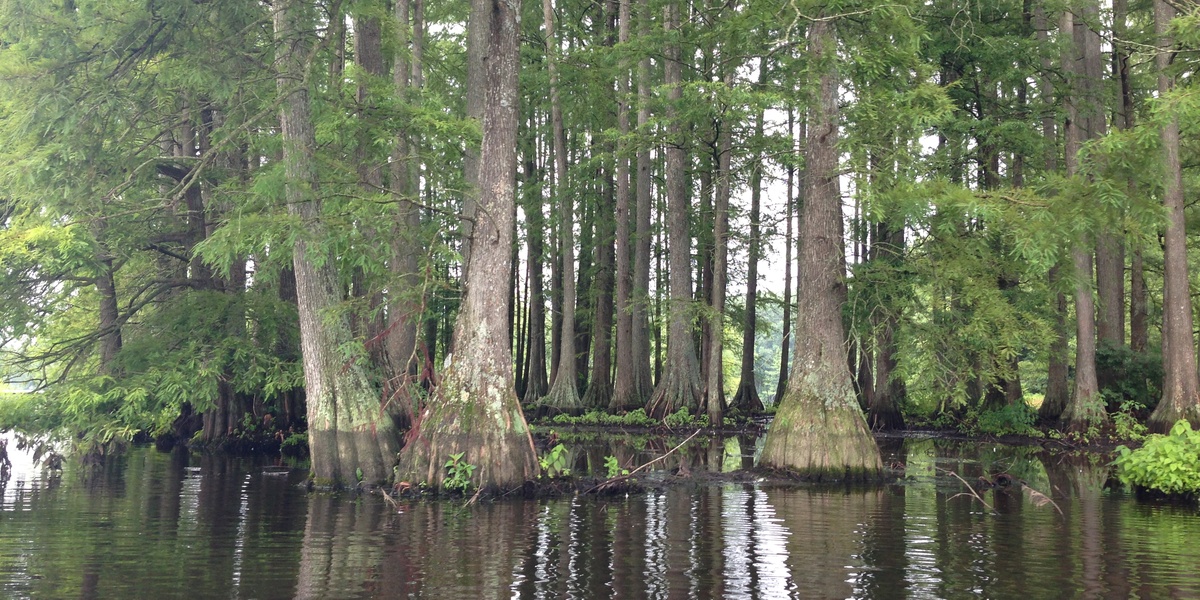
Florida’s swamps are a mosaic of standing water, peat, and tree islands where plants tolerate flooded soil, shifting seasons, and salty edges near the coast. These wetlands shape local ecosystems, provide habitat for birds and amphibians, and influence water quality across the state.
There are 49 florida swamp plants, ranging from Arrowhead to Yaupon. Each entry includes Scientific name,Height (cm),Habitat & range to help with identification and distribution; details are listed below.
How can I tell similar swamp plants apart in the field?
Look at a combination of features rather than one trait: leaf shape and size, flower structure, growth habit (emergent, floating, shrub), and typical habitat. Use the Scientific name and Height (cm) in the list to narrow possibilities, then confirm with Habitat & range and photos or a local field guide.
Should I be worried about poisonous or invasive species among these plants?
Some native swamp plants contain toxins (e.g., sap or seeds) and some non-natives can be invasive, altering hydrology and crowding natives. Use the list to check Habitat & range, avoid handling unknown plants, and consult local extension services before removing or planting species.
Florida Swamp Plants
| Common name | Scientific name | Height (cm) | Habitat & range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bald cypress | Taxodium distichum | 1,500-3,500 cm | Deep to seasonally flooded swamps statewide |
| Pond cypress | Taxodium ascendens | 1,200-2,500 cm | Cypress domes and acidic ponds central & south FL |
| Water tupelo | Nyssa aquatica | 1,200-2,500 cm | Floodplain swamps and riverbanks statewide |
| Swamp blackgum | Nyssa biflora | 800-1,500 cm | Wet flats and floodplain understory statewide |
| Red maple | Acer rubrum | 800-1,800 cm | Floodplain swamps and wet flatwoods statewide |
| Sweetbay magnolia | Magnolia virginiana | 500-900 cm | Hydric hammocks and swamp edges statewide |
| Swamp bay | Persea palustris | 600-1,800 cm | Fresh and brackish swamps coastal plains |
| Pond apple | Annona glabra | 400-1,000 cm | Brackish/fresh swamps, south Florida |
| Sweetgum | Liquidambar styraciflua | 1,200-2,000 cm | Bottomland swamps and floodplains north & central FL |
| Water elm | Planera aquatica | 600-1,200 cm | Swamp margins and streambanks statewide |
| Carolina ash | Fraxinus caroliniana | 500-1,800 cm | Swamps and wet hammocks southern FL |
| Black willow | Salix nigra | 500-1,500 cm | Stream banks and swamp edges statewide |
| Buttonbush | Cephalanthus occidentalis | 100-400 cm | Standing water edges, ponds, marshes statewide |
| Wax myrtle | Morella cerifera | 200-600 cm | Bayheads, swamp edges, and coastal wetlands statewide |
| Dahoon holly | Ilex cassine | 200-700 cm | Bayheads, swamp hammocks, coastal swamps south FL |
| Yaupon | Ilex vomitoria | 200-700 cm | Moist hammocks and swamp edges statewide |
| Swamp titi | Cyrilla racemiflora | 200-500 cm | Acid bogs, bayheads, and pocosins north & central FL |
| Virginia sweetspire | Itea virginica | 60-120 cm | Moist swamp margins and wet thickets statewide |
| Sawgrass | Cladium jamaicense | 50-300 cm | Freshwater marshes and seasonally flooded sloughs statewide |
| Maidencane | Panicum hemitomon | 100-200 cm | Freshwater marshes, sloughs, and wet prairies statewide |
| Cattail | Typha domingensis | 100-300 cm | Pond margins and shallow marshes statewide |
| Pickerelweed | Pontederia cordata | 30-100 cm | Shallow water, pond margins, and swamp pools statewide |
| Arrowhead | Sagittaria latifolia | 30-100 cm | Muddy shallows and pond edges in swamps statewide |
| Water lily | Nymphaea odorata | 5-50 cm | Floating mats in ponds and swamp pools statewide |
| Duckweed | Lemna minor | 0.1-0.5 cm | Surface mats on still water in swamps statewide |
| Hydrilla | Hydrilla verticillata | 10-200 cm | Submerged in slow-moving swamp waters, invasive statewide |
| Tape grass | Vallisneria americana | 20-200 cm | Submerged beds in clear freshwater pools and sloughs statewide |
| Blue flag iris | Iris virginica | 40-100 cm | Shallow water and wet soils in swamps statewide |
| Swamp milkweed | Asclepias incarnata | 80-150 cm | Wet meadows, ditchbanks, and swamp edges statewide |
| Joe-Pye weed | Eutrochium fistulosum | 150-300 cm | Wet thickets and swamp margins statewide |
| Swamp rose | Rosa palustris | 100-200 cm | Shrubby edges and wet thickets north & central FL |
| Cinnamon fern | Osmunda cinnamomea | 60-150 cm | Moist swamp thickets and seepage slopes statewide |
| Royal fern | Osmunda regalis | 60-150 cm | Bogs, swamps, and seepage wetlands north & central FL |
| Marsh fern | Thelypteris palustris | 30-90 cm | Marshes and swamp margins statewide |
| Woolgrass | Scirpus cyperinus | 80-150 cm | Shallow marshes and wet meadow edges statewide |
| Soft rush | Juncus effusus | 50-100 cm | Shallow water, ditches, and swamp edges statewide |
| Sedge (Lurid sedge) | Carex lurida | 40-80 cm | Shallow water, mudflats, and swamp margins statewide |
| Smilax laurifolia (laurel greenbrier) | Smilax laurifolia | 200-600 cm | Dense thickets in wet woods and swamp understory statewide |
| Catbrier | Smilax bona-nox | 100-400 cm | Vines in wet woods and swamp edges statewide |
| Poison ivy | Toxicodendron radicans | 30-600 cm | Climbing vine or shrub on trees and swamp edges statewide |
| Red mangrove | Rhizophora mangle | 1,000-3,000 cm | Coastal brackish swamps and mangrove forests south FL |
| Black mangrove | Avicennia germinans | 500-1,500 cm | Upper intertidal/brackish swamps southern FL |
| White mangrove | Laguncularia racemosa | 500-1,200 cm | Upper tidal swamps and coastal hammocks southern FL |
| Smooth cordgrass | Spartina alterniflora | 50-140 cm | Brackish tidal swamps and estuarine marshes Florida coast |
| Rose mallow | Hibiscus moscheutos | 50-150 cm | Brackish marshes and coastal swamp edges north & central FL |
| Swamp sunflower | Helianthus angustifolius | 60-200 cm | Wet meadows, ditchbanks, and swamp margins statewide |
| Taro (naturalized) | Colocasia esculenta | 50-200 cm | Freshwater swamps, ditches, and wet pastures statewide |
| Japanese climbing fern (invasive) | Lygodium japonicum | 100-1,000 cm | Climbing in wet woods and swamp canopies statewide |
| Brazilian pepper (invasive) | Schinus terebinthifolius | 200-700 cm | Invades freshwater and brackish swamps statewide |
Images and Descriptions

Bald cypress
Iconic buttressed trunk and “knees”; feathery deciduous needles and stringy bark. Grows in standing water and slow rivers; key swamp canopy tree used for wildlife habitat and flood attenuation; easily identified by flared base and cone-like seedballs.

Pond cypress
Similar to bald cypress but more shrub-like in drier sites; needles often shorter and branches more clustered. Forms dense domes in acid bogs and blackwater ponds; tolerates long hydroperiods and is common in south Florida.

Water tupelo
Large wetland tree with swollen buttress and smooth gray bark; glossy ovate leaves and small drupes. Dominant in deep-water swamps, important for honey production and wildlife; often found with cypress in floodplains.

Swamp blackgum
Smaller tupelo with crooked trunk and elliptical leaves that turn red in fall. Prefers wet soils and pond margins; fruits feed birds and mammals, and trunks sometimes form buttresses in saturated soils.

Red maple
Versatile fast-growing tree with red buds and samara fruits; leaves often three-lobed. Common in wet depressions and swamp margins; tolerates variable water levels and shows early spring flowers.

Sweetbay magnolia
Small evergreen/deciduous magnolia with fragrant white cup-shaped flowers and glossy leaves; silvery underside on coastal forms. Frequent in swamp margins and bayheads, noted for sweet scent and tolerant of periodic flooding.

Swamp bay
Evergreen laurel with aromatic leaves and small fruits; bark smooth and reddish. Found in bayheads and swamp hammocks; salt-tolerant forms occur in coastal brackish swamps.

Pond apple
Tropical tree with large glossy leaves and bumpy fruit; often forms dense thickets in south Florida wetlands. Considered invasive/established non-native in places; found in standing water and mangrove edges.

Sweetgum
Distinct star-shaped leaves and spiky gumballs; brilliant fall color in drier years. Found along swamp margins and floodplains, often on slightly higher hummocks within wet forests.

Water elm
Small wetland tree with rough bark and oblong serrated leaves; tolerant of prolonged flooding. Occurs in wet hardwood swamps and mixed floodplain forests, often alongside tupelo and cypress.

Carolina ash
Medium tree with pinnate leaves and samaras; tolerates seasonal flooding. Found in hydric hammocks and swampy sites in peninsular Florida; flowers in spring before leaf-out.

Black willow
Fast-growing willow with narrow lanceolate leaves and rough bark; catkins appear early spring. Common along waterways and in floodplains, easily identified by pliant branches and willow shoots.

Buttonbush
Showy spherical clusters of white tubular flowers attract bees and butterflies. Broad-leaved shrub found in inundated soils and pond margins; stems often tinged red and seedheads persist into winter.

Wax myrtle
Aromatic evergreen shrub with waxy berries used by birds; leaves variable, sometimes lobed. Forms dense thickets in hydric sites and provides cover and winter food for wildlife.

Dahoon holly
Evergreen holly with glossy leaves and red berries; prefers wet, acidic soils. Common in southern bayheads and swamp margins; berries feed birds and are notable in winter.

Yaupon
Evergreen shrub/tree with small serrated leaves and black berries. Tolerant of wet soils but also upland; used historically for tea, forms dense thickets in margins of swamps.

Swamp titi
Evergreen shrub/tree with racemes of white flowers in spring; narrow leathery leaves. Common in acidic wetland communities and contributes to dense understory structure.

Virginia sweetspire
Arching shrub with fragrant white drooping flower spikes in spring; glossy leaves turn red in fall. Prefers wet soils and is often planted for erosion control along waterways.

Sawgrass
Stiff, saw-edged leaves forming dense stands; dominant in Florida Everglades-type marshes. Emergent sedge with tall culms and brown flower clusters; key habitat for marsh wildlife.

Maidencane
Clump-forming perennial grass that creates dense mats in wetlands; erect stems with coarse leaves. Important for stabilizing mudflats and as cover for marsh birds and amphibians.

Cattail
Tall emergent with strap-like leaves and distinctive brown cylindrical flower spikes. Common at water’s edge; dense colonies stabilize banks and provide nesting material for wildlife.

Pickerelweed
Heart-shaped leaves and upright spikes of purple-blue flowers in summer. Roots in mud with floating leaves; attracts pollinators and is unmistakable in shallow swamp pools.

Arrowhead
Spear-shaped leaves and white three-petaled flowers; tuberous roots historically eaten by wildlife. Emergent plant forming colonies in shallow water, easy to ID by distinctive leaf shape.

Water lily
Large round floating leaves and fragrant white flowers that rise above the water. Roots anchored in muck; common in calm swamp pools and provides shade and habitat for aquatic life.
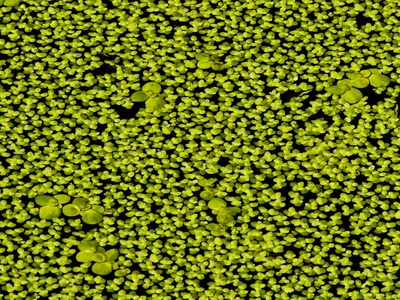
Duckweed
Tiny free-floating green leaves that form dense mats. Rapid growth in nutrient-rich waters; useful indicator of slow-moving or stagnant water and often covers pond surfaces in warm months.

Hydrilla
Highly invasive submerged aquatic with whorled leaves and brittle stems. Forms dense underwater mats that clog waterways and outcompete natives; identified by serrated leaf margins and turions.

Tape grass
Long ribbon-like leaves forming underwater meadows; produces emergent flower stalks. Important oxygenator and fish habitat in shallow clear water; leaves form dense beds in slow-moving water.

Blue flag iris
Clump-forming perennial with sword-like leaves and showy blue-violet flowers in spring. Grows in muddy edges and shallow pools; rhizomes anchored in wet muck, distinctive iris blooms.

Swamp milkweed
Tall perennial with clusters of pink flowers attracting monarch butterflies. Prefers saturated soils; opposite narrow leaves and milky sap identify it as a milkweed species.

Joe-Pye weed
Tall hollow-stemmed perennial with whorled leaves and pinkish clustered flower heads that attract pollinators. Common along swamp edges and in wet meadows; noticeable for height and late-summer bloom.

Swamp rose
Deciduous shrub with pink fragrant flowers and arching thorny stems. Grows in wet soils and along swamp margins; hips persist into fall and feed birds.

Cinnamon fern
Large bipinnate fronds with cinnamon-colored fertile fronds in the center. Distinctive fertile fronds and robust sterile fronds form clumps in acidic wet soils and swamp margins.

Royal fern
Large arching fronds with central fertile segments; prefers acidic, consistently wet soils. Often forms colonies in sphagnum-rich or hardwood swamp habitats and is easily spotted by height and frond texture.

Marsh fern
Delicate pinnate fronds forming clumps in saturated soils. Prefers shallow water or consistently wet ground; lighter green than many swamp ferns and forms low colonies in damp areas.

Woolgrass
Coarse sedge with distinctive fuzzy brown flower heads that sway in wind. Grows in standing water or saturated soils; a common emergent in freshwater marsh margins and roadside ditches.

Soft rush
Round unbranched stems and brownish flower clusters; forms dense clumps. Tolerant of standing water and compacted wet soils; common in ephemeral pools and wet roadside ditches.

Sedge (Lurid sedge)
Slender sedge with triangular stems and narrow leaves forming dense tussocks. Produces brownish seed spikes; common in freshwater wetlands and shallow standing water.

Smilax laurifolia (laurel greenbrier)
Evergreen vine/shrub with leathery unlobed leaves, tough thorny stems, and dark berries. Forms impenetrable tangles in swamps and bayheads; distinctive leathery foliage and spines identify it.

Catbrier
Climbing thorny vine with glossy heart-shaped leaves and black berries. Scrambles over shrubs and trees in swamp understory; spines and tough woody stems make it recognizable.

Poison ivy
Variable growth form (vine, shrub, groundcover) with pinnate leaves in threes. Causes allergic dermatitis; in swamps often climbs cypress and tupelo trunks, marked by glossy leaves that yellow in fall.

Red mangrove
Tree with distinctive prop roots and thick glossy leaves; salt-tolerant and forms seaward fringe of mangrove forests. Prop roots and viviparous seedlings identify it; critical for shoreline protection and nursery habitat.

Black mangrove
Displays pencil-like pneumatophores and salt-excreting leaves; gray-black bark. Occupies higher tidal elevations than red mangrove and often forms mixed stands in brackish swamp zones.

White mangrove
Small tree with rounded opposite leaves and peg-like glands at leaf base; occupies highest intertidal zones. Less obvious root structures than other mangroves; found in protected coastal swamps.

Smooth cordgrass
Salt-tolerant perennial grass forming dense stands in tidal marsh edges. Flat blades and jointed stems; zonation with tidal height is diagnostic and it stabilizes mudflats in brackish swamps.

Rose mallow
Large hibiscus-like flowers in pinks and whites; broad leaves and stout stems. Grows in brackish to fresh marsh edges; showy summer bloom makes it conspicuous in wet meadows.

Swamp sunflower
Tall perennial with narrow leaves and bright yellow sunflower heads in late summer. Colonizes wet soils and provides nectar late season; stems often reddish and seeded heads attract birds.

Taro (naturalized)
Large elephant-ear leaves on stout stems; non-native cultivated but often naturalized in wetlands. Grows in standing water or saturated soils; large heart-shaped leaves and tubers identify it.

Japanese climbing fern (invasive)
Vining fern with long, twining fronds that climb trees and shrubs. Highly invasive in Florida swamps, forms dense mats over canopy and understory; fronds with small pinnules are distinctive.

Brazilian pepper (invasive)
Aggressive evergreen shrub/tree forming dense monospecific stands; compound leaves and red berry clusters. Displaces native wetland plants and alters fire regimes; easily identified by peppery-smelling berries and compound foliage.





