Sri Lanka’s islands, rainforests, rivers and coastal wetlands support high biodiversity, but introduced plants, animals and insects can alter habitats, harm native species and affect agriculture and fisheries. Knowing which organisms are established helps conservationists, policymakers and local communities target prevention and control.
There are 38 Invasive Species in Sri Lanka, ranging from African catfish to Yellow crazy ant. For each entry you’ll find below the columns: Scientific name,Native range,Sri Lanka distribution to help with identification, comparison and management — you’ll find below.
How are invasive species detected and monitored in Sri Lanka?
Detection relies on a mix of research surveys, government monitoring, reports from local communities and NGOs, and increasingly citizen‑science apps; specialists use field sampling, trapping, habitat assessments and occasional genetic testing, while data are compiled to map spread and prioritize actions.
What can residents and visitors do to help prevent their spread?
Practical steps include reporting unusual species to local authorities, avoiding release of pets or aquarium organisms, cleaning boats and equipment between water bodies, choosing native plants for gardens, and supporting local eradication or containment efforts run by authorities or conservation groups.
Invasive Species in Sri Lanka
| Name | Scientific name | Native range | Sri Lanka distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lantana | Lantana camara | Central and South America | Lowland forests, roadsides, plantations nationwide |
| Mile-a-minute vine | Mikania micrantha | Neotropics (Central/South America) | Wet lowland forests, plantations, roadside vegetation |
| Siam weed | Chromolaena odorata | Neotropics | Roadsides, secondary forests, lowlands nationwide |
| Parthenium | Parthenium hysterophorus | Central Mexico/Argentina | Dry lowlands, roadsides, agricultural margins, widespread |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Amazon basin | Rivers, lakes, reservoirs nationwide |
| Salvinia | Salvinia molesta | Neotropics | Reservoirs, slow-moving waters, tanks |
| Water lettuce | Pistia stratiotes | Pantropical (likely Africa/Americas) | Tanks, lakes and slow-moving waters nationwide |
| Golden apple snail | Pomacea canaliculata | South America | Lowland paddy fields and irrigation canals |
| Giant African snail | Achatina fulica | East Africa | Urban gardens, agricultural lowlands across Sri Lanka |
| Nile tilapia | Oreochromis niloticus | Nile and African rivers | Reservoirs, lakes and lowland fresh waters |
| Mozambique tilapia | Oreochromis mossambicus | Southern Africa | Rivers, reservoirs and ponds |
| African catfish | Clarias gariepinus | Africa | Reservoirs and rivers, escaped from aquaculture |
| Mosquitofish | Gambusia affinis | Southeastern United States | Ponds, marshes and irrigation channels |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | Likely South/ Southeast Asia origin but broadly introduced | Urban, agricultural and island ecosystems nationwide |
| Brown rat | Rattus norvegicus | Eastern Asia | Urban areas, ports and agricultural zones nationwide |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Eurasia (commensal with humans) | Urban, agricultural and storage facilities |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | Worldwide (domesticated origin) | Urban edges, scrub, forests and protected areas |
| Feral dog | Canis familiaris | Worldwide (domesticated origin) | Rural and protected landscapes near villages |
| Prosopis | Prosopis juliflora | Mexico to tropical South America | Coastal arid zones, disturbed drylands |
| Leucaena | Leucaena leucocephala | Mexico/Central America | Lowland disturbed sites and dry zones |
| Eucalyptus | Eucalyptus globulus | Australia | Hill plantations and some lowland areas where planted |
| Caribbean pine | Pinus caribaea | Central America/Caribbean | Highland plantations and adjacent montane grasslands |
| Black wattle | Acacia mearnsii | Australia | Moist hill country plantations and slopes |
| African tulip tree | Spathodea campanulata | West Africa | Urban areas, forest edges and wet lowlands |
| Mexican sunflower | Tithonia diversifolia | Mexico/Central America | Roadsides, disturbed sites and secondary forests |
| Mimosa | Mimosa diplotricha | Neotropics | Roadsides, abandoned fields and moist lowlands |
| Fountain grass | Pennisetum setaceum | Africa/Middle East | Dry open slopes, roadsides and disturbed drylands |
| Woolly nightshade | Solanum mauritianum | South America | Upland and mid‑elevation disturbed forests |
| Common carp | Cyprinus carpio | Eurasia | Ponds, reservoirs and sluggish rivers |
| Yellow crazy ant | Anoplolepis gracilipes | Southeast Asia/Australia region expansion | Coastal forests, plantations and disturbed sites |
| Fall armyworm | Spodoptera frugiperda | Americas | Maize and cereal fields across dry and intermediate zones |
| Tomato leafminer | Tuta absoluta | South America | Tomato crops in lowland agricultural areas |
| Whitefly | Bemisia tabaci | Likely tropical Americas originally | Vegetable and fruit crops nationwide |
| Ageratum | Ageratum conyzoides | Tropical Americas | Roadsides, disturbed agricultural fields |
| Apple snail (other) | Pomacea maculata | South America | Freshwater canals and paddy edges where recorded |
| Tomato/tuber pest (other) | Tuta spp. | Neotropics | Occasional detections in vegetable farms |
| Rice hispa? Not included | |||
| Spreading balsam | Impatiens glandulifera | Himalayan origin? invasive elsewhere | Occasional in gardens and disturbed wet sites |
Images and Descriptions

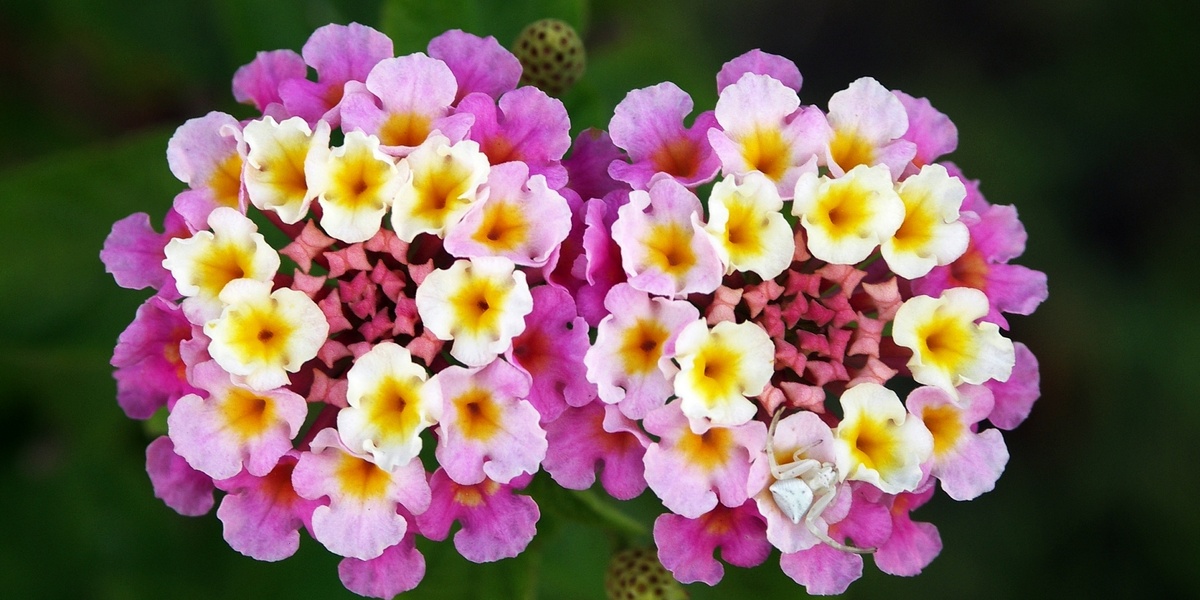
Lantana
A thorny shrub that forms dense thickets across disturbed lowlands and dry zones, smothering native plants, reducing grazing land and altering fire patterns. Introduced as an ornamental, now one of Sri Lanka’s most widespread invasive plants.

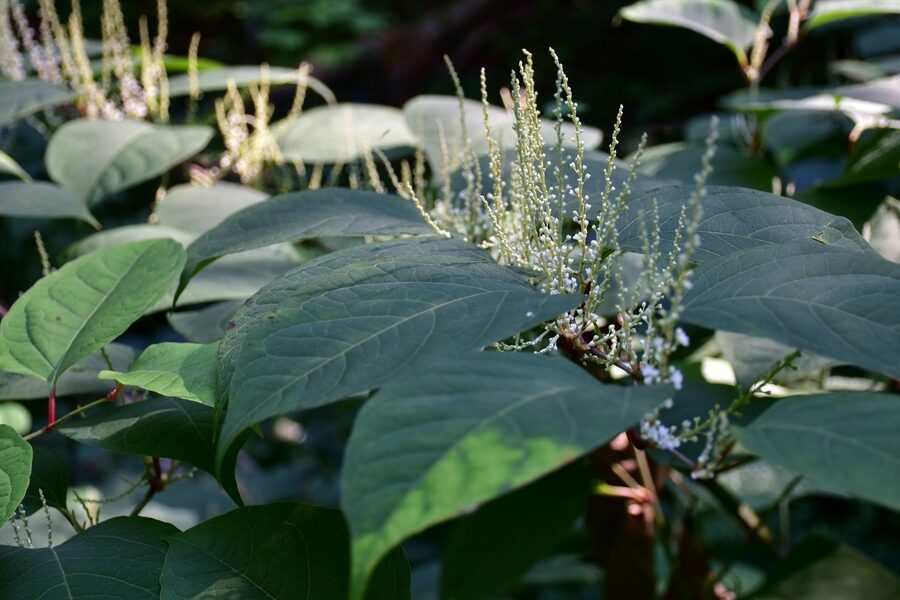
Mile-a-minute vine
A fast-growing creeping vine that smothers seedlings and crops, particularly tea and forest edges. Spreads quickly after disturbance, reducing native regeneration and increasing management costs for plantations and protected areas.

Siam weed
A shrubby invasive that rapidly colonizes disturbed ground and forest edges, forming dense stands that outcompete native vegetation and alter fire regimes. Harmful to reforestation and pasture productivity.

Parthenium
A highly allergenic weed causing respiratory and skin problems, reducing crop yields and pasture quality. Rapidly invading disturbed soils and roadsides since its arrival, making management a public health and agricultural priority.

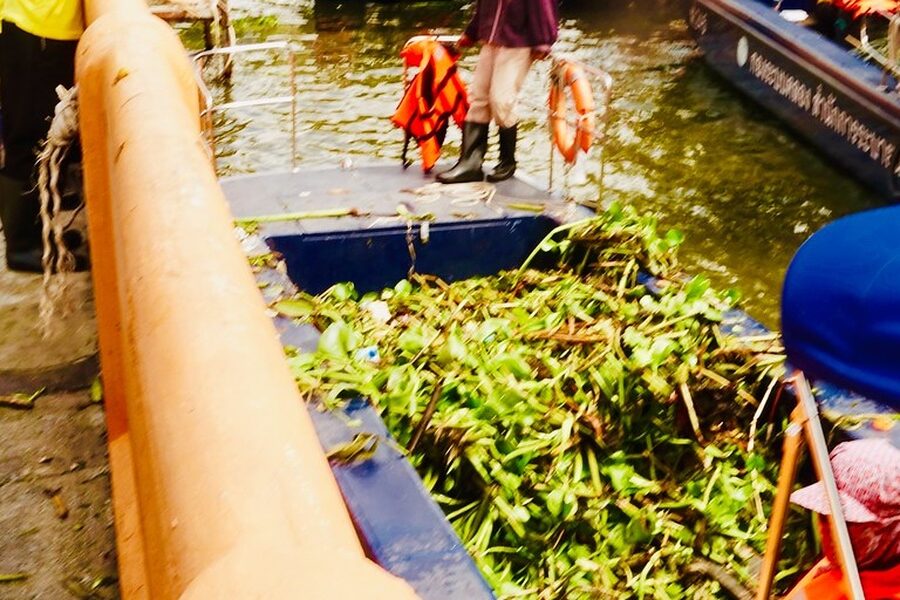
Water hyacinth
A free‑floating aquatic plant that forms thick mats blocking waterways, reducing oxygen, harming fisheries and clogging irrigation. Rapid multiplication causes economic losses in inland fisheries and increases vector habitat for disease.

Salvinia
An invasive free‑floating fern that rapidly covers water surfaces, obstructing navigation, reducing oxygen for aquatic life and complicating reservoir management. Often spreads by water transfer and human activity.

Water lettuce
A floating plant that forms dense mats similar to hyacinth, disrupting fisheries, irrigation and native aquatic plants. Persistent in warm waters and challenging to control once established.

Golden apple snail
An invasive freshwater snail that feeds on young rice seedlings and aquatic plants, causing serious damage to paddy cultivation. Spread via aquarium trade and accidental introductions, costing farmers time and yields.

Giant African snail
A large land snail that damages crops and ornamental plants and can carry parasites of human health concern. Highly reproductive and transported easily by humans, it’s a major horticultural pest.

Nile tilapia
Introduced for aquaculture and now widespread, tilapia compete with native fish, alter food webs and affect fisheries. Their fast reproduction and tolerance of degraded waters fuel their spread.

Mozambique tilapia
An introduced tilapia species that hybridizes with other tilapias and competes with native fishes. Established in many freshwater systems and problematic for native biodiversity and fisheries.

African catfish
Introduced for aquaculture; escaped populations prey on native fish and amphibians and compete with native predators. Their air‑breathing ability helps them survive in degraded waters and spread widely.

Mosquitofish
Introduced for mosquito control, mosquitofish eat native fish larvae and invertebrates, reducing biodiversity in small water bodies. Highly tolerant and aggressive, they displace native aquatic fauna.

Black rat
A commensal rodent that predates native birds, reptiles and invertebrates, contaminates food stores and spreads disease. Long established and a major threat to island biodiversity and agriculture.

Brown rat
A widespread introduced rodent that damages stored food, infrastructure and crops, and transmits pathogens. Thrives in human‑altered habitats and causes economic and health impacts.

House mouse
A tiny but impactful pest species in stores, homes and farms. Damages grains and equipment, transmits disease, and can prey on insects or eggs in sensitive sites.

Feral cat
Introduced domestic cats that have become feral are major predators of native birds, reptiles and small mammals. They are implicated in declines of endemic and ground‑nesting species across Sri Lanka.

Feral dog
Free‑roaming dogs attack wildlife, livestock and sometimes people, spread rabies and disturb native fauna and nesting birds. Packs near protected areas cause substantial conservation and human‑health concerns.

Prosopis
A thorny tree/shrub that invades dry coastal and arid shrublands, reduces grazing, displaces native vegetation and forms impenetrable thickets. Difficult to remove and spreads from planted windbreaks.

Leucaena
Planted for fodder and soil improvement, this fast‑growing legume invades pastures and fallow land, forming dense stands that reduce native plant diversity and hinder crop production.

Eucalyptus
Commonly planted for timber and fuelwood; some species spread beyond plantations, alter soil chemistry and water balance, and suppress native undergrowth, affecting highland ecosystems.

Caribbean pine
Planted pines escape from plantations and invade montane grasslands, changing fire regimes and shading out native montane flora. Pine invasion threatens unique highland ecosystems and endemic plants.

Black wattle
Introduced for timber and tannin, black wattle invades montane and submontane areas, changing soil nitrogen and outcompeting native shrubs and herbs, complicating restoration of native habitats.

African tulip tree
An ornamental tree that self‑seeds and invades disturbed wet forests and edges, shading out native seedlings and altering forest composition. Attractive flowers mask ecological impacts.

Mexican sunflower
A fast‑growing annual shrub that colonizes disturbed ground and competes with crops and native vegetation. Often spreads rapidly after land clearing and is hard to eradicate.

Mimosa
A prickly, climbing shrub that forms impenetrable thickets, smothering native plants and hindering access. Aggressive colonizer of disturbed sites and a nuisance for grazing and reforestation.

Fountain grass
An ornamental grass that invades dry habitats, increases fire risk, and displaces native grasses. Spreads from garden plantings into natural dry zones and reduces habitat quality for wildlife.

Woolly nightshade
A shrubby tree that invades highland forest edges and disturbed sites, competing with native trees and complicating restoration of montane forest and tea plantation borders.

Common carp
Introduced for aquaculture and ornamental ponds, carp uproot vegetation, increase turbidity and alter aquatic food webs, negatively affecting native fish and water quality.

Yellow crazy ant
An aggressive invasive ant that forms supercolonies, disrupts invertebrate communities, harms ground‑nesting fauna and can exacerbate pest outbreaks in plantations and forest fragments.

Fall armyworm
A recent invasive moth whose caterpillars rapidly defoliate maize and other cereals, causing severe yield losses. Arrived recently and spread quickly, prompting emergency pest management responses.

Tomato leafminer
A tiny moth whose larvae bore into tomato leaves, stems and fruits, causing severe crop losses. Rapid spread across Asia has made it a major threat to vegetable production.

Whitefly
A sap‑sucking insect complex that transmits plant viruses and damages broadleaf crops. Highly invasive, pesticide‑resistant biotypes cause major economic losses for farmers.

Ageratum
A common broadleaf weed that invades cropland and disturbed soils, suppressing seedlings and reducing crop yields. Spreads readily by wind and human movement of soil.

Apple snail (other)
A large apple snail species similar to P. canaliculata, reported in wetland habitats and damaging rice and aquatic vegetation; spreads via water transfer and aquarium trade.

Tomato/tuber pest (other)
Small moths of serious horticultural concern; larvae bore in foliage and fruits causing economic losses. Rapid detection and management are priorities to limit spread.

Rice hispa? Not included

Spreading balsam
An aggressive ornamental known to escape cultivation in some regions; occasional reports in Sri Lanka warrant monitoring though widespread establishment is limited.