Suriname’s markets and forests are a great place to see how tropical climate shapes local foodways. From roadside stalls to riverbank farms, the country’s fruits reflect a mix of Indigenous, African, Asian and European influences that show up in flavors, uses and seasonal rhythms.
There are 24 Fruits of Suriname, ranging from Ambarella to Tamarind; for each you’ll find below Local name,Scientific name,Season (months). The list is organized so you can quickly scan local names, the scientific name for identification, and when each fruit is typically in season — you’ll find below.
When are most of these fruits in season in Suriname?
Suriname’s fruit seasons follow the wet and dry cycles: many fruits peak during or just after the wet season when rainfall boosts flowering and fruit set, while others have clearer monthly windows (noted in the list below). Use the Season (months) column to plan visits or purchases—markets change weekly, but the column gives the typical harvest months.
Can I find or grow these fruits outside Suriname?
Some species are cultivated widely in similar tropical regions and in greenhouse/managed conditions elsewhere; others are more localized. The Scientific name column helps you research import availability, cultivation requirements and legal restrictions for moving plant material across borders.
Fruits of Suriname
| Name | Local name | Scientific name | Season (months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mango | mango (Sranan/Dutch) | Mangifera indica | Apr–Aug |
| Pineapple | ananas (Sranan/Dutch) | Ananas comosus | year-round |
| Banana | banaan (Sranan/Dutch) | Musa acuminata | year-round |
| Plantain | plantain/bakbanaan (Sranan/Dutch) | Musa × paradisiaca | year-round |
| Papaya | papaja (Sranan/Dutch) | Carica papaya | year-round |
| Guava | guave (Sranan/Dutch) | Psidium guajava | Jun–Sep |
| Soursop | zuurzak/guanábana (Sranan/Dutch) | Annona muricata | Jun–Aug |
| Surinam cherry | pitanga/Surinaamse kers (Sranan/Dutch) | Eugenia uniflora | Jun–Aug |
| Passionfruit | passievrucht/passionfruit (Sranan/Dutch) | Passiflora edulis | year-round |
| Coconut | kokosnoot (Sranan/Dutch) | Cocos nucifera | year-round |
| Breadfruit | broodvrucht/breadfruit (Sranan/Dutch) | Artocarpus altilis | Jun–Sep |
| Cashew apple | cashewappel/cashew apple (Sranan/Dutch) | Anacardium occidentale | May–Aug |
| Cupuaçu | cupuaçu (Sranan/Dutch) | Theobroma grandiflorum | May–Aug |
| Cacao | cacao (Sranan/Dutch) | Theobroma cacao | year-round |
| Starfruit | karambola/carambola (Sranan/Dutch) | Averrhoa carambola | year-round |
| Ambarella | ambarella/June plum (Sranan/Dutch) | Spondias dulcis | Jun–Aug |
| Tamarind | tamarin (Sranan/Dutch) | Tamarindus indica | Dec–Mar |
| Avocado | avocado (Sranan/Dutch) | Persea americana | Jun–Sep |
| Bilimbi | bilimbi (Sranan/Dutch) | Averrhoa bilimbi | year-round |
| Malay apple | waterappel/malay apple (Sranan/Dutch) | Syzygium malaccense | Jul–Sep |
| Sugar apple | sweetsop/sugar apple (Sranan/Dutch) | Annona squamosa | Jun–Aug |
| Açaí | açaí (Sranan/Dutch) | Euterpe oleracea | Jun–Sep |
| Goldenberry | physalis (Sranan/Dutch) | Physalis peruviana | year-round |
| Jackfruit | jackfruit (Sranan/Dutch) | Artocarpus heterophyllus | Jun–Sep |
Images and Descriptions

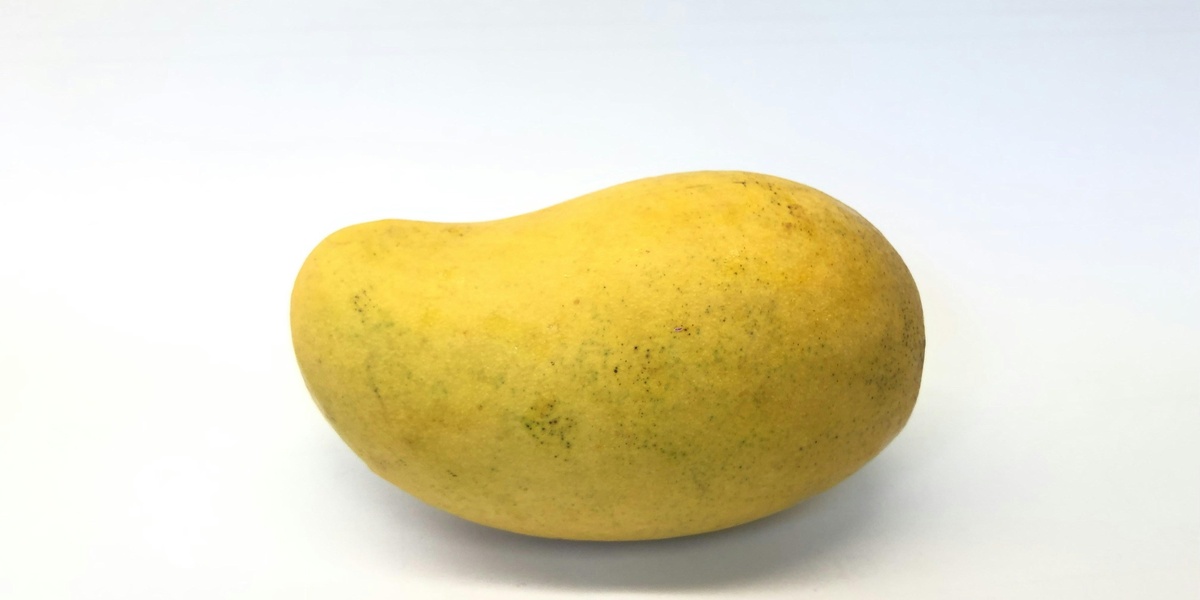
Mango
Fleshy orange-yellow fruit with sweet, tropical flavor. Widely cultivated since introduced; watch Apr–Aug markets across coastal towns and Paramaribo. Eaten fresh, in chutneys, juices, desserts; street stalls, roadside trees, and family orchards are common places to try.

Pineapple
Tropical bromeliad with juicy, sweet-tart flesh and spiky crown. Grown and sold year-round with coastal farm peaks; try fresh-cut at Paramaribo markets or roadside stands. Used in juices, grilled dishes, preserves, and local desserts; introduced and widely cultivated.

Banana
Soft, sweet elongated fruit available in many dessert cultivars. Grown year-round across Suriname; found in every market and street vendor. Eaten raw, fried, baked into breads or desserts; introduced species cultivated by smallholders and backyard gardens.

Plantain
Starchy, firm banana used as a cooking staple rather than dessert. Available year-round from markets and vendors; green plantains are fried, boiled or baked, ripe ones are sweeter. Introduced and central to Creole and Maroon cooking in coastal and interior regions.

Papaya
Soft orange-fleshed fruit with sweet, musky flavor and edible seeds. Grown year-round in gardens and sold at Paramaribo markets; common breakfast fruit or blended into smoothies, salads, and chutneys. Introduced but naturalized and widely used in home cooking.

Guava
Round green-to-yellow fruit with fragrant, sweet-tart flesh and many small seeds. Found in home gardens and markets, peak Jun–Sep; eaten fresh, in jams, juices, and desserts. Both native relatives and introduced cultivars are common across coastal and interior regions.

Soursop
Large spiny green fruit with soft, creamy white pulp and a sweet-tart tropical flavor. Collected from wild and home trees, season Jun–Aug; used in smoothies, ice creams, and traditional remedies. Native to the region and popular in markets and interior villages.

Surinam cherry
Small ribbed red fruit with tangy-sweet pulp and aromatic skin. Commonly called pitanga locally; fruiting peaks Jun–Aug and appears in markets and home hedges. Eaten fresh, made into jams and juices; native to the region and widely naturalized.

Passionfruit
Round to oval purple or yellow fruit with aromatic, seedy jelly and tart-sweet flavor. Grown year-round with market peaks; commonly juiced or used in desserts and sauces. Introduced vine cultivated in gardens and sold at Paramaribo markets and roadside stalls.

Coconut
Hard-shelled palm fruit containing sweet water and rich white flesh. Grown year-round along the coast; try fresh coconut water at beaches and Paramaribo markets. Used for milk, oil, desserts and savory dishes; native palms and introduced cultivars are widespread.

Breadfruit
Large starchy green fruit often roasted or boiled as a staple. Introduced and commonly found in coastal yards and markets, season Jun–Sep; served mashed, fried or in stews. Try at local eateries and Maroon villages where traditional preparations are common.

Cashew apple
Bright red-yellow swollen fruit above the cashew nut with tangy, astringent-sweet flesh. Harvest May–Aug from orchards and roadside trees; fresh juice, fermented drinks, jams, and chutneys are popular. Introduced but commonly grown and sold in coastal markets.

Cupuaçu
Large Amazonian relative of cacao with thick brown shell and tart-sweet white pulp. Found in interior and some coastal gardens, season May–Aug; used in juices, sweets, and regional desserts. Native to Amazonian forests and valued locally for flavor.

Cacao
Pod fruit containing sweet mucilaginous pulp around the beans used for chocolate. Grown in small plantations and wild stands year-round with harvest peaks; pulp is eaten fresh, beans fermented for cacao. Native-adapted trees are part of Suriname’s agroforestry.

Starfruit
Five-angled yellow fruit with crisp, juicy flesh and a mildly sweet-tart flavor. Grown in home gardens and markets year-round with peak fruiting; sliced for salads, juices, and garnishes. Introduced and popular in Paramaribo markets and roadside stalls.

Ambarella
Oval, golden fruit with crisp flesh that tastes sweet-tart and slightly resinous. Also called June plum, fruiting Jun–Aug in coastal gardens and markets; eaten fresh, pickled, or made into chutneys and juices. Introduced and commonly available from street vendors.

Tamarind
Brown pod with tangy-sweet sticky pulp used as a souring agent. Trees fruit Dec–Mar and pods appear in markets and home yards; pulp is used in sauces, drinks, and desserts. Introduced centuries ago and common in coastal culinary uses.

Avocado
Creamy green fruit with rich, buttery texture and mild flavor. Trees fruit mainly Jun–Sep but available much of the year; widely eaten on toasts, in salads, and sandwiches. Introduced cultivars are common in gardens, markets, and Paramaribo produce stalls.

Bilimbi
Small oblong green fruit extremely sour when raw, often used as a cooking acid. Trees fruit year-round with market availability; used to flavor fish, curries, and pickles. Introduced from Southeast Asia and grown in Javanese and home gardens.

Malay apple
Bell-shaped red fruit with crisp, watery, mildly sweet flesh and floral perfume. Found in gardens and local markets, fruiting Jul–Sep; eaten fresh or lightly cooked. Introduced from Asia, popular in coastal yards and sold at Paramaribo stalls.

Sugar apple
Lumpy green fruit with sweet, custardy white segments and many seeds. Trees fruit Jun–Aug and are common in backyard gardens and neighborhood markets; eaten fresh or used in desserts and smoothies. Introduced and commonly cultivated in home plots.

Açaí
Small dark purple palm berries with earthy, rich flavor used mostly for pulp. Harvest peaks Jun–Sep in swampy coastal forests and interior; blended into drinks and bowls or eaten locally. Native to Amazonian wetlands and increasingly found in markets.

Goldenberry
Small orange lantern-like berry with tart-sweet, tropical flavor encased in papery husk. Grown in gardens and sold at markets year-round; eaten fresh, in jams, or as a snack. Introduced but popular for its bright acidity and portability.

Jackfruit
Massive green fruit with sweet, fragrant yellow flesh used both ripe and unripe. Trees fruit Jun–Sep and are grown in yards; ripe bulbs eaten fresh or in desserts, unripe used in savory dishes. Introduced and found in markets and family gardens.