Wales’ coasts, rivers and uplands are home to a wide mix of native wildlife — and increasingly, non-native species that change habitats, harm fisheries or compete with local plants and animals. Communities, anglers and conservation groups all want clear, practical information about what to watch for and why it matters.
There are 32 Invasive Species in Wales, ranging from American mink to Zebra mussel. Each entry is presented with key details (Scientific name,Type,Status) so you can quickly see what the organism is, its category and whether it’s established or under control — you’ll find below.
How do I report a sighting of an invasive species in Wales?
If you spot a suspected invasive species, take clear photos, note the exact location (GPS or nearest landmark) and report it to your local wildlife trust or Natural Resources Wales; many councils also have online reporting forms. Quick, accurate reports help authorities verify records and respond faster.
Which invasive species should residents be most concerned about?
Priorities vary by habitat, but look out for species that alter ecosystems or infrastructure — for example American mink (impacting birds and fish), Zebra mussel (clogging waterways), Japanese knotweed and signal crayfish — and report any unusual finds promptly.
Invasive Species in Wales
| Name | Scientific name | Type | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese knotweed | Fallopia japonica | plant | Schedule 9, widespread |
| Himalayan balsam | Impatiens glandulifera | plant | Invasive, widespread |
| Giant hogweed | Heracleum mantegazzianum | plant | Schedule 9, invasive |
| Gorse rhododendron | Rhododendron ponticum | plant | Schedule 9, invasive |
| New Zealand pygmyweed | Crassula helmsii | plant | Schedule 9, aquatic invasive |
| Floating pennywort | Hydrocotyle ranunculoides | plant | Invasive, aquatic |
| Parrot’s feather | Myriophyllum aquaticum | plant | Invasive, aquatic |
| Nuttall’s waterweed | Elodea nuttallii | plant | Invasive, freshwater |
| Canadian waterweed | Elodea canadensis | plant | Non-native, widespread aquatic |
| Spartina | Spartina anglica | plant | Invasive in estuaries |
| Rosa rugosa | Rosa rugosa | plant | Invasive on coasts |
| Montbretia | Crocosmia x crocosmiiflora | plant | Invasive, local coastal spread |
| Harlequin ladybird | Harmonia axyridis | invertebrate | Established, invasive |
| New Zealand flatworm | Arthurdendyus triangulatus | invertebrate | Established, invasive |
| Spanish slug | Arion vulgaris | invertebrate | Invasive, widespread |
| Signal crayfish | Pacifastacus leniusculus | invertebrate | Invasive, widespread |
| Zebra mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | invertebrate | Established in some waterways |
| New Zealand mud snail | Potamopyrgus antipodarum | invertebrate | Invasive freshwater snail |
| Slipper limpet | Crepidula fornicata | invertebrate | Invasive marine |
| Colonial sea squirt | Didemnum vexillum | invertebrate | Invasive marine tunicate |
| Clubbed tunicate | Styela clava | invertebrate | Invasive marine tunicate |
| Japanese wireweed | Sargassum muticum | plant | Invasive marine algae |
| Wakame | Undaria pinnatifida | plant | Invasive marine algae |
| Pacific oyster | Magallana gigas | invertebrate | Non-native, established invasive in places |
| Sudden oak/larch pathogen | Phytophthora ramorum | pathogen | Notifiable, regulated outbreaks |
| Ash dieback | Hymenoscyphus fraxineus | fungus | Widespread pathogen |
| American mink | Neovison vison | mammal | Invasive, controlled |
| Grey squirrel | Sciurus carolinensis | mammal | Invasive, widespread |
| Muntjac deer | Muntiacus reevesi | mammal | Established, spreading |
| Sika deer | Cervus nippon | mammal | Established in parts of Wales |
| Canada goose | Branta canadensis | bird | Non-native, widespread |
| Azolla water fern | Azolla filiculoides | plant | Non-native, locally invasive |
Images and Descriptions

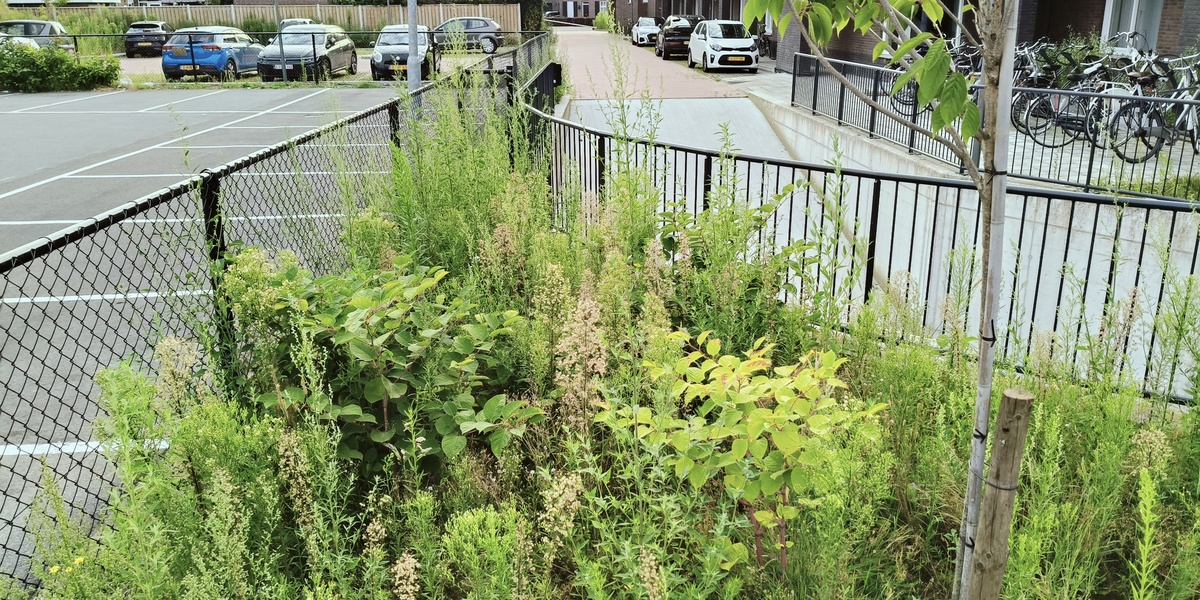
Japanese knotweed
A tall, bamboo-like perennial invading riverbanks, roadsides and brownfield sites across Wales. It damages built structures and native plants; control by licensed contractors. Report sightings to Natural Resources Wales (NRW) and the GB Non-native Species Secretariat (NNSS).

Himalayan balsam
Annual riverside plant forming dense stands along Welsh waterways, outcompeting native flora and increasing erosion. Pulling before seed-set helps; do not compost. Report infestations to NRW or local wildlife trusts and support riverbank clearance events.

Giant hogweed
Very large umbellifer found on riverbanks and disturbed ground in Wales; its sap can cause severe skin burns. Do not touch; report locations to NRW and local authorities for safe removal by trained teams.

Gorse rhododendron
Widespread in Welsh woodlands and uplands, shading and acidifying soils while displacing native plants and birds. Removal is costly and ongoing; report dense stands to NRW or local land managers for coordinated control.

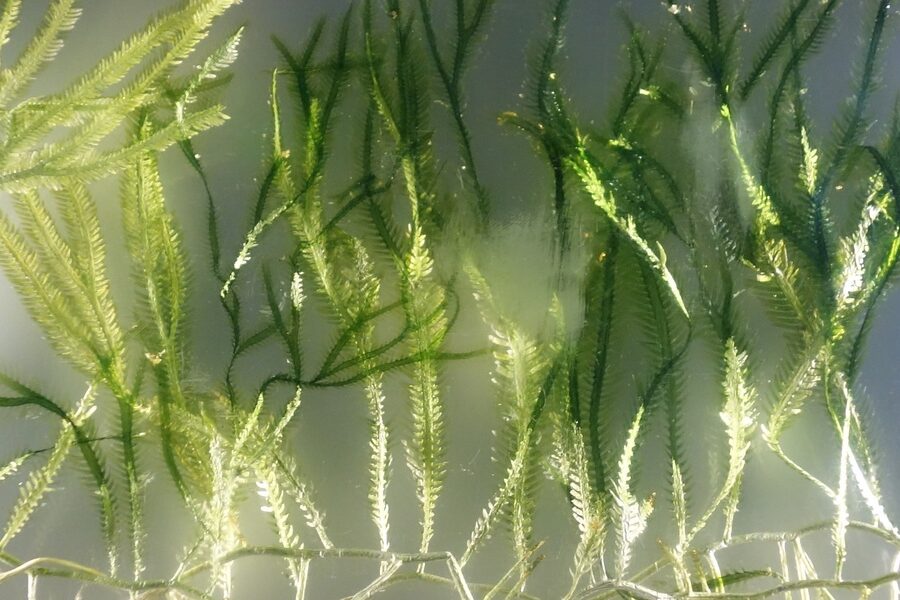
New Zealand pygmyweed
Evergreen mat-forming pond plant found in ponds and wetlands in Wales; smothers native aquatic life and is hard to eradicate. Do not release plant material; report sightings to NRW and clean equipment between sites.

Floating pennywort
Fast-growing water plant blocking channels, canals and slow rivers in parts of Wales, harming boating and wildlife. Manual and chemical control used; clean boats and nets and report records to NRW and NNSS.

Parrot’s feather
Feather-like submerged plant forming dense stands in ponds and canals across Wales, lowering oxygen and displacing natives. Remove carefully and never dump garden waste; report infestations to NRW and follow biosecurity guidance.

Nuttall’s waterweed
Aggressive submerged weed in Welsh rivers and reservoirs; clogs waterways and outcompetes native plants. Spread on angling and boating gear — clean kit and report sightings to NRW or local record centres.

Canadian waterweed
Early-introduced submerged plant now widespread in Welsh still waters and slow rivers; can become dominant and impact water use. Manage mechanically and practice good biosecurity; report new outbreaks to NRW.

Spartina
Hybrid cordgrass invading mudflats and saltmarshes in Welsh estuaries, altering sedimentation and bird habitats. Control and monitoring occur in sensitive sites; report local patches to NRW or coastal managers for assessment.

Rosa rugosa
Thick, thorny coastal scrub on dunes and shoreline in Wales; crowds out dune specialists and changes sand dynamics. Remove seedlings and hips where advised and report persistent stands to local authorities or NRW.

Montbretia
Garden escape with bright orange flowers invading hedgerows, dunes and verges in west Wales. Forms dense clumps that suppress native flora; control by careful lifting and disposal and report spreading populations to NRW.

Harlequin ladybird
Introduced beetle now common across Wales, often in buildings; outcompetes and preys on native ladybirds and eats fruit. Record sightings with local recording schemes and avoid moving specimens between sites to reduce spread.

New Zealand flatworm
Predatory flatworm found in Welsh gardens and grassland that eats earthworms, harming soil health. Avoid moving compost or soil; report records to NRW or national recording schemes and follow biosecurity advice.

Spanish slug
Large slug causing serious garden and crop damage across Wales, displacing native slugs. Hand-pick, trap and use cultural controls; report unusual surges to local councils and practice biosecurity to limit spread.

Signal crayfish
Non-native crayfish in many Welsh rivers and lakes; burrows destabilise banks and it spreads crayfish plague, outcompeting native white-clawed crayfish. Never release; report captures to NRW and follow guidelines for handling or humane dispatch.

Zebra mussel
Freshwater mussel recorded in UK inland waters including reservoirs that can foul infrastructure, alter ecosystems and block pipes. Clean boats, trailers and equipment; report sightings to NRW and reservoir managers.

New Zealand mud snail
Small snail now recorded in Welsh rivers and lakes in large numbers, altering food webs and fouling gear. Clean boots and equipment between waters and report new records to NRW or freshwater recording schemes.

Slipper limpet
Marine gastropod established on parts of the Welsh coast; forms dense beds that smother sediments and shellfish grounds. Report finds to marine recording programmes and avoid moving shellfish or fouling material.

Colonial sea squirt
Aggressive fouling organism found in harbours and marinas in Wales that smothers shellfish and structures. Report to NRW/Marine Recorder, maintain hull cleaning regimes and follow aquaculture biosecurity.

Clubbed tunicate
Fouling tunicate recorded on Welsh marinas and aquaculture gear; can damage farmed stocks and infrastructure. Report sightings to marine authorities, practice hull hygiene and clean gear between sites.

Japanese wireweed
Large brown seaweed found on Welsh coasts and harbour walls, outcompeting native algae and fouling structures. Remove only where safe, report to marine recorders, and follow boat hygiene guidance to limit spread.

Wakame
Non-native kelp recorded in marinas and rocky shores around Wales; it can establish in sheltered harbours and impact native communities. Report sightings to NRW or marine monitoring projects and clean subtidal equipment.

Pacific oyster
Introduced for aquaculture but now wild in Welsh estuaries, changing habitats and competing with native oysters. Movement of stock is regulated; report unusual colonisation to NRW and fisheries authorities.

Sudden oak/larch pathogen
Water-borne oomycete causing larch and oak disease in Wales; affected forests have been subject to felling and controls. Report suspect symptoms to Forestry Commission/NRW TreeHealth and follow plant health regulations.

Ash dieback
Fungal disease causing crown loss and dieback of ash trees across Wales, altering woods and hedgerows. Report suspect cases to TreeAlert/NRW, do not move infected timber and follow local council safety guidance.

American mink
Semi-aquatic predator established along many Welsh coasts and rivers; preys on birds, fish and small mammals. Managed by trapping programmes run by conservation groups; report sightings to NRW or local wildlife organisations.

Grey squirrel
Non-native squirrel widespread across lowland Wales, damaging trees and displacing red squirrels. Control occurs in red squirrel strongholds; report sightings in protected red squirrel areas to NRW or local conservation groups.

Muntjac deer
Small deer expanding in parts of south Wales and woodlands; browsing causes damage to ground flora and young trees. Report new local populations to NRW or landowners so appropriate deer management can be planned.

Sika deer
Non-native deer present in Welsh woodlands and uplands; grazing and hybridisation can affect native species and forestry. Managed through culling and deer management groups; report sightings in protected areas to NRW.

Canada goose
Large grazing waterfowl common on parks, farmland and estuaries in Wales causing fouling, crop damage and displacement of native birds. Local councils may manage problem flocks; report nuisance birds to local authority environmental health teams.

Azolla water fern
Floating fern that can blanket ponds and slow waterways in Wales, reducing oxygen and biodiversity. Remove carefully where possible, avoid spreading fragments and report records to NRW or pond conservation groups.