Sweden’s lakes, forests and coastline make it a refuge for many native species, but they also create entry points for non‑native plants and animals. Increased trade, travel and changing temperatures mean more species arrive and sometimes establish, altering ecosystems and local economies.
There are 76 Invasive Species in Sweden, ranging from African Clawed Frog to Zebra Mussel. For each entry the data are organized as Scientific name, Status (Sweden), Regions in Sweden; you’ll find below.
How do I report a suspicious sighting of an invasive species in Sweden?
Report sightings to your county administrative board (Länsstyrelsen) or through the national observation portal (Artportalen), and include clear photos, location (GPS if possible), date and number observed; local authorities use these reports to prioritize response and verify records.
What practical steps can I take to prevent spreading invasive species?
Clean boats, fishing gear and garden equipment between sites, never release pets or plants into the wild, choose native species for planting, and follow local biosecurity guidance—small actions reduce accidental introductions and help protect local habitats.
Invasive Species in Sweden
| Common name | Scientific name | Status (Sweden) | Regions in Sweden |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Crayfish | Pacifastacus leniusculus | Established, Spreading, Regulated | Southern and Central Sweden |
| American Mink | Neovison vison | Established, Spreading, Regulated | Widespread across the country |
| Raccoon Dog | Nyctereutes procyonoides | Established, Spreading, Regulated | Northern Sweden (Norrbotten, Västerbotten) |
| Spanish Slug | Arion vulgaris | Established, Spreading | Widespread, especially Southern Sweden |
| Giant Hogweed | Heracleum mantegazzianum | Established, Controlled, Regulated | Southern and Central Sweden |
| Himalayan Balsam | Impatiens glandulifera | Established, Spreading, Regulated | Southern and Central Sweden |
| Japanese Knotweed | Reynoutria japonica | Established, Spreading, Regulated | Southern and Central Sweden |
| Raccoon | Procyon lotor | Spreading, Regulated | Scattered sightings, mainly Southern Sweden |
| Zebra Mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | Established, Spreading | Major lakes (Mälaren, Hjälmaren), spreading |
| Canadian Goose | Branta canadensis | Established, Spreading | Widespread across the country |
| Pink Salmon | Oncorhynchus gorbuscha | Established, Spreading | Northern rivers, West coast |
| Harlequin Ladybug | Harmonia axyridis | Established, Spreading | Southern and Central Sweden |
| Quagga Mussel | Dreissena rostriformis bugensis | Established, Spreading | Major lakes (Vänern, Vättern) |
| American Lobster | Homarus americanus | Spreading, Regulated | West coast (Skagerrak) |
| Round Goby | Neogobius melanostomus | Established, Spreading | Baltic Sea coast, Gothenburg harbor |
| Persian Hogweed | Heracleum persicum | Established, Controlled, Regulated | Scattered, mainly Southern Sweden |
| Turkish Snail | Helix lucorum | Established, Spreading | Southern Sweden (especially Skåne) |
| Lupin | Lupinus polyphyllus | Established, Spreading | Widespread, especially along roadsides |
| Pond Slider Turtle | Trachemys scripta | Established, Regulated | Ponds in Southern Sweden |
| New Zealand Mud Snail | Potamopyrgus antipodarum | Established, Spreading | Brackish waters and some freshwater lakes |
| Water Hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Regulated | Potential threat, not established outdoors |
| Siberian Chipmunk | Eutamias sibiricus | Regulated | Not established, but risk of escape |
| Coati | Nasua nasua | Regulated | Not established, but risk of escape |
| Egyptian Goose | Alopochen aegyptiaca | Spreading, Regulated | Southern Sweden (Skåne) |
| Sacred Ibis | Threskiornis aethiopicus | Regulated | Occasional sightings, not established |
| Brook Trout | Salvelinus fontinalis | Established | Northern Sweden streams |
| Spiny Waterflea | Bythotrephes longimanus | Established, Spreading | Major lakes and Baltic Sea |
| Chinese Mitten Crab | Eriocheir sinensis | Established | Lakes and rivers connected to Baltic Sea |
| American Skunk Cabbage | Lysichiton americanus | Established, Spreading, Regulated | Southern and Western Sweden |
| Parrot’s Feather | Myriophyllum aquaticum | Established, Regulated | Ponds in Southern Sweden |
| Water Fern | Azolla filiculoides | Established, Regulated | Ponds and slow-moving water, Southern Sweden |
| Japanese Oyster | Magallana gigas | Established, Spreading | West coast (Bohuslän) |
| Whitetail Deer | Odocoileus virginianus | Eradicated | Formerly in Finland, risk of crossing border |
| Ruddy Duck | Oxyura jamaicensis | Regulated, Controlled | Occasional sightings |
| Small-leaved Cotoneaster | Cotoneaster horizontalis | Established, Spreading | Southern Sweden, especially on islands |
| Sycamore Maple | Acer pseudoplatanus | Established, Spreading | Southern and Central Sweden |
| Virginia Creeper | Parthenocissus quinquefolia | Established, Spreading | Gardens and urban areas, Southern Sweden |
| Large-flowered Tickseed | Coreopsis grandiflora | Established, Spreading | Scattered, often along railways and roads |
| Beach Rose | Rosa rugosa | Established, Spreading | Coastal areas, widespread |
| Common Carp | Cyprinus carpio | Established | Southern and Central lakes |
| Pumpkinseed | Lepomis gibbosus | Established | Scattered ponds and lakes, Southern Sweden |
| Wels Catfish | Silurus glanis | Established | Southern rivers (Helge å, Emån) |
| Black Bullhead | Ameiurus melas | Established | A few ponds in Skåne |
| Comb Jelly | Mnemiopsis leidyi | Established | Baltic Sea, West coast |
| Bay Barnacle | Amphibalanus improvisus | Established | Baltic Sea, West coast |
| Mud Crab | Rhithropanopeus harrisii | Established | Brackish coastal waters |
| Killer Shrimp | Dikerogammarus villosus | Spreading | Lake Vättern, Mälaren, Vänern |
| Opossum Shrimp | Katamysis warpachowskyi | Established | Northern Baltic Sea (Bothnian Bay) |
| Sudan Grass | Sorghum drummondii | Regulated | Potential threat, not established |
| Alligator Weed | Alternanthera philoxeroides | Regulated | Potential threat, not established |
| Curly Waterweed | Lagarosiphon major | Regulated | Ponds in Southern Sweden |
| Indian Balsam | Impatiens balfourii | Established | Gardens in Southern Sweden |
| Chilean Gunnera | Gunnera tinctoria | Regulated | Gardens, very rare escapes |
| Hog’s-fennel | Peucedanum ostruthium | Established | Mountain regions (Jämtland) |
| Garden Lupin | Lupinus x regalis | Established, Spreading | Widespread along roadsides |
| Montbretia | Crocosmia x crocosmiiflora | Established, Spreading | West coast and Southern Sweden |
| Red-eared Slider | Trachemys scripta elegans | Established, Regulated | Ponds in Southern Sweden |
| Manchurian Ash | Fraxinus mandshurica | Spreading | Planted in urban areas, spreading |
| Pallas’s Squirrel | Callosciurus erythraeus | Regulated | Not established, but risk of escape |
| Grey Squirrel | Sciurus carolinensis | Regulated | Not established, but risk of escape |
| Muntjac Deer | Muntiacus reevesi | Regulated | Not established, risk of escape/spread |
| Fox Squirrel | Sciurus niger | Regulated | Not established, but risk of escape |
| American Bullfrog | Lithobates catesbeianus | Regulated | Not established |
| Pallas’s Fish Eagle | Haliaeetus leucoryphus | Regulated | Occasional vagrant |
| Coypu | Myocastor coypus | Regulated | Eradicated, risk of reintroduction |
| African Clawed Frog | Xenopus laevis | Regulated | Not established |
| Floating Pennywort | Hydrocotyle ranunculoides | Established, Regulated | Southern Sweden (Skåne) |
| Water Primrose | Ludwigia grandiflora | Regulated | Gardens, risk of escape |
| Waterweed | Elodea nuttallii | Established, Spreading | Southern and Central Sweden |
| Fringed Water-lily | Nymphoides peltata | Established, Spreading | Lakes in Southern Sweden |
| Japanese Slipper Limpet | Crepidula fornicata | Established | West coast |
| American Razor Clam | Ensis leei | Established, Spreading | West coast |
| Ash Dieback Fungus | Hymenoscyphus fraxineus | Established, Spreading | Widespread |
| Crayfish Plague | Aphanomyces astaci | Established, Spreading | Widespread in waters with Signal Crayfish |
| Potato Late Blight | Phytophthora infestans | Established | Widespread in agricultural areas |
| Dutch Elm Disease | Ophiostoma novo-ulmi | Established, Spreading | Southern and Central Sweden |
Images and Descriptions

Signal Crayfish
A North American crayfish that carries the crayfish plague, which is fatal to Sweden’s native Noble crayfish. It aggressively outcompetes native species for food and shelter, and its spread is a major ecological threat.

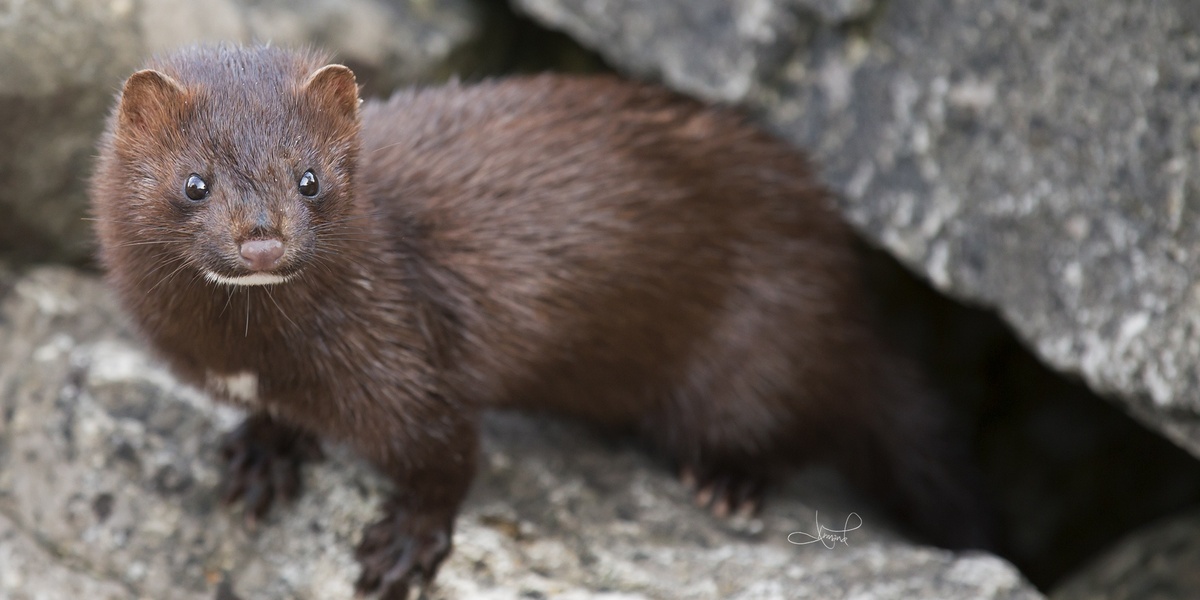
American Mink
Originally from North America, this predator escaped from fur farms. It has severely impacted native wildlife, especially ground-nesting birds in archipelagoes and the threatened native European polecat.

Raccoon Dog
An adaptable canid from East Asia, it spreads diseases like rabies and parasites. It is a major threat to ground-nesting birds and amphibians, and there is an ongoing effort to stop its spread southwards.

Spanish Slug
Often called the “killer slug,” this large garden pest from the Iberian Peninsula devours a wide range of plants and crops. It reproduces rapidly and has few natural predators in Sweden, making it a major nuisance for gardeners.

Giant Hogweed
This massive plant from the Caucasus contains a toxic sap that causes severe burns and blisters on skin exposed to sunlight. It forms dense stands that crowd out native flora. Do not touch and report it to your municipality.

Himalayan Balsam
An attractive but aggressive plant from the Himalayas. It colonizes riverbanks, outcompeting native plants and leading to soil erosion when it dies back in winter. Its seed pods explode when touched, spreading seeds widely.

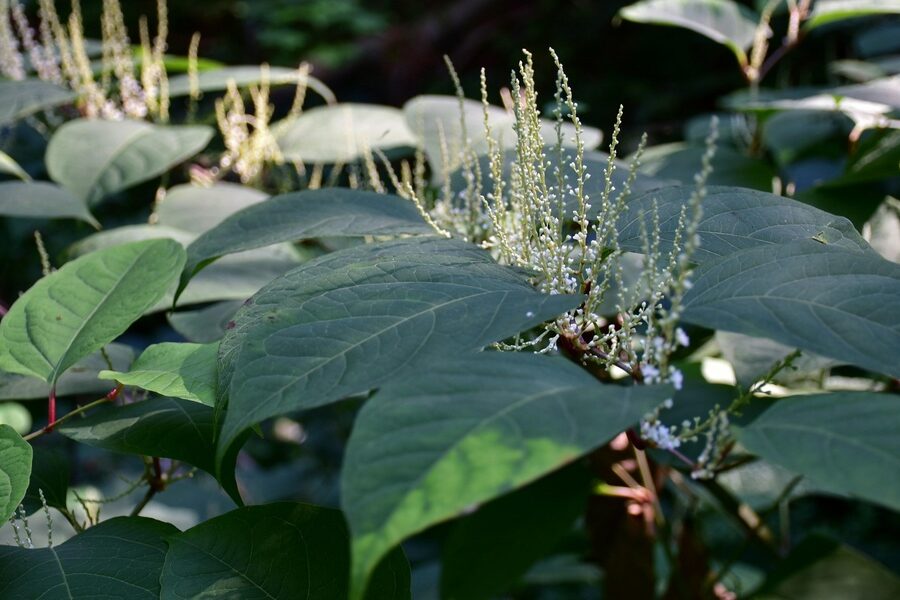
Japanese Knotweed
An extremely destructive plant from East Asia whose roots can damage building foundations, pavement, and flood defenses. It is incredibly difficult to remove and forms dense thickets that eliminate all other vegetation.

Raccoon
An adaptable omnivore from North America, the raccoon is a potential threat due to its ability to carry diseases (like rabies) and prey on native birds and amphibians. It is crucial to report any sightings.

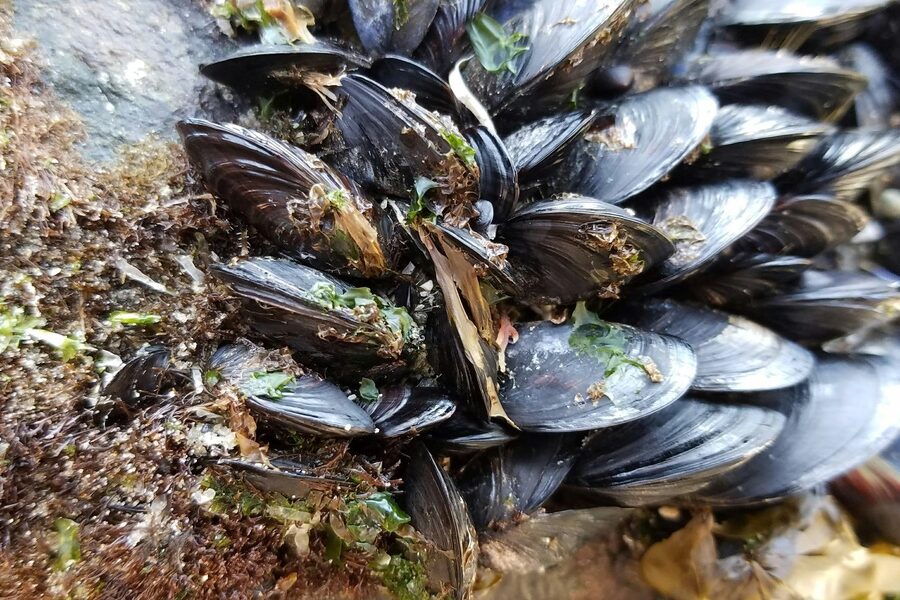
Zebra Mussel
A small freshwater mussel from the Ponto-Caspian region that forms incredibly dense colonies. It clogs water intake pipes for industry and power plants, and fundamentally alters aquatic ecosystems by filter-feeding.

Canadian Goose
Introduced from North America for hunting, its large populations cause problems by overgrazing parks and farmlands. Their droppings can degrade water quality in lakes and on beaches, leading to health concerns.

Pink Salmon
A Pacific salmon species that has established reproducing populations in Norwegian and Swedish rivers. It has a strict two-year life cycle, and there are concerns it competes with native Atlantic salmon for resources.

Harlequin Ladybug
An Asian ladybug introduced for biocontrol, it now outcompetes and preys on native ladybugs. It can be a nuisance when it swarms indoors in autumn and can taint wine grapes if harvested with the fruit.

Quagga Mussel
Similar to the zebra mussel, this invasive mollusc is even more aggressive. It can colonize soft surfaces, clogs pipes, and outcompetes native species. Its spread threatens the ecosystems of Sweden’s largest lakes.

American Lobster
Non-native lobsters from North America, likely released illegally. They pose a threat to the native European lobster by competing for resources and potentially spreading diseases to which the native species has no immunity.

Round Goby
A bottom-dwelling fish from the Black and Caspian Seas, likely spread via ballast water. It is an aggressive predator of fish eggs and invertebrates, disrupting coastal food webs and outcompeting native fish.

Persian Hogweed
Similar to Giant Hogweed, this invasive plant from Southwest Asia also has a phototoxic sap that can cause severe skin burns. It is a threat to biodiversity as it forms dense stands that shade out other plants.

Turkish Snail
A large land snail, larger than the native Roman snail, that has become a pest in gardens and horticultural areas. It is believed to have been introduced accidentally through the plant trade.

Lupin
A North American plant now common along Swedish roads. While beautiful, it is toxic to livestock, fixes nitrogen which alters soil chemistry, and outcompetes native meadow flowers, reducing biodiversity.

Pond Slider Turtle
These popular pet turtles from North America are often released into the wild. They can survive Swedish winters and compete with native wildlife for food and basking spots, and may also carry diseases.

New Zealand Mud Snail
A tiny but highly invasive snail that can reach densities of over 300,000 per square meter. It outcompetes native grazers for food, altering the base of the aquatic food web.

Water Hyacinth
A free-floating aquatic plant from the Amazon basin, listed as a major threat by the EU. It is illegal to own or trade in Sweden as it can completely cover water surfaces, blocking sunlight and killing life below.

Siberian Chipmunk
This small rodent from Asia is a popular but regulated pet. If escaped, it could compete with native small mammals and potentially transmit diseases like tick-borne encephalitis.

Coati
A member of the raccoon family from South America, regulated by the EU. Kept as a pet, escaped individuals could potentially establish populations and harm native birds and small animals.

Egyptian Goose
This distinctive goose from Africa is spreading north through Europe. It is aggressive towards other waterfowl, competing for nesting sites and food, and can cause grazing damage in agricultural areas.

Sacred Ibis
An African bird that established feral populations in Europe. It is a regulated invasive species due to its predation on the eggs and chicks of other birds, including rare terns and herons.

Brook Trout
A North American fish introduced for sport fishing. It competes heavily with and can displace native Brown trout and Arctic char, especially in smaller, colder streams, posing a threat to native fish populations.

Spiny Waterflea
A tiny crustacean from Eurasia that has invaded the Great Lakes and Swedish waters. It preys on smaller zooplankton, disrupting the food web, and its long tail spine clogs fishing lines and gear.

Chinese Mitten Crab
Named for its furry claws, this crab from East Asia burrows into riverbanks, causing erosion and damaging flood defenses. It also preys on native invertebrates and can clog water systems.

American Skunk Cabbage
A large, foul-smelling plant from western North America, introduced to gardens. It spreads rapidly in wet woodlands and along streams, forming dense colonies that crowd out native ground flora.

Parrot’s Feather
An aquatic plant from South America, popular in garden ponds. When it escapes, it can form dense mats that clog waterways, block sunlight, and disrupt recreational activities like boating and fishing.

Water Fern
A small, free-floating fern from the Americas that can reproduce extremely quickly. It forms a thick mat on the water surface, blocking light and oxygen, which can kill fish and native aquatic plants.

Japanese Oyster
Also known as the Pacific Oyster, it was introduced for aquaculture. It now forms dense reefs that change the habitat, and its sharp shells can be a hazard on bathing beaches. It outcompetes the native European flat oyster.

Whitetail Deer
A North American deer that carries a brain worm parasite that is harmless to it but fatal to native moose and reindeer. Sweden maintains vigilance to prevent it from crossing the border from Finland.

Ruddy Duck
A North American duck that threatens the endangered native White-headed Duck through hybridization. Aggressive eradication and control programs across Europe have greatly reduced its numbers.

Small-leaved Cotoneaster
A popular garden shrub from China. Its seeds are spread by birds, allowing it to invade natural habitats like the rocky shores of archipelagos, where it outcompetes fragile native plant communities.

Sycamore Maple
A European tree that is not native to Scandinavia. It spreads aggressively into forests and nature reserves, where its dense canopy shades out native trees and ground-level flora, reducing biodiversity.

Virginia Creeper
A climbing vine from North America widely used in gardens. It can escape cultivation and smother native vegetation, including large trees, and its berries are poisonous to humans.

Large-flowered Tickseed
A North American garden plant that has escaped and naturalized. It can form dense stands in sunny, dry habitats, displacing native grassland and meadow species that are important for pollinators.

Beach Rose
An Asian rose species planted to stabilize sand dunes. It has become highly invasive, forming impenetrable thorny thickets that crowd out native coastal plants and alter the dune ecosystem.

Common Carp
While long-established, this Asian fish is considered non-native and problematic. Its bottom-feeding behavior stirs up sediment, increasing water turbidity and uprooting aquatic plants, which degrades habitat for other species.

Pumpkinseed
A small, colourful sunfish from North America, likely introduced through the aquarium trade. It is a voracious predator of invertebrates and fish eggs, potentially impacting native fish populations like perch and roach.

Wels Catfish
A massive predatory catfish native to Central and Eastern Europe, but introduced to several Swedish river systems. It can decimate local fish populations and alter the entire aquatic food web due to its size and appetite.

Black Bullhead
A catfish species from North America. It is extremely hardy and can tolerate poor water quality. It competes with native fish for food and can stir up bottom sediments, degrading water clarity.

Comb Jelly
An American comb jelly that arrived in ballast water. In the Black Sea, its population exploded and devastated fisheries by consuming fish eggs and larvae. It poses a similar threat in the Baltic Sea ecosystem.

Bay Barnacle
A small barnacle that likely arrived on ships from the Americas. It is a major fouling organism on ships, buoys, and industrial water intakes. It can outcompete native barnacles for space in some areas.

Mud Crab
A small crab from the Atlantic coast of North America, spread via ballast water. It has established itself in the Baltic Sea, where it preys on native invertebrates and competes with other species.

Killer Shrimp
An aggressive amphipod from the Ponto-Caspian region. It is a voracious predator that kills other invertebrates even without consuming them, drastically altering food webs and outcompeting native shrimp species.

Opossum Shrimp
Another Ponto-Caspian crustacean that has invaded the Baltic. It competes with native mysid shrimp, which are a crucial food source for commercially important fish like herring and cod.

Sudan Grass
A fast-growing grass from Africa, listed as an invasive species of EU concern. It is banned in Sweden as it could outcompete agricultural crops and native grassland species if it were to establish.

Alligator Weed
A South American amphibious weed that can grow on land and in water. It forms dense mats that block waterways and degrade habitats. It is on the EU’s list of regulated species, making it illegal in Sweden.

Curly Waterweed
An aquatic plant from Southern Africa, often used in aquariums and ponds. It grows into dense underwater masses that choke out native plants and impede water flow, swimming, and boating. It is regulated by the EU.

Indian Balsam
Similar to its relative Himalayan Balsam, this Asian plant can escape gardens and colonize disturbed areas. While less aggressive, it still has the potential to displace native flora in sensitive habitats.

Chilean Gunnera
A massive rhubarb-like plant from South America, regulated under EU law. Its huge leaves can form a dense canopy that shades out all other plants, posing a threat to native ecosystems if it establishes in the wild.

Hog’s-fennel
A plant native to the mountains of Central Europe, it was likely introduced as a medicinal herb. It has now naturalized in Swedish mountain meadows, where it competes with rare and sensitive native alpine flora.

Garden Lupin
This is the common hybrid Lupin seen across Sweden. A cross between L. polyphyllus and other species, it shares the same invasive traits: outcompeting native meadow flowers and altering soil chemistry.

Montbretia
A popular garden plant that spreads via underground corms. It can escape to form dense, spreading clumps in the wild, particularly in milder coastal areas, where it displaces native vegetation.

Red-eared Slider
This is the most common subspecies of the Pond Slider turtle, identifiable by the red stripe on its head. Often released from captivity, it competes with native wildlife and is regulated by the EU.

Manchurian Ash
An Asian ash tree species planted as a replacement for native ash trees suffering from ash dieback. However, it has started to spread into natural areas, raising concerns about it becoming the next invasive tree.

Pallas’s Squirrel
An Asian tree squirrel regulated by the EU. If it were to escape from captivity and establish a population, it could compete with the native red squirrel and cause damage by stripping bark from trees.

Grey Squirrel
A North American squirrel that has decimated native red squirrel populations in the UK and Italy by outcompeting them and carrying a squirrelpox virus. It is strictly regulated to prevent its introduction into Sweden.

Muntjac Deer
A small deer from Asia that has established wild populations in the UK. It browses heavily on woodland undergrowth, preventing tree regeneration and impacting birds and butterflies. It is regulated by the EU.

Fox Squirrel
The largest tree squirrel in North America. Like the grey squirrel, it is regulated by the EU due to the risk of it competing with native red squirrels and causing ecological damage if it were to become established.

American Bullfrog
A very large, voracious frog from North America. It preys on almost anything it can fit in its mouth, including native frogs, snakes, and birds. It also carries the chytrid fungus, which is lethal to many amphibians.

Pallas’s Fish Eagle
An Asian bird of prey. While only seen as a rare visitor, it is on the EU invasive list due to concerns about potential hybridization with native White-tailed eagles and competition for resources if it were to establish.

Coypu
A large, semi-aquatic rodent from South America, also known as nutria. It was eradicated from Sweden but is regulated by the EU because its burrowing damages riverbanks and it can be destructive to crops.

African Clawed Frog
A South African frog widely used in laboratories. It is a carrier of the devastating chytrid fungus and is a voracious predator. It is on the EU’s regulated list to prevent its introduction into the wild.

Floating Pennywort
An aquatic plant from the Americas that can grow up to 20 cm per day. It forms dense floating mats that deoxygenate the water, kill fish, and make recreation impossible. Subject to control measures.

Water Primrose
A South American aquatic plant that is on the EU’s regulated list. It can form dense mats in slow-moving water, disrupting ecosystems and water flow. It is illegal to plant or sell in Sweden.

Waterweed
A North American aquatic plant that spreads easily by fragmentation. It forms dense underwater beds that crowd out native aquatic plants and can interfere with boating, fishing, and hydroelectric power generation.

Fringed Water-lily
An aquatic plant with small, water-lily-like leaves. It is native to Eurasia but not Sweden. It spreads rapidly, covering the water surface and outcompeting native vegetation.

Japanese Slipper Limpet
A marine snail from North America that forms distinctive, curved stacks of individuals. It competes with native filter-feeders like oysters and mussels for food and space on the seabed.

American Razor Clam
A North American clam that has become abundant on the Swedish west coast. It can reach high densities and may be outcompeting native clam species, altering the sandy seabed ecosystem.

Ash Dieback Fungus
An invasive microfungus from Asia that causes the lethal disease ash dieback. It has devastated populations of the native European ash (Fraxinus excelsior) across Sweden and the rest of Europe.
Crayfish Plague
A water mould, not a species itself, but an invasive pathogen introduced with the Signal Crayfish. It is 100% lethal to the native Noble crayfish, which has no resistance to the disease.

Potato Late Blight
The water mould responsible for the Irish Potato Famine. Originating from the Americas, it remains a serious and economically damaging pathogen for potato and tomato farmers in Sweden.

Dutch Elm Disease
A fungal disease spread by bark beetles that has wiped out most of the mature elm trees in Sweden. It is an aggressive, invasive pathogen that has fundamentally changed many landscapes and cityscapes.