth Cordgrass | Spartina alterniflora | Plant (Grass) | Atlantic coast of Americas |
| Ruddy Duck | Oxyura jamaicensis | Bird | The Americas |
| Knotweed (Japanese) | Fallopia japonica | Plant | East Asia |
| Green Iguana | Iguana iguana | Reptile (Lizard) | Central and South America |
| Wild Boar (non-native genotypes) | Sus scrofa | Mammal | Eurasia |
| Alexandrine Parakeet | Psittacula eupatria | Bird | South and Southeast Asia |
| Zebra Mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | Mollusc (Bivalve) | Southeastern Russia |
| Golden Mussel | Limnoperna fortunei | Mollusc (Bivalve) | China, Southeast Asia |
| Pine Wood Nematode | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | Pathogen (Nematode) | North America |
| Potato Cyst Nematode | Globodera rostochiensis | Pathogen (Nematode) | Andes |
| Chytrid Fungus | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Pathogen (Fungus) | Likely East Asia (invasive strains) |
| White-nose Syndrome Fungus | Pseudogymnoascus destructans | Pathogen (Fungus) | Europe |
| Cane Toad | Rhinella marina | Amphibian | Central and South America |
| Bumblebee (Buff-tailed) | Bombus terrestris | Insect (Bee) | Europe |
| Cabbage White Butterfly | Pieris rapae | Insect (Butterfly) | Europe, North Africa, Asia |
| Four-spined Jewel Beetle | Agrilus planipennis | Insect (Beetle) | East Asia (invasive in N. America) |
| (Correction for above: Emerald Ash Borer) | Agrilus planipennis | Insect (Beetle) | East Asia |
| (Entry Correction/Replacement: A more suitable insect) Fall Armyworm | Spodoptera frugiperda | Insect (Moth) | The Americas |
| Giant African Snail | Lissachatina fulica | Mollusc (Snail) | East Africa |
| New Zealand Flatworm | Arthurdendyus triangulatus | Flatworm | New Zealand |
| Sweet Tanglehead | Heteropogon contortus | Plant (Grass) | Tropics/Subtropics (invasive strains) |
| Common Milkweed | Asclepias syriaca | Plant | North America |
| Parthenium Weed | Parthenium hysterophorus | Plant | Tropical America |
| Lantana | Lantana camara | Plant (Shrub) | Tropical Americas |
| Leucaena | Leucaena leucocephala | Plant (Tree/Shrub) | Mexico, Central America |
| Miconia | Miconia calvescens | Plant (Tree) | Central and South America |
| Kahili Ginger | Hedychium gardnerianum | Plant | Himalayas |
| Ice Plant | Carpobrotus edulis | Plant (Succulent) | South Africa |
| Pampas Grass | Cortaderia selloana | Plant (Grass) | South America |
| Butterfly Bush | Buddleja davidii | Plant (Shrub) | China |
| Sycamore Maple | Acer pseudoplatanus | Plant (Tree) | Europe, Western Asia |
| Yellow Perch | Perca flavescens | Freshwater Fish | North America |
| Cuban Treefrog | Osteopilus septentrionalis | Amphibian | Caribbean |
| Brown Anole | Anolis sagrei | Reptile (Lizard) | Cuba, The Bahamas |
| Common Wall Lizard | Podarcis muralis | Reptile (Lizard) | Europe |
| Sika Deer | Cervus nippon | Mammal | East Asia |
| Silver Carp | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | Freshwater Fish | East Asia (China/Siberia) |
| Bighead Carp | Hypophthalmichthys nobilis | Freshwater Fish | East Asia (China) |
| Grass Carp | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Freshwater Fish | East Asia (China/Siberia) |
| Common Sunfish (Pumpkinseed) | Lepomis gibbosus | Freshwater Fish | North America |
| Fat Mucket | Lampsilis siliquoidea | Mollusc (Bivalve) | North America |
| Chinese Mitten Crab | Eriocheir sinensis | Crustacean | East Asia (China/Korea) |
| Northern Snakehead | Channa argus | Freshwater Fish | East Asia (China, Russia, Korea) |
| Veined Rapa Whelk | Rapana venosa | Mollusc (Snail) | Sea of Japan, Yellow Sea |
| Didemnum vexillum (Sea Squirt) | Didemnum vexillum | Tunicate (Sea Squirt) | Uncertain, possibly Japan |
| Harlequin Ladybeetle | Harmonia axyridis | Insect (Beetle) | East Asia |
| (Entry Correction/Replacement: Better example) Azolla (Water Fern) | Azolla filiculoides | Aquatic Plant | The Americas |
| Parrot’s Feather | Myriophyllum aquaticum | Aquatic Plant | Amazon River |
| Asiatic Dayflower | Commelina communis | Plant | East Asia |
| Yellow Flag Iris | Iris pseudacorus | Plant | Europe, Western Asia, NW Africa |
| Purple Loosestrife | Lythrum salicaria | Plant | Eurasia |
| Mile-a-minute Weed | Persicaria perfoliata | Plant (Vine) | East Asia |
| Garlic Mustard | Alliaria petiolata | Plant | Europe, Asia |
| Tomato Leafminer | Tuta absoluta | Insect (Moth) | South America |
| Western Flower Thrips | Frankliniella occidentalis | Insect (Thrips) | North America |
| Silverleaf Whitefly | Bemisia tabaci | Insect (Whitefly) | Uncertain (likely Africa/Asia) |
| Spotted Lanternfly | Lycorma delicatula | Insect (Planthopper) | China, Vietnam |
| Coqui Frog | Eleutherodactylus coqui | Amphibian | Puerto Rico |
Images and Descriptions

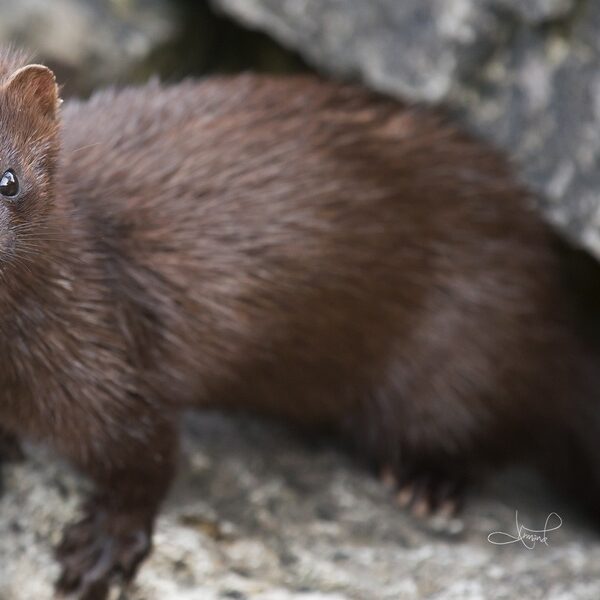
Raccoon
Widespread across Japan from pet releases. Damages crops, homes, and cultural sites while preying on native amphibians and birds. Designated as a top-priority Invasive Alien Species (IAS) for control.

Largemouth Bass
Found in lakes and rivers nationwide due to illegal stocking for sport fishing. A voracious predator, it has decimated native fish populations like ayu and crucian carp. Designated as an IAS.

American Bullfrog
Introduced for food, now common in wetlands across Japan. It preys on native insects, fish, and even other frogs, disrupting local food webs. It also carries the deadly chytrid fungus.

Red-eared Slider
Extremely common in ponds and rivers nationwide from pet releases. It outcompetes native turtle species like the Japanese pond turtle for food and basking sites. Designated as a Conditionally Specified Alien Species.

Javan Mongoose
Introduced to Okinawa and Amami Islands to control snakes. Instead, it preyed on endangered native species like the Amami rabbit and Okinawa rail, causing severe ecological damage. Subject to intensive eradication programs.

Bluegill
Introduced alongside largemouth bass, now found in many lakes and ponds. It aggressively preys on the eggs and fry of native fish, significantly impacting their populations. Designated as an IAS.

Nutria
Originally imported for fur, escaped individuals established populations mainly in western Japan. Their burrowing damages riverbanks and irrigation systems, and they destroy aquatic vegetation and rice paddies. Designated as an IAS.

Canada Goldenrod
Introduced as an ornamental flower, it now dominates riverbanks, roadsides, and abandoned fields across Japan. It forms dense monocultures that crowd out native plants and reduce biodiversity.

Argentine Ant
Forms massive “supercolonies” in urban and disturbed areas, displacing nearly all native ant species. They invade homes, protect agricultural pests like aphids, and can harm ground-nesting birds.

Red Swamp Crayfish
Originally introduced as food for bullfrogs, now ubiquitous in rice paddies and slow-moving water. It destroys aquatic plants, preys on small fish, and its burrowing can damage irrigation levees.

Masked Palm Civet
Established populations from escaped or released animals, particularly in central and western Japan. They raid fruit farms, damage homes by nesting in attics, and may compete with native mammals.

Snapping Turtle
Established in various regions, especially around the Tokyo area, from pet releases. As a large, aggressive predator, it consumes native fish, birds, and other turtles, posing a threat to both ecosystems and public safety.

Tall Goldenrod
Similar to Canada Goldenrod, this species forms dense, aggressive stands in open habitats throughout Japan. It outcompetes native flora and is a major pollen source, contributing to autumn hay fever.

Water Hyacinth
A free-floating plant that forms dense mats on ponds and slow rivers, blocking sunlight, killing submerged native plants, and depleting oxygen. It also clogs waterways and irrigation infrastructure.

Bur-cucumber
An aggressive annual vine found along riverbanks and disturbed lands across Japan. It grows rapidly, smothering native trees and shrubs under a thick blanket, blocking sunlight and killing the underlying vegetation.

Common Ragweed
A widespread weed of roadsides, fields, and urban areas. It aggressively colonizes disturbed ground, outcompeting native pioneer species. It is also a primary cause of autumn hay fever for millions of people.

Signal Crayfish
Introduced for aquaculture, it has established populations in cool lakes and streams, including Lake Mashu in Hokkaido. It outcompetes the native Japanese crayfish and carries the crayfish plague fungus.

Alligator Weed
An invasive aquatic and terrestrial plant found in southern Japan. It forms dense mats that clog waterways, shade out native plants, and interfere with rice cultivation and flood control.

Channel Catfish
Established in rivers like the Tone River system near Tokyo. This large predatory fish consumes a wide variety of native fish and invertebrates, altering the local aquatic ecosystem.

Rose-ringed Parakeet
Escaped pets have formed breeding populations in urban areas like Tokyo. They can damage crops, compete with native birds for nesting cavities, and create noise disturbances.

Common Myna
Introduced to several regions, with established populations in and around cities. They are aggressive competitors that can displace native bird species from nesting sites and food sources.

Bermuda Grass
While native to parts of Asia, aggressive cultivars from elsewhere are invasive in Japan. It forms a dense turf on riverbanks and fields, crowding out native grasses and other low-growing plants.

Hairy Fleabane
A common weed in urban areas, agricultural fields, and roadsides throughout Japan. It is highly adaptable and has developed resistance to herbicides, making it difficult to control and displacing native vegetation.

Redback Spider
Accidentally introduced, now established in areas like Osaka and Fukuoka. Its venomous bite poses a public health risk. Found in urban environments, hiding in drains, outdoor furniture, and parks.

Western Mosquitofish
Introduced for mosquito control, but found to be a highly aggressive predator of the eggs and larvae of native fish and amphibians, with little impact on mosquito populations. Widespread in shallow waters.

Japanese White-eye
While native to mainland Japan, the subspecies *Z. j. alani* was introduced to the Ogasawara Islands, where it hybridizes with the endemic Bonin White-eye, threatening it with genetic extinction.

Feral Goat
Introduced populations on remote islands, like the Ogasawara and Uji Islands, cause severe overgrazing. They destroy native vegetation, trigger soil erosion, and threaten entire island ecosystems.

Feral Cat
Found throughout Japan, especially on islands. They are highly effective predators of native birds, small mammals, and reptiles, posing a severe threat to endangered island species like the Iriomote cat (through disease/competition).

Green Anole
Introduced to the Ogasawara Islands and Okinawa. This lizard preys heavily on native insects, including important pollinators, causing a cascade effect that disrupts the entire island ecosystem.

Guppy
Released from aquariums, now found in warm springs and thermally polluted waters across Japan. They compete with and prey upon native medaka (rice fish) and other small aquatic life.

Red Imported Fire Ant
Detected in ports and surrounding areas. Known for its painful sting and aggressive swarming behavior, it poses a threat to public health, agriculture, and native biodiversity by outcompeting local insects.

Brown Trout
Introduced for sport fishing, now established in cold-water rivers and lakes, particularly in Hokkaido. It preys on and competes with native salmonids like the Dolly Varden char.

Rainbow Trout
Widely stocked for fishing and aquaculture, with self-sustaining populations in many rivers. They compete with and prey on native trout and chars, and can hybridize with native salmonids.

Common Carp
While present for centuries, aggressive European strains are invasive. Their bottom-feeding behavior stirs up sediment, destroying aquatic vegetation and degrading water quality for native species.

Muskrat
Established populations, particularly in the Kanto region, after escaping from fur farms. Their burrowing activity damages riverbanks and agricultural dikes, and they consume large amounts of aquatic vegetation.

Italian Ryegrass
Widely planted for forage and erosion control, it has escaped and become a common weed in fields and roadsides. It outcompetes native grasses and can be an agricultural pest.

Black Locust
Planted for erosion control and honey production, now naturalized along riverbanks and in disturbed forests. It fixes nitrogen, altering soil chemistry, and its dense stands shade out native plants.

Smooth Cordgrass
Introduced for erosion control in tidal flats. It grows into dense meadows that transform mudflat ecosystems, destroying vital feeding grounds for shorebirds and habitats for native benthic organisms.

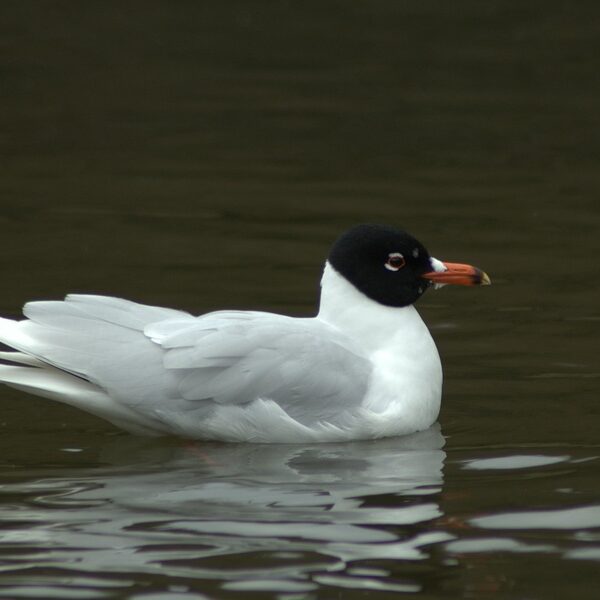
Ruddy Duck
Escaped from captivity, with occasional sightings. It poses a major threat through hybridization with the globally endangered White-headed Duck, whose range it is expanding towards in Eurasia.

Knotweed (Japanese)
While native to Japan, aggressive clones have been reintroduced and behave invasively, particularly in urban and disturbed areas. It forms dense thickets that exclude all other vegetation.

Green Iguana
Established on Ishigaki Island from escaped pets. These large lizards consume native vegetation, and their burrowing can damage infrastructure. Eradication efforts are underway.

Wild Boar (non-native genotypes)
While native, boars with European genotypes were introduced for hunting. They hybridize with native populations, altering genetics, and are major agricultural pests, also damaging forest undergrowth.

Alexandrine Parakeet
Like the Rose-ringed Parakeet, escaped pets have established small breeding populations in urban parks. They compete with native birds for tree cavities needed for nesting.

Zebra Mussel
While not yet widely established, it is a high-risk species monitored at ports. It clogs water intake pipes, encrusts all hard surfaces, and filters water so heavily it disrupts food webs.

Golden Mussel
A freshwater mussel that poses a similar threat to the zebra mussel. It can clog industrial and power plant water systems and fundamentally alter aquatic ecosystems by filter-feeding.
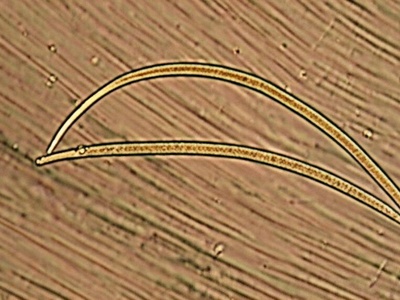
Pine Wood Nematode
The cause of pine wilt disease, which has devastated Japan’s pine forests. The nematode is native to North America and is spread by a native longhorn beetle, making it an invasive pathogen.
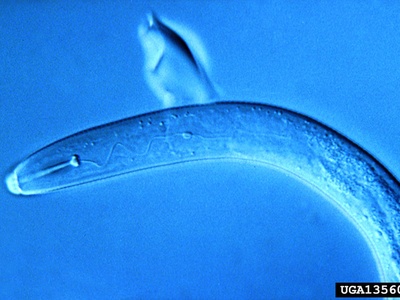
Potato Cyst Nematode
A major agricultural pest that attacks the roots of potatoes and tomatoes, causing significant crop losses. Found in potato-growing regions like Hokkaido, requiring strict quarantine and control measures.
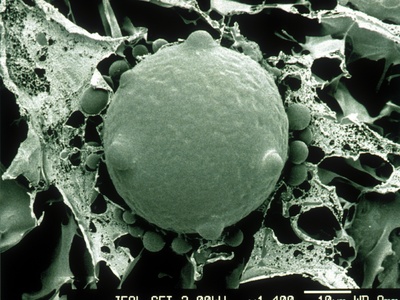
Chytrid Fungus
A pathogenic fungus driving global amphibian declines. While potentially originating in Asia, virulent global strains are invasive threats to Japan’s unique amphibian populations, spread by invasive species like bullfrogs.

White-nose Syndrome Fungus
The fungus that causes a devastating disease in bats. While not yet confirmed to have caused mass mortality in Japan, its presence is a major concern for native bat populations.

Cane Toad
Introduced to some southern islands (e.g., Daito Islands) for pest control. It failed to control pests but became a toxic threat to native predators that try to eat it.

Bumblebee (Buff-tailed)
Imported commercially for crop pollination, escaped queens have established wild populations, especially in Hokkaido. They compete with native bumblebees and may spread diseases to native pollinators.

Cabbage White Butterfly
An agricultural pest whose larvae (cabbageworms) feed on cabbage, broccoli, and other cruciferous crops. It is widespread throughout Japan and causes significant economic damage.

Four-spined Jewel Beetle
While native to East Asia, its behavior and impact in new ecosystems define it as invasive. It’s listed here for context, as it’s a major invasive from the region, though not invasive *within* Japan.

(Correction for above: Emerald Ash Borer)
This entry clarifies the above. While native to the region including Japan, its devastating impact in North America makes it a globally recognized invasive. It is not considered invasive within its native Japanese range.

(Entry Correction/Replacement: A more suitable insect) Fall Armyworm
A highly destructive agricultural pest that arrived in Japan in 2019. Its larvae feed on over 350 plant species, including rice, corn, and vegetables, posing a major threat to food security.

Giant African Snail
Introduced to the Ogasawara and Okinawa islands. It is a voracious agricultural and garden pest, consumes native plants, and can carry the rat lungworm parasite, which is harmful to humans.

New Zealand Flatworm
A predatory flatworm that feeds on earthworms. By reducing earthworm populations, it can seriously degrade soil structure and fertility, impacting both agriculture and natural ecosystems.

Sweet Tanglehead
While native to parts of southern Japan, aggressive, non-native strains have been introduced. These can dominate pastures and natural grasslands, reducing forage quality and displacing native species.

Common Milkweed
Introduced as an ornamental, this plant can be invasive in open, disturbed areas. Its milky sap is toxic, and it can form dense colonies that displace native vegetation.

Parthenium Weed
A highly aggressive and allergenic weed found in some parts of Japan. It rapidly colonizes disturbed land, outcompetes crops and native plants, and can cause dermatitis and respiratory problems in humans.

Lantana
A popular ornamental shrub that has escaped into the wild, especially in southern Japan and the Ryukyu Islands. It forms dense, impenetrable thickets that smother native vegetation.

Leucaena
Promoted for forage and firewood, it has become highly invasive on subtropical islands like Okinawa and Ogasawara. It forms dense stands that prevent the regeneration of native forests.
Miconia
Known as the “purple plague” or “green cancer” in other regions. It is a high-alert species for Japan, as it forms dense canopies that shade out and kill all native plants beneath it.

Kahili Ginger
An ornamental plant that has become invasive in forests. It spreads via rhizomes and seeds, forming dense stands on the forest floor that prevent the regeneration of native trees and shrubs.

Ice Plant
Planted for soil stabilization, it has escaped and now blankets coastal dunes and cliffs. It forms a dense mat that displaces native coastal plant communities and alters soil chemistry.

Pampas Grass
A large ornamental grass that produces thousands of wind-dispersed seeds. It invades open, sunny habitats like dunes, grasslands, and wetlands, forming massive tussocks that exclude native species.

Butterfly Bush
A popular garden shrub whose seeds spread into the wild, particularly along riverbanks and railways. It can form dense thickets that outcompete native shrubs and herbaceous plants.

Sycamore Maple
A fast-growing tree that can invade native woodlands. It produces a large number of “helicopter” seeds that disperse widely, and its seedlings can create a dense carpet that shades out native flora.

Yellow Perch
Illegally introduced and found in some lakes. It competes with native species for food and can become overabundant, stunting its own growth and disrupting the lake’s food web.

Cuban Treefrog
Found near US military bases in Okinawa, likely a stowaway in cargo. It is a voracious predator of native frogs and insects and can secrete a skin toxin irritating to humans.

Brown Anole
Another anole species found in Okinawa and other southern islands. It is highly adaptable and competes with the Green Anole and native lizards, further disrupting island insect populations.

Common Wall Lizard
Established from released pets. It competes with native lizards for food and habitat. Its adaptability to human-modified landscapes allows it to thrive in urban and suburban areas.

Sika Deer
While native to most of Japan, populations introduced to other islands (e.g., Nakanoshima Island) or those with non-native genetics are considered invasive, causing severe overgrazing and forest damage.

Silver Carp
Introduced for aquaculture and water quality control. It is a large filter feeder that consumes vast amounts of plankton, directly competing with native fish and altering the entire aquatic food web.
Bighead Carp
Similar to the Silver Carp, it was introduced for aquaculture. It also filter-feeds on plankton and can grow to a very large size, outcompeting native species for food resources in lakes and rivers.

Grass Carp
Introduced to control aquatic weeds. However, its voracious appetite for vegetation can strip lakes and ponds of all aquatic plants, destroying critical habitat for native fish and invertebrates.

Common Sunfish (Pumpkinseed)
Another member of the sunfish family illegally introduced for angling. It competes with native species, particularly Bluegill where they co-occur, for food like insects and snails.

Fat Mucket
A freshwater mussel likely introduced with imported game fish. It can compete with native freshwater mussels, which are among Japan’s most endangered faunal groups.

Chinese Mitten Crab
An estuarine crab whose burrowing can damage flood-control levees and riverbanks. It is also a potential host for the human lung fluke parasite. Its native range is close, but it is invasive in new systems.

Northern Snakehead
An air-breathing predatory fish that can tolerate poor water conditions. It preys on native fish and amphibians and can move short distances over land, allowing it to colonize new water bodies.

Veined Rapa Whelk
A large predatory sea snail. While native to some Japanese waters, its range is expanding. It is a voracious predator of commercial bivalves like clams and oysters, causing economic damage.

Didemnum vexillum (Sea Squirt)
A colonial sea squirt that forms extensive mats, smothering shellfish beds, fishing gear, and other marine organisms. Ironically, it may be native to Japan but is behaving invasively globally and in new local areas.

Harlequin Ladybeetle
Native to Japan, but introduced globally as a biocontrol agent where it is highly invasive. It is included to highlight that “invasive” can be context-dependent. It outcompetes and preys on native ladybeetles abroad.

(Entry Correction/Replacement: Better example) Azolla (Water Fern)
A small, free-floating fern that can rapidly cover the surface of still or slow-moving freshwater bodies. This dense mat blocks sunlight and oxygen, killing off submerged plants and fish.

Parrot’s Feather
An aquatic plant sold for aquariums and ponds that has escaped into the wild. It forms dense mats of vegetation that clog waterways, shade out native aquatic plants, and provide habitat for mosquito larvae.

Asiatic Dayflower
Though native, non-native and aggressive genotypes can be considered invasive. It is a common weed in gardens, fields, and disturbed areas, where it can compete with crops and native flora for resources.

Yellow Flag Iris
An ornamental pond plant that has escaped into wetlands, stream banks, and marshes. It forms dense stands that displace native wetland vegetation and can be toxic to livestock if ingested.

Purple Loosestrife
A notorious wetland invader. It forms dense, single-species stands in marshes and along riversides, eliminating native plants and reducing habitat quality for wetland wildlife.

Mile-a-minute Weed
Native to the region but can behave invasively. It’s a fast-growing vine that smothers other plants, including crops and young trees, by forming dense mats over them. Its barbs make it difficult to remove.

Garlic Mustard
A biennial herb that invades forest understories. It releases chemicals into the soil that inhibit the growth of other plants and fungi, allowing it to create dense monocultures and disrupt forest ecology.

Tomato Leafminer
A highly destructive pest of tomato plants that has recently been detected in Japan. The larvae mine the leaves, stems, and fruit, leading to severe crop losses if not controlled.

Western Flower Thrips
A major pest in greenhouses and fields, attacking a wide range of vegetable and ornamental crops. It causes damage by feeding and by transmitting plant viruses like Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus.

Silverleaf Whitefly
A tiny insect that is a major agricultural pest worldwide. It damages plants by feeding on sap and transmitting hundreds of plant viruses, causing billions of dollars in crop losses.

Spotted Lanternfly
A high-threat pest not yet widely established but with incursions. It feeds on over 70 plant species, including grapevines and fruit trees, causing significant economic damage. Its feeding also promotes sooty mold growth.

Coqui Frog
Established in Okinawa. While small, the males produce an extremely loud “ko-kee” call, reaching 90-100 decibels. The incessant noise disrupts residents and can lower property values.