The Pantanal’s slow rivers, oxbow lakes and seasonal floodplains host an unusually rich freshwater fauna. Local fishing communities and scientists alike rely on simple species lists to track what turns up in nets, seasonal movements and habitat changes across the wet and dry cycles.
There are 80 pantanal fish, ranging from Acará to Zebra Pleco. For each, the list shows Scientific name,Max length (cm),Habitat & location — details you’ll find below.
How can I use this list to identify fish in the Pantanal?
Use the Scientific name and Max length (cm) together with the Habitat & location column to narrow candidates: measure the specimen, note whether it came from river, lagoon or flooded pasture, then match those traits. Cross-check with photos or regional field guides and record local common names and a photo to confirm ID and help others.
Which species on this list are threatened and what practical steps help them?
Some Pantanal species face pressure from habitat loss, overfishing and water quality changes; check local conservation listings for specifics. Practical actions include avoiding collection of rare species, reporting unusual catches to researchers, supporting habitat protection initiatives, and following sustainable fishing rules when visiting.
Pantanal Fish
| Name | Scientific name | Max length (cm) | Habitat & location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dourado | Salminus brasiliensis | 110 | Main river channels, rapids, corixos. Widespread in clear, flowing waters. |
| Pintado | Pseudoplatystoma corruscans | 166 | Deep river channels, flooded plains, lakes (baías). Throughout the Paraguay River basin. |
| Pacu | Piaractus mesopotamicus | 88 | Flooded forests (mata de galeria), river channels, and permanent lakes. |
| Jaú | Zungaro zungaro | 150 | Deep pools in large rivers, often near rocky bottoms or submerged logs. |
| Red Piranha | Pygocentrus nattereri | 35 | Rivers, lakes, and flooded plains. Abundant and widespread. |
| Cachara | Pseudoplatystoma fasciatum | 120 | Large rivers, tributaries, and associated lagoons. Often found in faster currents. |
| Piraputanga | Brycon hilarii | 60 | Clear, flowing rivers and streams (corixos), especially near gallery forests. |
| Tucunaré | Cichla piquiti | 80 | Lakes, lagoons, and slow-moving river sections, preferring clear water with structure. |
| Traíra | Hoplias malabaricus | 65 | Shallow, slow-moving or stagnant waters with dense vegetation, like lakes and marshes. |
| Curimbatá | Prochilodus lineatus | 80 | Rivers, streams, and flooded areas. Highly migratory and forms large schools. |
| Piapara | Leporinus elongatus | 80 | Main river channels and tributaries, prefers moderate to fast currents. |
| Piau | Schizodon borellii | 40 | Rivers, streams, and lagoons with abundant vegetation. Often in schools. |
| Armado | Pterodoras granulosus | 70 | Deep channels of large rivers. Nocturnal and bottom-dwelling. |
| Barbado | Pinirampus pirinampu | 120 | Deep river channels, often found in areas with moderate to strong currents. |
| Jurupoca | Hemisorubim platyrhynchos | 55 | Open waters of rivers and large lagoons, often near the surface at night. |
| South American Lungfish | Lepidosiren paradoxa | 125 | Swamps, marshes, and slow-moving waters with low oxygen levels. |
| Silver Arowana | Osteoglossum bicirrhosum | 100 | Surface of calm, blackwater rivers, swamps, and flooded forests. |
| Ocellate River Stingray | Potamotrygon motoro | 100 | Sandy or muddy bottoms of rivers, streams, and lagoons. |
| Electric Eel | Electrophorus varii | 180 | Slow-moving rivers, swamps, and stagnant pools with muddy bottoms. |
| Peixe-Cachorro | Acestrorhynchus pantaneiro | 40 | Open waters of rivers and lagoons, often found in schools. |
| Spotted Piranha | Serrasalmus maculatus | 30 | Lakes, rivers, and flooded areas. Extremely common and widespread. |
| Mandi | Pimelodus maculatus | 50 | Rivers and lagoons, often in schools near the bottom. |
| Bico-de-Pato | Sorubim lima | 60 | Rivers and lakes, often hovering motionlessly in vegetated areas. |
| Jacundá | Crenicichla lepidota | 25 | Shallow, clear waters with sandy bottoms and vegetation. Widespread in smaller streams. |
| Jundiá | Rhamdia quelen | 70 | Lakes, rivers, and streams, highly adaptable to various environments. |
| Black Skirt Tetra | Gymnocorymbus ternetzi | 8 | Slow-moving streams, tributaries, and flooded areas with dense vegetation. |
| Corvina | Plagioscion squamosissimus | 80 | Large rivers and lakes, prefers deeper, open water. |
| Oscar | Astronotus ocellatus | 45 | Slow-moving, clear water rivers and lagoons with submerged wood. |
| Jewel Tetra | Hyphessobrycon eques | 5 | Calm, slow-moving waters like lagoons and ponds with dense vegetation. |
| Armau | Megalodoras uranoscopus | 60 | Deep channels of large rivers, often found in woody debris. |
| Sardinha-de-rabo-amarelo | Astyanax altiparanae | 15 | Rivers, streams, and lagoons. Extremely abundant and widespread. |
| Tuvira | Gymnotus carapo | 75 | Shallow, heavily vegetated, slow-moving or stagnant waters. |
| Pati | Luciopimelodus pati | 100 | Deep channels of major rivers. Often found in turbid waters. |
| Black Piranha | Serrasalmus rhombeus | 45 | Deep river channels and lakes, often more solitary than other piranhas. |
| Cascudo | Hypostomus spp. | 50 | Attached to rocks, wood, and substrate in various flowing water habitats. |
| Sardinha | Triportheus paranensis | 20 | Surface of open waters in rivers and lagoons. Often in large schools. |
| Mandubé | Ageneiosus inermis | 55 | Rivers and lagoons, hides in woody debris or vegetation during the day. |
| Cangati | Trachelyopterus galeatus | 25 | Slow-moving waters with abundant cover like vegetation or leaf litter. |
| Cará | Gymnogeophagus balzanii | 20 | Slow-moving streams and lagoons with sandy or muddy bottoms. |
| Black Ghost Knifefish | Apteronotus albifrons | 50 | Fast-flowing, sandy-bottomed rivers. Strictly nocturnal. |
| Acará | Geophagus sveni | 25 | Clear or blackwater streams with sandy bottoms. |
| Falkner’s Stingray | Potamotrygon falkneri | 90 | Sandy and muddy bottoms in a variety of riverine habitats. |
| Peixe-Cão | Cynopotamus argenteus | 25 | Open waters of rivers and streams, often found in shoals. |
| Annual Killifish | Austrolebias nigripinnis | 8 | Temporary seasonal ponds and flooded grasslands that dry up completely. |
| Sardinha-larga | Pellona flavipinnis | 60 | Main channels of large rivers and associated lagoons. Often near the surface. |
| Boga | Leporinus friderici | 40 | Rivers and streams with moderate current, often near vegetation or rocks. |
| Piranha-branca | Serrasalmus brandtii | 25 | Rivers and lakes, often in clear water habitats. |
| Jurupensen | Sorubim maniradii | 45 | Slow-moving rivers and lakes, particularly in areas with submerged vegetation. |
| Canivete | Eigenmannia trilineata | 35 | Slow-moving, heavily vegetated waters. Strictly nocturnal. |
| Viola | Loricariichthys platymetopon | 40 | Sandy bottoms of rivers and streams with moderate current. |
| Borboleta | Carnegiella strigata | 4 | Surface of calm, slow-moving blackwater streams and swamps. |
| Pintadinho | Pimelodella gracilis | 20 | Various habitats, from small streams to large rivers. Often near the bottom. |
| Peixe-Vidro | Charax stenopterus | 15 | Quiet, vegetated waters of lagoons and slow-moving rivers. |
| Saicanga | Acestrorhynchus lacustris | 30 | Lakes, lagoons, and the margins of large rivers. |
| Cachorrinha | Oligosarcus pintoi | 15 | Small streams and the margins of larger rivers with vegetation. |
| Beijador | Geophagus brasiliensis | 28 | Adaptable to many habitats, including lagoons, rivers, and estuaries. |
| Tigre de Río | Salminus hilarii | 50 | Headwaters and clearer, faster-flowing tributaries. |
| Manjuba | Anchoviella pantaneira | 10 | Surface waters of large rivers and lagoons, forms vast schools. |
| Ituí-corpo-fino | Brachyhypopomus bombilla | 15 | Shallow, heavily vegetated areas and leaf litter in slow-moving waters. |
| Piaba | Moenkhausia sanctaefilomenae | 7 | Small streams and tributaries with clear water and some vegetation. |
| Traíra-Tigre | Hoplias intermedius | 80 | Main river channels and faster flowing waters than its common relative. |
| Peixe-Lápis | Nannostomus eques | 5 | Surface of calm, heavily vegetated, blackwater habitats. |
| Acará-severo | Heros efasciatus | 25 | Slow-moving rivers and pools with submerged tree roots and leaf litter. |
| Piau-flamengo | Leporinus octofasciatus | 30 | Rocky areas with fast-flowing water in clear rivers. |
| Limpa-vidro | Otocinclus vittatus | 4 | Attached to plants, wood, and other surfaces in slow-moving waters. |
| Borracha | Bunocephalus coracoideus | 15 | Bottom of slow-moving streams and swamps, buried in leaf litter. |
| Zebra Pleco | Hypancistrus zebra | 9 | Rocky rapids and fast-flowing, well-oxygenated waters. |
| Agulhinha | Potamorrhaphis eigenmanni | 25 | Surface of still or slow-flowing waters, often among floating plants. |
| Piracanjuba | Brycon orbignyanus | 80 | Main channels of large rivers. A migratory species. |
| Cascudo-abacaxi | Megalancistrus parananus | 60 | Deep, fast-flowing river channels with rocky bottoms. |
| Apistograma | Apistogramma commbrae | 6 | Shallow, slow-moving streams and pools with abundant leaf litter. |
| Dourado-prateado | Salminus hilarii | 50 | Clear headwater streams and rivers with moderate to fast current. |
| Bagre-Sapo | Pseudopimelodus bufonius | 25 | Bottom of rivers and streams, hiding among rocks and woody debris. |
| Canivete-marmorata | Steatogenys duidae | 25 | Slow-moving, sandy-bottomed streams with leaf litter. Nocturnal. |
| Arraia-maçã | Paratrygon aiereba | 160 | Sandy bottoms of large, deep rivers. |
| Coridora | Corydoras aeneus | 8 | Bottom of slow-moving, clear streams and tributaries with sandy substrate. |
| Cigarra | Laetacara dorsigera | 7 | Shallow, densely vegetated lagoons and stream margins. |
| Espada | Aphyocharax rathbuni | 5 | Middle to upper water layers in clear, slow-moving streams. |
| Piava | Megaleporinus macrocephalus | 60 | Main river channels and lagoons, often in schools. |
| Mocinha | Characidium G. anale | 10 | Fast-flowing, rocky riffles and rapids in clear streams. |
Images and Descriptions

Dourado
Known as the “river tiger,” this powerful golden-scaled predator is the Pantanal’s most iconic game fish. It’s famous for its aggressive strikes and acrobatic leaps when hooked, preying mainly on smaller fish like lambaris during its seasonal migrations.

Pintado
A giant migratory catfish with a flattened head and a body covered in distinct dark spots. This nocturnal hunter is a top predator and is highly prized by both sport and commercial fishers for its size, strength, and excellent taste.

Pacu
A large, deep-bodied fish with powerful, human-like molars used for crushing nuts and fruits. It plays a vital role as a seed disperser, venturing into flooded forests during high water to feed. It is a very important species for local cuisine.

Jaú
One of the true giants of the Pantanal, this massive, olive-brown catfish is a solitary bottom-dwelling predator. Known for its immense strength and slow growth, it’s a legendary catch for trophy anglers who seek out the river’s deepest holes to find it.

Red Piranha
The most famous fish of the Pantanal, easily identified by its powerful jaw and vibrant red belly. While having a fearsome reputation, it is primarily an opportunistic scavenger that forms schools for protection, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem’s clean-up crew.

Cachara
A large catfish closely related to the Pintado, but distinguished by dark vertical or oblique bars instead of spots. Like its cousin, the Cachara is a strong migratory predator, highly valued by anglers and a key part of the regional fishery.

Piraputanga
A beautiful silver-scaled fish with a bright orange-red tail and fins. It’s an omnivore known for leaping from the water to grab fruits and insects from overhanging trees. Tourists often see them in large schools at popular snorkeling spots.

Tucunaré
An introduced but now widespread apex predator, the blue peacock bass is famed for its aggressive behavior and fighting ability. It is easily recognized by its vibrant colors, body bars, and a distinct ocellus (eyespot) on its tail fin.

Traíra
A highly resilient and ambush predator with a cylindrical body, large mouth, and sharp teeth. The traíra can breathe atmospheric air, allowing it to survive in low-oxygen conditions. It’s a common catch for local anglers using surface lures.

Curimbatá
An essential species in the Pantanal’s food web, the curimbatá is a detritivore, feeding on organic matter and mud from the river bottom. It undertakes massive annual migrations (piracema) to spawn, forming the basis of many commercial fisheries.

Piapara
A powerful and streamlined fish known for its strong fight when hooked. It has a distinctive mouth structure for scraping algae and plants from rocks but will also eat insects and small fish. It’s a popular target for sport fishing.

Piau
A common, medium-sized fish with three dark spots along its silver flank. It’s primarily a herbivore, feeding on aquatic plants, algae, and terrestrial vegetation that falls into the water, making it important for controlling plant growth.

Armado
A robust catfish protected by a line of bony plates, or scutes, along its sides. Known for making audible grunting sounds, it is a detritivore and undertakes long reproductive migrations. Its flesh is appreciated in local dishes like ‘caldo de piranha’.

Barbado
A large, silvery catfish with extremely long barbels that can reach its tail fin. It is a nocturnal predator that uses its sensitive barbels to locate prey on the riverbed. It is an important species for both sport and commercial fishing.
Jurupoca
A uniquely shaped catfish with a very long, shovel-like snout, giving it the name “turtle-nose catfish”. It is a nocturnal predator that feeds on smaller fish in open water. Its unusual appearance makes it a fascinating find for anglers.

South American Lungfish
A primitive, eel-like fish that is an obligate air-breather, possessing a single “lung”. During the dry season, it can survive by burrowing into the mud and entering a state of aestivation, breathing through a small air hole.

Silver Arowana
A prehistoric-looking surface-dweller with large, silvery scales and a drawbridge-like mouth. It is an adept jumper, known to leap out of the water to catch insects, small birds, and bats from overhanging branches. It is a mouthbrooder.

Ocellate River Stingray
A freshwater stingray easily identified by its disc-shaped body covered in vibrant orange spots with black rings. It spends most of its time buried in the sand, ambushing small fish and invertebrates, and possesses a venomous tail barb for defense.
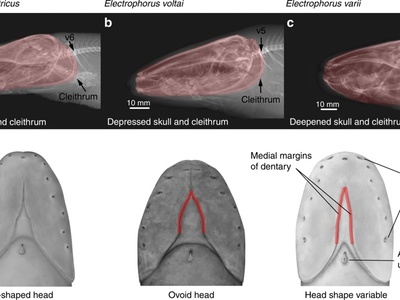
Electric Eel
Not a true eel, but a type of knifefish capable of generating powerful electric shocks up to 860 volts to stun prey and deter predators. It is an air-breather, needing to surface regularly, and navigates murky waters using a low-voltage electric field.
Peixe-Cachorro
A swift, slender predator known as the “dog fish” due to its prominent, sharp canine teeth that protrude even when its mouth is closed. It hunts in packs, preying on smaller fish like lambaris with incredible speed and agility.

Spotted Piranha
A common piranha species often found alongside the Red Piranha. It is distinguished by its silvery body covered in dark spots and a more solitary or small-group behavior compared to its red-bellied cousin. It is an opportunistic carnivore.

Mandi
A medium-sized catfish recognized by its silvery body with large, distinct dark spots and long barbels. It’s a common catch for both subsistence and sport fishers and is known for the sharp, serrated spines on its dorsal and pectoral fins.

Bico-de-Pato
Named “duck-beak” for its distinctly long and flattened snout, this slender catfish is a master of camouflage. It ambushes smaller fish from cover in weedy areas. It is nocturnal and often found in small groups.

Jacundá
A colorful and aggressive cichlid, also known as a pike cichlid, with an elongated body built for ambush predation. It exhibits complex parental care, with both parents guarding their eggs and fry fiercely against any perceived threat.

Jundiá
A common, dark-colored catfish with a broad head and a stout body. It is a resilient and opportunistic omnivore, feeding on anything from insects and fish to fruits. It is widely used in aquaculture and is a common catch for local anglers.

Black Skirt Tetra
A popular aquarium fish native to the Pantanal, known for its distinct black dorsal and anal fins that look like a flowing skirt. In the wild, they are shoaling fish that feed on small insects, worms, and crustaceans.

Corvina
A freshwater drum that looks much like its marine relatives. It uses special muscles attached to its swim bladder to produce distinct “croaking” sounds, especially during mating season. It is a predator of small fish and shrimp.

Oscar
Known locally as Apaiari, this large and intelligent cichlid is a popular aquarium species worldwide. Wild Oscars have a distinct red-ringed eyespot on their tail to confuse predators and are devoted parents that protect their young.

Jewel Tetra
A small, brightly colored tetra known for its deep red body and a prominent black mark behind the gill plate. They are peaceful shoaling fish, often seen fluttering in large groups through submerged plants, feeding on tiny invertebrates.

Armau
Also known as the Giant Raphael Catfish, this species is heavily armored with sharp, hook-like bony plates. It is a nocturnal omnivore that primarily feeds on fruits (especially palms) and snails, which it crushes with its powerful jaws.

Sardinha-de-rabo-amarelo
A common small tetra, known as the yellow-tailed lambari. They form massive schools and are a fundamental food source for larger predators like Dourado, piranhas, and birds. They are omnivorous and feed voraciously on insects, algae, and organic debris.

Tuvira
A nocturnal knifefish with an elongated, eel-like body that navigates and finds food in murky water by generating a weak electric field. It moves by undulating its long anal fin, allowing it to swim forwards and backwards with equal ease.

Pati
A large, migratory catfish with a silvery body and a distinctive forked tail. It is a nocturnal predator, feeding on fish and invertebrates on the river bottom. It is an important species in the commercial fisheries of the Paraguay River basin.

Black Piranha
The largest species of piranha, the black piranha is a powerful predator with a fearsome reputation. As it matures, its body darkens to a deep grey or black. It is a formidable hunter, capable of taking chunks out of larger fish.

Cascudo
This is a general name for many species of armored suckermouth catfishes. They are vital algae-eaters and detritivores, using their specialized mouths to scrape surfaces clean. Their bony plates provide excellent protection from predators.

Sardinha
A silvery, hatchet-shaped fish that lives near the surface, feeding on insects, zooplankton, and plant matter. Its enlarged pectoral fins allow it to make short leaps out of the water to escape predators or catch insects.

Mandubé
A unique-looking catfish where the males have a modified, enlarged maxillary barbel that is used to hold the female during courtship. It is a nocturnal predator that feeds on smaller fish and crustaceans.

Cangati
A small, dark-colored driftwood catfish that is nocturnal and reclusive. It is known for its ability to produce audible squeaking sounds when captured or distressed. It feeds primarily on aquatic insects and small crustaceans.

Cará
A beautiful cichlid where mature males develop a prominent nuchal hump on their foreheads. They are substrate sifters, taking mouthfuls of sand to filter out small invertebrates. They are also known for their dedicated parental care.

Black Ghost Knifefish
Known locally as Ituí-cavalo, this fish navigates and hunts in total darkness using a weak electrical field. It swims by undulating its long anal fin, giving it a ghostly, flowing appearance. It is a popular, though delicate, aquarium species.

Acará
An “eartheater” cichlid that spends its day sifting through sand for small invertebrates and organic matter. It is a peaceful fish recognized by its iridescent scales and elongated fin rays. It practices biparental mouthbrooding to protect its young.

Falkner’s Stingray
A large freshwater stingray with a highly variable pattern, ranging from spots to intricate vermiculated or ocellated markings. Like other rays, it has a venomous tail spine and should be handled with extreme care. It feeds on fish and invertebrates.

Peixe-Cão
A characin with a silvery, compressed body and a mouth full of sharp, canine-like teeth, similar to the Peixe-Cachorro but generally smaller. It is a fast-moving predator that feeds on smaller fish and insects.

Annual Killifish
A remarkable fish with an annual life cycle. It grows rapidly, reproduces, and lays drought-resistant eggs in the mud before its pond habitat disappears in the dry season. The embryos wait in diapause until the next rains to hatch.

Sardinha-larga
A freshwater herring with a deep, compressed, silvery body. It forms schools in open water and feeds primarily on small fish and crustaceans. It is an important prey species for larger predators like the Dourado.

Boga
A common and widespread species of Leporinus, characterized by its elongated body and downward-pointing mouth. It is an omnivore, adept at scraping algae from surfaces but also consuming insects, seeds, and small fish.

Piranha-branca
Also known as the white piranha, this species has a more elongated snout compared to other piranhas. It is a fin-nipper when young, transitioning to a more predatory diet on whole fish as it matures. It is generally less aggressive than the red piranha.

Jurupensen
A smaller relative of the Bico-de-pato, this catfish also has a distinctive long, flat snout. It is a camouflaged ambush predator that often rests vertically among aquatic plants, waiting for unsuspecting small fish to pass by.

Canivete
A type of glass knifefish that is semi-transparent, allowing its organs to be faintly visible. It uses a weak electric organ for navigation and communication. It often hides in dense vegetation or rock crevices during the day.

Viola
A type of armored catfish with a flattened, slender body, resembling a violin or “viola” in Portuguese. It buries itself in the sand with only its eyes protruding, ambushing small invertebrates that drift by.

Borboleta
A freshwater hatchetfish with a deeply compressed, axe-shaped body. It has powerful pectoral muscles that allow it to leap from the water and “fly” for short distances to escape predators or catch terrestrial insects, a truly unique adaptation.

Pintadinho
A small, slender catfish with long barbels and a prominent dark lateral stripe running the length of its body. It is a common, nocturnal omnivore that feeds on insects, small crustaceans, and organic debris.

Peixe-Vidro
Known as the glass headstander, this small tetra often swims at a peculiar head-down angle. Its body is somewhat translucent, hence the name “glass fish”. It is a micro-predator, feeding on tiny invertebrates among the plants.

Saicanga
Another species of “peixe-cachorro,” this swift predator is common in the Pantanal’s lentic environments. It has the characteristic prominent canine teeth of its genus and hunts smaller fish in open-water schools.

Cachorrinha
A small, active characin that is a voracious predator despite its size. With a streamlined body and sharp teeth, it preys on insects and the fins or scales of other fish. It is often found in small, aggressive groups.

Beijador
Known as the Pearl Cichlid, this species is named “kisser” (beijador) for its mouth-to-mouth fighting behavior. It is an “eartheater” that sifts sand for food and is known for its beautiful iridescent blue-green spots.

Tigre de Río
A smaller cousin of the Dourado, this fish shares the same predatory nature and golden sheen but prefers smaller river environments. It has a distinct dark spot behind the gill cover and is an agile hunter of smaller fish.

Manjuba
A small, silvery freshwater anchovy that is a crucial link in the food web. These plankton-feeders form immense schools that are constantly hunted by a wide variety of larger fish and fish-eating birds like terns and kingfishers.

Ituí-corpo-fino
A small, blunt-nosed knifefish that is an expert at hiding. Like its larger relatives, it uses a weak electric field to navigate and find insect larvae and other small invertebrates in complex, dark environments at night.

Piaba
The Redeye Tetra is a popular aquarium fish found in the Pantanal. It’s a peaceful, shoaling species recognized by its silvery body and a bright red iris. In the wild, it feeds on small insects and crustaceans.

Traíra-Tigre
A larger, more robust species of traíra that prefers riverine environments. It is a powerful ambush predator with a mottled, tiger-like pattern that provides camouflage against the riverbed. It preys on large fish, crabs, and amphibians.

Peixe-Lápis
A small, slender characin known as the hockeystick pencilfish. It swims at a distinct oblique, nose-up angle and lives near the surface, picking small insects and invertebrates from plants and the water’s surface.

Acará-severo
The Severum is a beautiful, disc-shaped cichlid that is a popular aquarium fish. It is a peaceful omnivore, feeding on plant matter, fruits, and small invertebrates. Parents are known to be highly dedicated to their young.

Piau-flamengo
A stunningly beautiful fish with alternating black and yellow-orange vertical bands, resembling the uniform of the Flamengo football team. It is a specialized herbivore that scrapes algae and biofilm from submerged rocks.

Limpa-vidro
A tiny, peaceful suckermouth catfish known as the “window cleaner”. It is a tireless algae-eater, often found in groups, and is a popular addition to aquariums for its cleaning abilities and small size.

Borracha
The Banjo Catfish has a flattened head and a mottled brown, warty body that perfectly mimics a dead leaf. It is a sedentary, nocturnal ambush predator, lying motionless on the bottom until a small invertebrate or fish comes within reach.

Zebra Pleco
An iconic and critically endangered ornamental fish known for its striking black and white striped pattern. While more famous from the Xingu River, populations have been recorded in the Pantanal’s headwaters. It is a prized but protected species.

Agulhinha
A freshwater needlefish with a long, slender body and a beak-like jaw. It is a surface-dwelling predator that feeds on terrestrial insects that fall onto the water and small aquatic invertebrates. Its shape provides excellent camouflage.

Piracanjuba
A large, powerful characin similar to the Piraputanga but with a more silvery appearance and yellowish fins. It is an omnivore with a preference for fruits, seeds, and insects. Its populations have declined, making it a conservation concern.

Cascudo-abacaxi
Known as the “pineapple pleco” due to its large, spiny, and heavily armored body. This is one of the largest Loricariid catfishes. It is an omnivore, feeding on algae, invertebrates, and carrion.

Apistograma
A dwarf cichlid that exhibits fascinating social behavior and parental care. The males are larger and more colorful than the females. They sift through detritus on the bottom to find small crustaceans and insect larvae.

Dourado-prateado
A smaller relative of the famous golden Dourado, this “silver dourado” is also a voracious predator. It is more slender and silvery, adapted to hunting in the smaller, clearer streams of the Pantanal highlands.
Bagre-Sapo
The “toad-catfish” has a broad, flattened head and a mottled pattern that camouflages it perfectly on the riverbed. It is a sedentary ambush predator with a huge mouth, capable of swallowing surprisingly large prey.

Canivete-marmorata
A beautiful knifefish with a marbled or blotched pattern. It uses its weak electric sense to probe the sandy substrate for buried insect larvae and worms. It spends the day hidden in the sand or under leaves.

Arraia-maçã
The “apple stingray” is a giant of the Pantanal’s freshwater ray family, potentially reaching over a meter in disc width. It has a more rounded, apple-like disc shape and is a powerful predator of fish, crabs, and snails.

Coridora
A small, peaceful, and social armored catfish that is a very popular aquarium species. In the wild, they are bottom-dwellers that search for worms and small crustaceans in the sand using their sensitive barbels. They often dash to the surface to gulp air.

Cigarra
The Red-breasted Acara is a small, colorful cichlid. During breeding, the male and female display a vibrant red coloration on their “chest”. They are peaceful fish that form monogamous pairs and provide dedicated care for their offspring.

Espada
The Rathbun’s Bloodfin is a small tetra with a striking red coloration on its fins and tail. It is a peaceful, shoaling fish that adds a splash of color to the vegetated margins of Pantanal streams.

Piava
A large and robust species of herbivorous characin. It is an important species for commercial and subsistence fisheries. It has powerful jaws adapted for feeding on tough vegetation and seeds.

Mocinha
A small, bottom-oriented characin known as a darter tetra. It uses its large pectoral fins to hold its position in strong currents, darting between rocks to prey on insect larvae. Its mottled pattern provides excellent camouflage.





