Temperate grasslands stretch from North American prairies to Eurasian steppes and parts of southern Africa, creating wide-open habitats shaped by seasonal climate, grazing, and fire. Those conditions favor a distinctive mix of herbivores, predators, and omnivores adapted to life on the plains.
There are 40 Temperate Grasslands Consumers, ranging from Aardvark to Wedge-tailed Eagle. For each species you’ll find the Scientific name, Trophic role, Region — details you’ll find below.
Which consumers am I most likely to encounter in a given region?
It depends on where you are: North American grasslands favor bison, pronghorn and prairie dogs plus coyotes and raptors, while Eurasian steppes include saiga, marmots and steppe eagles; southern African grasslands show different grazers and insectivores. Check the Region column below to narrow the list to your area.
How can this list be useful for studying food webs or conservation?
Use the Scientific name to avoid confusion, the Trophic role to map feeding interactions, and the Region to focus on local communities; together these columns let you identify key consumers, flag potential keystone species, and prioritize monitoring or habitat management below.
Temperate Grasslands Consumers
| Name | Scientific name | Trophic role | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Bison | Bison bison | Primary consumer (herbivore) | North American prairies |
| Pronghorn | Antilocapra americana | Primary consumer (herbivore) | North American prairies |
| Black-tailed Prairie Dog | Cynomys ludovicianus | Primary consumer (herbivore) | North American prairies |
| Saiga Antelope | Saiga tatarica | Primary consumer (herbivore) | Eurasian steppe |
| Przewalski’s Horse | Equus ferus przewalskii | Primary consumer (herbivore) | Eurasian steppe |
| Guanaco | Lama guanicoe | Primary consumer (herbivore) | South American pampas & Patagonia |
| Pampas Deer | Ozotoceros bezoarticus | Primary consumer (herbivore) | South American pampas |
| Viscacha | Lagostomus maximus | Primary consumer (herbivore) | South American pampas |
| Eastern Grey Kangaroo | Macropus giganteus | Primary consumer (herbivore) | Australian temperate grasslands |
| Black Wildebeest | Connochaetes gnou | Primary consumer (herbivore) | South African highveld |
| Grasshopper | Order Orthoptera | Primary consumer (herbivore) | Grasslands worldwide |
| Thirteen-lined Ground Squirrel | Ictidomys tridecemlineatus | Primary/secondary consumer (omnivore) | North American prairies |
| Coyote | Canis latrans | Secondary/tertiary consumer (omnivore) | North American prairies |
| American Badger | Taxidea taxus | Secondary consumer (carnivore/omnivore) | North American prairies |
| Striped Skunk | Mephitis mephitis | Primary/secondary consumer (omnivore) | North American prairies |
| Maned Wolf | Chrysocyon brachyurus | Primary/secondary consumer (omnivore) | South American grasslands (Cerrado) |
| Greater Rhea | Rhea americana | Primary/secondary consumer (omnivore) | South American pampas |
| Emu | Dromaius novaehollandiae | Primary/secondary consumer (omnivore) | Australian grasslands |
| Aardvark | Orycteropus afer | Secondary consumer (insectivore) | African veld & savanna |
| Bat-eared Fox | Otocyon megalotis | Secondary consumer (insectivore) | African veld |
| Black-footed Ferret | Mustela nigripes | Secondary/tertiary consumer (carnivore) | North American prairies |
| Swift Fox | Vulpes velox | Secondary consumer (omnivore/carnivore) | North American prairies |
| Ferruginous Hawk | Buteo regalis | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | North American prairies |
| Prairie Rattlesnake | Crotalus viridis | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | North American prairies |
| Gray Wolf | Canis lupus | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | North American prairies & Eurasian steppe |
| Steppe Eagle | Aquila nipalensis | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | Eurasian steppe |
| Pallas’s Cat | Otocolobus manul | Secondary consumer (carnivore) | Eurasian steppe |
| Puma | Puma concolor | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | North & South American grasslands |
| Pampas Fox | Lycalopex gymnocercus | Secondary consumer (omnivore/carnivore) | South American pampas |
| Geoffroy’s Cat | Leopardus geoffroyi | Secondary consumer (carnivore) | South American pampas |
| Secretarybird | Sagittarius serpentarius | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | African veld |
| Caracal | Caracal caracal | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | African veld |
| Wedge-tailed Eagle | Aquila audax | Tertiary consumer (carnivore) | Australian grasslands |
| Turkey Vulture | Cathartes aura | Decomposer (scavenger) | North & South American grasslands |
| Dung Beetle | Family Scarabaeidae | Decomposer (detritivore) | Grasslands worldwide |
| Earthworm | Class Oligochaeta | Decomposer (detritivore) | Grasslands worldwide |
| Termite | Order Isoptera | Primary consumer & decomposer | Grasslands in warmer regions |
| American Burying Beetle | Nicrophorus americanus | Decomposer (detritivore) | North American prairies |
| Southern Caracara | Caracara plancus | Secondary consumer & decomposer | South American pampas |
| Black-backed Jackal | Lupulella mesomelas | Secondary consumer & decomposer | African veld |
Images and Descriptions

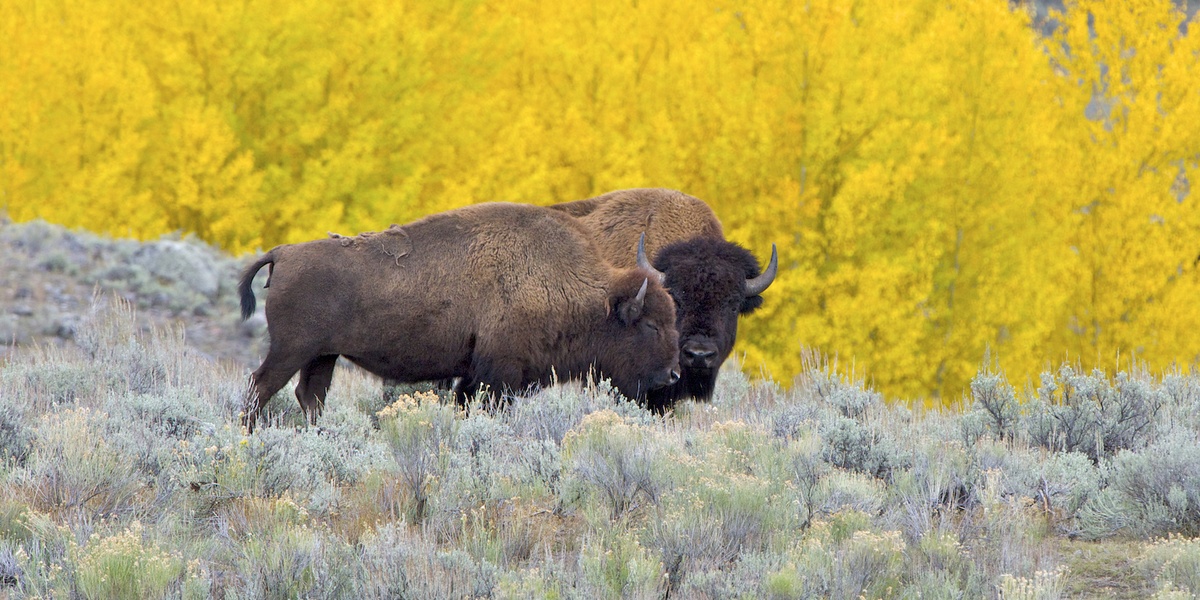
American Bison
A keystone grazer that shapes the entire ecosystem. By eating grasses and trampling the ground, bison create diverse habitats that benefit countless other plants and animals, making them essential grassland engineers.

Pronghorn
The fastest land animal in North America, the pronghorn is a browser that feeds on forbs and shrubs. Its incredible speed is a defense against predators that once roamed the continent, like the American cheetah.

Black-tailed Prairie Dog
These highly social rodents live in vast underground “towns” and are a keystone species. Their burrows provide homes for other animals, and they are a primary food source for predators like the black-footed ferret.

Saiga Antelope
Known for its unique, oversized nose that warms frigid air, the critically endangered saiga grazes on various grasses and herbs. It migrates in large herds, playing a vital role in the steppe food web.

Przewalski’s Horse
The last truly wild horse, this endangered species grazes on steppe vegetation. Reintroduction programs are helping it reclaim its ancestral role as a key grazer, influencing plant communities and enriching the ecosystem.

Guanaco
A wild relative of the llama, the guanaco is a resilient herbivore adapted to the open pampas. It grazes on tough grasses and acts as an important prey species for pumas and other large predators.

Pampas Deer
A slender, graceful deer native to the grasslands of South America. It feeds selectively on high-quality grasses and forbs, making it an important herbivore in a rapidly shrinking habitat due to agriculture.

Viscacha
A large, social rodent resembling a long-tailed rabbit, the viscacha lives in extensive burrow systems. It forages at night on grasses and seeds, and its digging aerates the soil, impacting plant life.

Eastern Grey Kangaroo
A common sight in eastern Australia, this marsupial is a grazer that feeds primarily on grasses. Kangaroos play a role similar to deer or antelope in other continents, shaping vegetation through their feeding habits.

Black Wildebeest
Also known as the white-tailed gnu, this antelope is a bulk grazer, consuming large quantities of grass. Its herds are a key part of the food chain, supporting predators and shaping the grassland landscape.

Grasshopper
An abundant and critical primary consumer, grasshoppers feed on a wide variety of plants. They are a fundamental food source for birds, reptiles, and mammals, linking plant energy to higher trophic levels.

Thirteen-lined Ground Squirrel
This distinctively striped squirrel eats seeds, leaves, and insects. Its burrowing activity aerates the soil, and it serves as a common prey item for hawks, snakes, and coyotes, making it a key link in the food web.

Coyote
Highly adaptable, the coyote eats almost anything from fruits and insects to rodents and deer fawns. As a key predator and scavenger, it helps regulate small mammal populations and keep the ecosystem clean.

American Badger
A powerful digger, the badger is a formidable predator of burrowing animals like prairie dogs and ground squirrels. Its abandoned burrows often become shelters for other species like swift foxes and burrowing owls.

Striped Skunk
Famous for its chemical defense, the skunk is an opportunistic omnivore. It forages for insects, grubs, small rodents, eggs, and plants, helping to control pest populations and dispersing seeds.

Maned Wolf
Despite its name, it’s not a true wolf. This long-legged canid eats small animals like rodents and birds, but over 50% of its diet consists of fruit, making it an important seed disperser in its habitat.

Greater Rhea
South America’s largest bird, the flightless rhea is an omnivore that consumes broad-leaved plants, seeds, fruits, and insects. It travels in flocks and plays a role similar to the emu or ostrich on other continents.

Emu
Australia’s largest bird, the emu forages for a wide variety of plants, seeds, fruits, and insects. Its long-distance travel makes it a crucial long-range seed disperser, helping maintain plant genetic diversity.

Aardvark
A unique nocturnal mammal, the aardvark uses its powerful claws and long snout to dig into termite mounds and ant nests. Its digging aerates dense soils and its abandoned burrows provide homes for many other animals.

Bat-eared Fox
Named for its enormous ears, this fox specializes in eating insects, particularly termites and dung beetles. Its ears help it locate insects underground, and it plays a major role in controlling insect populations.

Black-footed Ferret
One of North America’s most endangered mammals, this specialist predator relies almost exclusively on prairie dogs for food and their burrows for shelter. Its survival is directly tied to healthy prairie dog colonies.

Swift Fox
This small, swift fox preys on rodents, rabbits, and insects. It is heavily reliant on open prairie landscapes and often uses dens dug by other animals like badgers, highlighting the interconnectedness of grassland species.

Ferruginous Hawk
The largest hawk in North America, this powerful raptor is a top predator of the open plains. It primarily hunts prairie dogs, ground squirrels, and jackrabbits, helping to control rodent populations from above.

Prairie Rattlesnake
A pit viper that uses heat-sensing pits to hunt rodents and other small mammals in their burrows. As a key mid-level predator, it helps control small animal populations and is, in turn, prey for hawks and eagles.

Gray Wolf
An apex predator that hunts in packs to take down large herbivores like bison, elk, and deer. By regulating herbivore populations, wolves create a cascading effect that improves the health of the entire ecosystem.

Steppe Eagle
A large, powerful bird of prey that hunts small mammals like ground squirrels (susliks) and other rodents on the open steppe. It is a vital apex predator, controlling rodent populations across its vast range.

Pallas’s Cat
This small, flat-faced wildcat is a master of camouflage in the rocky steppes. It is a specialist hunter of small rodents like pikas and voles, playing a key role as a mid-level predator in its harsh environment.

Puma
Also known as the cougar or mountain lion, this adaptable apex predator hunts in grasslands and other habitats. Its prey includes everything from deer and guanacos to smaller animals, making it a critical regulator of herbivore populations.

Pampas Fox
A common fox of the pampas, it has a varied diet of rodents, birds, insects, and fruits. Its adaptability allows it to thrive in modified habitats, where it helps control pest species and disperse seeds.

Geoffroy’s Cat
A small, spotted wildcat that is an agile hunter of rodents, small birds, and lizards in the grasslands. As a nocturnal predator, it helps to keep populations of small animals in check, filling an important niche.

Secretarybird
This unique, long-legged bird of prey hunts on foot, famously stomping on snakes and other small animals. It is a conspicuous and important predator of the open African grasslands, keeping reptile and rodent numbers in balance.

Caracal
A medium-sized wildcat known for its incredible leaping ability, used to catch birds in mid-air. It also hunts rodents and small antelopes, acting as a stealthy and effective predator in the grasslands.

Wedge-tailed Eagle
Australia’s largest bird of prey, this eagle is an apex predator that hunts a wide range of animals, including rabbits, kangaroos, and reptiles. It also scavenges, playing a dual role as a hunter and a cleaner.

Turkey Vulture
The ultimate recycler, the turkey vulture uses its keen sense of smell to locate carrion. By cleaning up dead animals, it prevents the spread of disease and efficiently returns nutrients back into the ecosystem.

Dung Beetle
These remarkable insects are crucial decomposers, breaking down animal waste. By burying dung for food and nesting, they aerate the soil, recycle nutrients, and help control fly populations, supporting pasture health.

Earthworm
These subterranean ecosystem engineers are vital for soil health. They decompose dead organic matter, aerate the soil with their burrows, and mix nutrients, creating the fertile soil that underpins the entire grassland ecosystem.

Termite
Termites are major decomposers, breaking down tough plant fibers like wood and dead grass that other organisms cannot digest. They create nutrient-rich soil and their mounds can become habitat for other species.
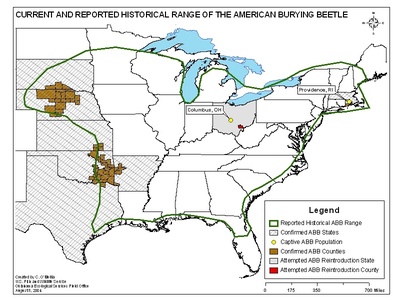
American Burying Beetle
This critically endangered beetle plays a unique role by finding small dead animals, burying them, and using the carcass to raise its young. This process efficiently recycles nutrients and enriches the soil.

Southern Caracara
An opportunistic raptor that is both a predator and a scavenger. It walks on the ground to find insects and small animals but also feeds on carrion, acting as a versatile cleanup crew on the pampas.

Black-backed Jackal
A highly adaptable canid that is a skilled hunter of small mammals and birds. It is also an important scavenger, often following larger predators to clean up kills, playing a key role in nutrient cycling.