Senegal’s landscapes — from the Atlantic coast across the Casamance wetlands to the Sahelian north — host a wide range of vegetation that shapes local livelihoods, seasonal rhythms, and biodiversity studies. This list brings that variety into one practical resource for anyone curious about the country’s flora.
There are 96 Senegal’s native plants, ranging from A-nyara to Winter Thorn. For each entry you’ll find below the data organized as Scientific name,Height (m),Habitat and Senegal distribution to make comparisons and field checks simple; the columns help show where a species grows, how tall it gets, and its scientific identity, so you can locate or research any item on the list.
How can I use the list to identify plants in the field?
Use the Scientific name to cross-check authoritative guides or online databases, compare the noted Height (m) and Habitat with what you observe, and narrow choices by the listed Senegal distribution; carrying a small notebook or phone photos of key features (leaves, flowers, bark) speeds matching.
Are any species on the list protected or of conservation concern?
Some entries are locally rare or have restricted ranges; the Habitat and Senegal distribution columns flag limited occurrences, but check national conservation lists, IUCN/CITES listings, or local authorities before collecting or disturbing plants.
Senegal’s Native Plants
| Name | Scientific name | Height (m) | Habitat and Senegal distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baobab | Adansonia digitata | 15-25 | Savannas and dry woodlands; widespread nationally |
| African Mahogany | Khaya senegalensis | 15-30 | Riverine forests and Sudanian savannas; south and east |
| Gum Arabic Tree | Senegalia senegal | 4-6 | Arid Sahelian zones; northern Senegal and Ferlo region |
| Shea Tree | Vitellaria paradoxa | 10-15 | Dry savannas and parklands; mainly south and east |
| Winter Thorn | Faidherbia albida | 10-25 | Agroforestry parklands and floodplains; widespread |
| African Locust Bean | Parkia biglobosa | 7-20 | Sudanian savanna and parklands; widespread in south |
| Desert Date | Balanites aegyptiaca | 3-10 | Sahel and arid savannas; northern and central regions |
| Ron Palm | Borassus aethiopum | 20-30 | Savannas and riverbanks; widespread, especially Casamance |
| African Oil Palm | Elaeis guineensis | 10-20 | Moist forests and riverine areas; Casamance region |
| Tamarind | Tamarindus indica | 15-25 | Dry savannas and woodlands; widespread |
| African Rosewood | Pterocarpus erinaceus | 12-15 | Dry forests and Sudanian savannas; south and east |
| Kapok Tree | Ceiba pentandra | 20-40 | Moist to dry forests and savannas; widespread |
| Doum Palm | Hyphaene thebaica | 6-10 | Arid riverbanks and oases; Senegal River valley |
| Marula Tree | Sclerocarya birrea | 9-18 | Woodlands and savannas; eastern Senegal |
| Kinkeliba | Combretum micranthum | 2-5 | Dry, rocky savannas; widespread, especially in Sahelian zone |
| Indian Jujube | Ziziphus mauritiana | 5-12 | Dry woodlands and bushlands; widespread |
| African Grape | Lannea microcarpa | 8-15 | Sudanian savannas and woodlands; common in the south |
| African Ebony | Diospyros mespiliformis | 15-25 | Savannas and riverine forests; south and east |
| Saba Fruit | Saba senegalensis | 3-5 (liana) | Savannas and gallery forests; southern Senegal |
| Wild Custard Apple | Annona senegalensis | 2-6 | Open woodlands and savannas; widespread |
| Spiny Monkey Orange | Strychnos spinosa | 4-8 | Coastal thickets and savannas; widespread |
| Bissap | Hibiscus sabdariffa | 1.5-2.5 | Cultivated and wild in savannas; widespread |
| African Teak | Adina microcephala | 15-30 | Riverine and gallery forests; Casamance and eastern Senegal |
| Egyptian Thorn | Vachellia nilotica | 5-20 | Floodplains and savannas; Senegal River valley, Ferlo |
| Red Acacia | Vachellia seyal | 5-12 | Sahel and dry savannas; northern and central regions |
| Red Mangrove | Rhizophora mangle | 5-10 | Coastal estuaries and lagoons; Saloum Delta, Casamance |
| Black Mangrove | Avicennia germinans | 4-10 | Coastal mudflats and mangrove swamps; Saloum Delta, Casamance |
| White Mangrove | Laguncularia racemosa | 5-12 | Upper intertidal zones of estuaries; Saloum Delta, Casamance |
| A-nyara | Cochlospermum tinctorium | 0.5-1.5 | Rocky savannas and fallow land; widespread |
| Guiera | Guiera senegalensis | 1-3 | Sandy soils in Sahel and savanna; widespread |
| Gamba Grass | Andropogon gayanus | 2-4 | Sudanian savannas; widespread in the south |
| Black Vetiver | Vetiveria nigritana | 1.5-2.5 | Marshy areas and floodplains; southern and eastern Senegal |
| African Lowland Bamboo | Oxytenanthera abyssinica | 4-10 | Savannas and rocky hillsides; southeastern Senegal |
| African Linden | Mitragyna inermis | 8-15 | Seasonally flooded areas and riverbanks; widespread |
| Ditax | Detarium senegalense | 15-30 | Dry forests and savannas; southern Senegal |
| Red-flowered Silk Cotton | Bombax costatum | 10-25 | Dry, rocky savannas; south and east |
| Large-leafed Cordia | Cordia africana | 7-15 | Savannas and woodlands; southern Senegal |
| Sycamore Fig | Ficus sycomorus | 15-25 | Riverine forests and savannas; widespread |
| Pink Jacaranda | Stereospermum kunthianum | 5-12 | Woodlands and rocky savannas; southeastern Senegal |
| African Oak | Afzelia africana | 15-30 | Sudanian savannas and dry forests; south and east |
| African Copaiba Balsam | Daniellia oliveri | 15-25 | Woodlands and savannas; southern Senegal |
| Doka | Isoberlinia doka | 12-20 | Sudanian savannas; southeastern Senegal (Niokolo-Koba) |
| Large-winged Terminalia | Terminalia macroptera | 10-18 | Moist savannas and gallery forests; southern Senegal |
| African Birch | Anogeissus leiocarpa | 15-25 | Savannas and dry forests; widespread in south and east |
| African Mesquite | Prosopis africana | 8-20 | Savannas and dry woodlands; widespread |
| Senegal Asparagus | Asparagus flagellaris | 1-2 (climber) | Undergrowth in savannas and thickets; widespread |
| Bitterleaf | Vernonia amygdalina | 2-5 | Forest margins and savannas; southern Senegal |
| Bush Mango | Irvingia gabonensis | 15-30 | Moist forests; Casamance region |
| Water-berry | Syzygium guineense | 10-15 | Riverine forests and wetlands; southern Senegal |
| Wild Plum | Ximenia americana | 3-6 | Woodlands, coastal thickets, and savannas; widespread |
| Nerve Plant | Crateva adansonii | 8-15 | Riverbanks and savannas; widespread |
| Corkwood | Hymenocardia acida | 4-8 | Wooded savannas; widespread in south |
| African Myrrh | Commiphora africana | 3-5 | Arid savannas and Sahel; northern Senegal |
| Bushwillow | Combretum glutinosum | 5-10 | Sahel and Sudanian savannas; widespread |
| Candle Bush | Senna alata | 1.5-3 | Moist savannas and disturbed areas; southern Senegal |
| African Fan Palm | Hyphaene guineensis | 8-15 | Coastal savannas and estuaries; coastal regions |
| False Shea | Lophira lanceolata | 8-12 | Sudanian savannas; southern and eastern Senegal |
| Sandpaper Tree | Ficus exasperata | 10-20 | Gallery forests and moist savannas; southern Senegal |
| Black Plum | Vitex doniana | 8-15 | Savannas and woodlands; widespread in south |
| Wild Loofah | Luffa cylindrica | 3-6 (climber) | Riverbanks and disturbed areas; widespread |
| Poison-arrow Tree | Adenium obesum | 1-3 | Dry, rocky areas; eastern Senegal |
| Buffalo Thorn | Ziziphus mucronata | 4-10 | Savannas and riverine thickets; widespread |
| Wild Coffee | Coffea stenophylla | 2-4 | Gallery forests; found in southeastern Senegal |
| African Peach | Sarcocephalus latifolius | 5-12 | Savannas and fallow lands; widespread |
| Velvet Tamarind | Dialium guineense | 10-25 | Forests and savannas; southern Senegal |
| Camwood | Baphia nitida | 5-10 | Forest understory; Casamance region |
| Jiga | Securidaca longipedunculata | 4-8 | Wooded savannas; widespread in south |
| African Canarium | Canarium schweinfurthii | 20-40 | Forests; Casamance region |
| Water-lettuce | Pistia stratiotes | 0.1-0.2 (floating) | Freshwater bodies, rivers; widespread |
| African Dragon’s Blood Tree | Dracaena mannii | 5-12 | Coastal and riverine forests; Casamance region |
| Sausage Tree | Kigelia africana | 10-20 | Savannas and riverbanks; widespread in south |
| African Star Apple | Chrysophyllum albidum | 20-35 | Forests; Casamance region |
| Fara | Parkinsonia aculeata | 4-8 | Dry, disturbed areas; northern Senegal |
| African Fan-weed | Flabellaria paniculata | 5-10 (liana) | Forests and thickets; southern Senegal |
| Casamance Tam-tam | Zanha golungensis | 10-20 | Dry forests and savannas; southern Senegal |
| Sudan Teak | Pterocarpus lucens | 8-12 | Dry savannas and rocky hills; northern and eastern Senegal |
| Water Cabbage | Nymphaea lotus | 0.2-0.5 (aquatic) | Ponds, lakes, slow rivers; widespread |
| Senegal Date Palm | Phoenix reclinata | 3-6 | Riverbanks and swampy areas; widespread |
| Blackwood | Dalbergia melanoxylon | 5-10 | Dry savannas and woodlands; eastern Senegal |
| Senegal Indigo | Indigofera arrecta | 1-2 | Savannas and grasslands; widespread |
| Wild Melon | Citrullus lanatus | 0.2 (vine) | Sandy soils, dry areas; widespread |
| African Foxglove | Ceratotheca sesamoides | 0.5-1 | Cultivated ground and fallow fields; widespread |
| African Olive | Olea europaea subsp. cuspidata | 5-10 | Dry forests and rocky outcrops; rare in eastern Senegal |
| Bird Plum | Berchemia discolor | 6-15 | Woodlands and riverine fringes; eastern Senegal |
| Wild Abutilon | Abutilon pannosum | 1-2 | Dry, disturbed areas; northern Senegal |
| Gao Tree | Anogeissus dhofarica | 10-15 | Arid, rocky hillsides; rare in eastern Senegal |
| Sickle Bush | Dichrostachys cinerea | 3-7 | Savannas and woodlands; widespread |
| Jumping Seed Tree | Sapium ellipticum | 10-20 | Forests and savannas; southern Senegal |
| Wild Medlar | Vangueria senegalensis | 3-5 | Woodlands and savannas; widespread |
| Tallow Tree | Pentadesma butyracea | 15-25 | Gallery forests and swampy areas; Casamance region |
| Devil’s Thorn | Tribulus terrestris | 0.1 (prostrate) | Disturbed sandy soils; widespread |
| Marlberry | Ardisia crispa | 1-2 | Forest understory; Casamance region |
| African Cucumber | Momordica balsamina | 2-4 (climber) | Disturbed areas and bushland; widespread |
| Red Stinkwood | Prunus africana | 10-25 | Montane forest remnants; southeastern Senegal (Fouta Djallon foothills) |
| Bush Banana | Uvaria chamae | 1-2.5 | Savanna and forest understory; widespread |
| Cat’s Whiskers | Clerodendrum capitatum | 2-4 | Thickets and forest margins; southern Senegal |
Images and Descriptions

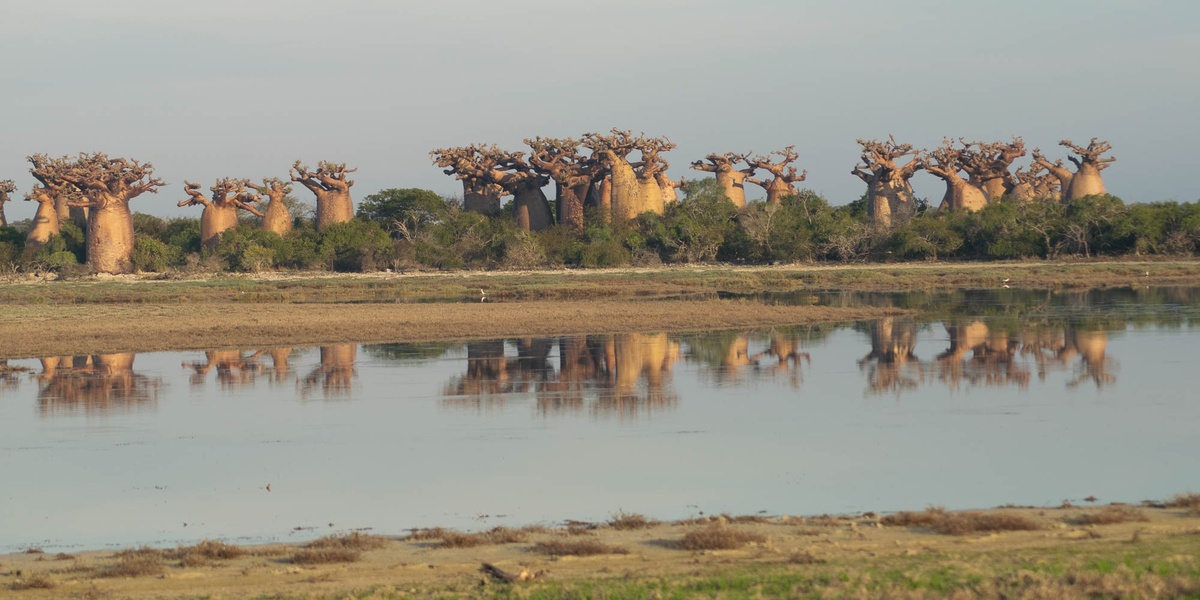
Baobab
The iconic “upside-down tree” is Senegal’s national emblem. Its massive trunk stores water, and its fruit, ‘bouye’, creates a nutritious drink. Every part of this culturally significant, long-lived tree has a traditional use, from bark fiber to medicinal leaves.

African Mahogany
A large, deciduous tree prized for its high-quality, reddish-brown timber used in furniture and construction. Its bitter bark is a famous traditional medicine for fevers. Over-harvesting has led to conservation concerns, making it an economically important and protected species in many areas.

Gum Arabic Tree
This small, thorny tree is a cornerstone of the Sahelian economy. It produces gum arabic, a hardened sap harvested for use as a stabilizer in foods and industries. Its resilience in dry conditions makes it vital for combating desertification and supporting local livelihoods.

Shea Tree
Known as the karité tree, it produces a nutrient-rich nut from which shea butter is extracted. This valuable fat is used globally in cosmetics and locally for cooking and medicine. The tree is protected in many communities due to its immense economic and cultural importance.

Winter Thorn
This remarkable tree exhibits reverse phenology, dropping its leaves in the rainy season and growing them in the dry season. This unique trait makes it an ideal agroforestry species, providing shade, fodder for livestock, and nitrogen fixation when other resources are scarce.

African Locust Bean
This spreading tree produces long pods with seeds embedded in a sweet pulp. The fermented seeds, known as ‘nététou’ or ‘soumbala’, are a vital, protein-rich food condiment. The tree also improves soil fertility and provides shade for crops and livestock.

Desert Date
A spiny, incredibly drought-resistant tree that is a true survivor of the Sahel. Its bitter-sweet, date-like fruit is edible, and a high-quality oil is extracted from the seed. The tree’s durable wood and extensive traditional medicinal uses make it highly valuable.

Ron Palm
A majestic fan palm with a distinct swollen trunk. It is a multi-purpose species; the fruit is edible, the sap is tapped for palm wine, and the fronds are used for weaving and construction. Its termite-resistant wood is also used for building.

African Oil Palm
Native to West Africa’s riverine forests, this palm is the primary source of palm oil, extracted from both the fruit pulp and kernel. It is culturally significant and economically important, though wild populations are distinct from the high-yield plantation varieties seen globally.

Tamarind
This long-lived tree is famous for its curved pods containing a tart, sticky pulp. The pulp is a key ingredient in drinks, sauces, and traditional medicine. Its dense, durable wood is also highly valued, and the tree provides excellent shade in hot climates.

African Rosewood
Also known as ‘kosso’, this tree is highly valued for its beautiful, durable, and termite-resistant timber. It also yields a red sap used as a dye. Overexploitation for the timber trade has made it one of West Africa’s most threatened native tree species.

Kapok Tree
A giant of the forest with a buttressed trunk often studded with conical spines. Its seed pods are filled with a cotton-like fiber called kapok, which is buoyant and water-resistant. Historically, it was used for stuffing life preservers, mattresses, and pillows.

Doum Palm
This palm is distinctive for its branching trunk, a rare trait among palms. It produces a hard, gingerbread-flavored fruit that is edible. The fronds are a primary material for weaving baskets, mats, and rope in desert communities, making it a vital local resource.

Marula Tree
Famed for its delicious, vitamin C-rich fruit, which is eaten fresh, made into juices, and fermented into alcoholic beverages. The oil-rich kernel is also edible and used in cosmetics. The tree is an important source of food and income in rural areas.

Kinkeliba
A scrambling shrub whose leaves are widely used to make a popular herbal tea known as ‘kinkeliba’. Considered a health tonic, it is used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments. It is an important non-timber forest product across the region.

Indian Jujube
Despite its common name, this spiny shrub is native to the region. It produces a small, apple-like fruit that is sweet and nutritious, providing a key source of food in the dry season. It is extremely drought-tolerant and important for local ecosystems.

African Grape
This deciduous tree produces clusters of small, acidic, grape-like fruits that are eaten fresh or used in drinks. The tree has many medicinal uses, and its inner bark can be used to make rope. It is a common and useful species in savanna parklands.

African Ebony
A tall, evergreen tree that yields a valuable, dark heartwood similar to true ebony. It produces a sweet, edible fruit that is popular with both humans and wildlife. The tree is slow-growing and is considered sacred in many local cultures.

Saba Fruit
A woody vine, or liana, that climbs on other trees. It produces a large, hard-shelled fruit filled with tangy, sweet-sour pulp-covered seeds. Known as ‘madd’ in Wolof, the fruit is a very popular local delicacy often eaten with sugar and spices.

Wild Custard Apple
A small tree or shrub that produces an aromatic, edible fruit with a flavor reminiscent of pineapple or apricot. The fruit, leaves, and roots are all used extensively in traditional medicine. It is a hardy species, capable of surviving frequent bush fires.

Spiny Monkey Orange
This small, spiny tree bears a hard-shelled, yellow fruit with a sweet-sour, aromatic pulp. The fruit is edible, but the seeds are toxic. It is an important food source for wildlife and people, and its hard wood is used for tool handles.

Bissap
While widely cultivated, this species has native wild populations in the region. Its fleshy red calyces are famously used to make a refreshing, ruby-red drink called ‘bissap’, the national drink of Senegal. The leaves are also used as a souring agent in cooking.

African Teak
A large tree found near water, valued for its fine-grained, yellowish, and termite-resistant wood, which is used in construction and for making canoes. Its round, distinctive flower heads give it the common name “head-flower tree” in some regions.

Egyptian Thorn
Formerly an Acacia, this thorny tree is a vital resource in arid zones. It provides excellent firewood and charcoal, tannin for leather-making from its pods, and nutritious fodder for livestock. Its presence often indicates seasonally flooded, fertile soils.

Red Acacia
Identified by its rusty-red or yellowish powdery bark, this tree is a key species of the Sahel. It produces a lower-quality gum arabic and is an important source of fodder and fuel. It is also a host for ants that protect it from herbivores.

Red Mangrove
Identified by its tangled, reddish prop roots that arch above the water, this tree is a foundational species of mangrove ecosystems. It stabilizes coastlines, provides a crucial nursery for fish and crustaceans, and protects inland areas from storm surges.

Black Mangrove
This mangrove species is distinguished by its numerous vertical root projections, called pneumatophores, that stick up from the mud to help it breathe. It is highly salt-tolerant and plays a critical role in colonizing new mudflats and protecting shorelines.

White Mangrove
Often found further inland than red or black mangroves, this species is noted for the two salt-excreting glands at the base of each leaf. It contributes to the biodiversity of the mangrove ecosystem and helps stabilize coastal soils against erosion.

A-nyara
A small, fire-resistant shrub known for its large, bright yellow flowers that appear before the leaves. Its rhizome produces a yellow dye used for coloring food and textiles, and it holds a significant place in traditional medicine for treating liver ailments.

Guiera
This common, multi-stemmed shrub is an indicator species of overgrazed or degraded land, but it is also a vital resource. Its leaves are used in medicine to treat respiratory and digestive issues, and it is a key source of fuelwood for local communities.

Gamba Grass
A tall, robust perennial grass that forms large tussocks. It is a highly valued native pasture grass for livestock due to its productivity and nutritional quality. However, in other parts of the world, it has become a highly invasive species.

Black Vetiver
This dense, clump-forming grass is prized for its aromatic roots, which are woven into fans and mats that release a pleasant scent when wet. The root system is incredibly deep and dense, making it excellent for controlling soil erosion on riverbanks.

African Lowland Bamboo
The only bamboo species native to Senegal, it forms dense thickets. The hollow culms (stems) are strong and versatile, used for construction, furniture, and making musical instruments. The young shoots are also edible, providing a seasonal food source.

African Linden
A medium-sized tree that thrives in wet soils. Its leaves and bark contain alkaloids and are used in traditional veterinary and human medicine to treat a range of diseases. It is an important species for stabilizing riverbanks and providing shade.

Ditax
This large tree produces a round, edible fruit with a sweet, fibrous green pulp that has a strong vitamin C content. The dense, hard timber is also used for construction. The fruit is popular in local markets and is eaten fresh or processed into drinks.

Red-flowered Silk Cotton
A deciduous tree easily recognized by its large, vibrant red flowers that bloom on bare branches. The seed pods contain a cotton-like fiber, and the flower calyces are used in sauces. It is a visually striking tree that also provides food and materials.

Large-leafed Cordia
This fast-growing tree is known for its large, rough leaves and clusters of white, fragrant flowers. The wood is lightweight and used for making furniture, beehives, and drums. Its fruit is edible, and the tree is often planted for shade and ornamental purposes.

Sycamore Fig
A large, spreading fig tree that often grows along watercourses. It produces clusters of edible figs directly on its trunk and main branches. The tree is culturally significant, considered sacred in many traditions, and its wood was historically important in ancient Egypt.

Pink Jacaranda
Despite its common name, it’s not a true jacaranda. This small, slender tree produces beautiful, drooping clusters of pink, trumpet-shaped flowers, making it a stunning sight in the savanna. Its pods are long and spirally twisted, and the bark has medicinal uses.

African Oak
A highly prized timber tree with very hard, durable, and termite-resistant wood, often used as a substitute for teak. The seeds, with their distinctive red aril, are used for decoration. Over-harvesting has led to it becoming a threatened species.

African Copaiba Balsam
This tree is notable for the fragrant oleoresin, or balsam, that can be tapped from its trunk, used in traditional varnishes and medicines. The wood is light and easy to work with, making it useful for canoes, drums, and domestic utensils.

Doka
A dominant tree species of the Sudanian savanna woodland, often forming extensive stands. It is a key species for the ecosystem, providing habitat for many animals. Its wood is used for fuel and heavy construction, and it is host to an edible mushroom.

Large-winged Terminalia
Recognized by its large, winged fruits, this tree is well-adapted to areas with seasonal waterlogging. Its leaves, bark, and roots are a cornerstone of traditional medicine, used to treat a wide array of illnesses, from wounds to yellow fever.

African Birch
A graceful tree with somewhat drooping branches, it yields a very hard, dense, and strong wood used for tool handles and charcoal. The bark contains tannins used for dyeing and tanning, and its leaves are used in traditional medicine.

African Mesquite
A slow-growing, resilient tree with dark, rough bark and feathery leaves. Its hard, heavy wood is excellent for high-quality charcoal. The seeds can be fermented into a food condiment similar to that from the African locust bean tree.

Senegal Asparagus
A climbing, perennial herb with wiry, spiny stems and fine, needle-like leaves. The young shoots are harvested and eaten as a wild vegetable, much like cultivated asparagus. It provides a seasonal source of food and is also used in traditional medicine.

Bitterleaf
A shrub whose leaves have a potent bitter taste that is reduced by washing before cooking. The leaves are a popular vegetable in stews and soups and are a major ingredient in traditional medicine for treating malaria, diabetes, and gastrointestinal issues.

Bush Mango
While more common further south, this tree is found in Senegal’s southern forests. It produces a mango-like fruit, but its true value is in the seed kernel (ogbono), which is ground and used as a powerful thickening agent for traditional soups and stews.

Water-berry
This evergreen tree is typically found near water. It produces small, fleshy, purple-black fruits that are edible and have a slightly acidic taste. The tree is important for stabilizing riverbanks, and its bark and leaves have medicinal properties.

Wild Plum
A spiny, sprawling shrub or small tree that produces a tart, plum-like fruit rich in vitamin C. The kernel of the seed yields a non-drying oil used for cosmetics and cooking. The plant is very drought-resistant and has many uses in traditional medicine.

Nerve Plant
A deciduous tree known for its showy clusters of white to yellowish flowers with long, purple stamens. It is widely used in traditional medicine, particularly for nervous system disorders. The fruit and leaves are also sometimes eaten after cooking.

Corkwood
A small, twisted tree with a flaky, reddish bark. It is easily recognized by its heart-shaped, two-winged fruit that turns reddish-brown when mature. The plant has acidic leaves and is extensively used in traditional medicine and for making a red dye.

African Myrrh
A spiny, deciduous shrub or small tree with a peeling, papery bark. When the bark is cut, it exudes a fragrant, oily resin known as bdellium or African myrrh, which is used as incense and in traditional perfumes and medicines.

Bushwillow
A common, hardy savanna tree that is a key source of high-quality charcoal. It is very resistant to fire and drought. Its leaves are glutinous (sticky) to the touch, and it is widely used in traditional medicine, particularly for treating coughs and colds.

Candle Bush
This shrub is notable for its erect, candle-like clusters of bright yellow flowers. The leaves contain effective fungicidal compounds, making them a famous traditional remedy for skin diseases like ringworm. It is a fast-growing and visually striking plant.

African Fan Palm
Similar to the Doum Palm, this species also has branching trunks but is typically found in coastal environments. The fronds are used for weaving and thatch, and the fruit is edible. It is an important part of the coastal landscape and local economies.

False Shea
This tree resembles the true Shea tree but is distinguished by its longer, narrower leaves. It produces an oil from its seeds that is used for cooking and soap-making. The wood is extremely hard and durable, making it resistant to termites and fire.

Sandpaper Tree
The leaves of this fig tree are famously rough and abrasive, like sandpaper, and are used traditionally for smoothing wood and scouring pots. The plant also has various applications in traditional medicine, including as a treatment for hypertension.

Black Plum
An attractive tree with dark green foliage that produces a sweet, black, olive-like fruit. The fruit is popular and nutritious, eaten fresh or made into a jam or wine. The leaves are also edible as a vegetable, and the wood is useful.

Wild Loofah
A vigorous climbing vine whose young fruit is edible as a vegetable. When the fruit matures and dries, it leaves behind a fibrous skeleton that is used as a natural scrubbing sponge (loofah). The plant is both a food source and a useful household item.

Poison-arrow Tree
Known as the Desert Rose, this succulent shrub has a swollen, water-storing base (caudex) and stunning pink or red flowers. Despite its beauty, its sap is highly toxic and was historically used as an arrow poison for hunting.

Buffalo Thorn
A spiny shrub or small tree, named for its hooked and straight thorns that resemble a buffalo’s horns. The fruit is edible, and it is an important plant in many cultures, often associated with spiritual beliefs regarding ancestral spirits and burials.

Wild Coffee
A rare, wild coffee species native to West Africa. It has a complex flavor profile comparable to high-quality Arabica but is much more tolerant of high temperatures. Rediscovered in the wild, it holds promise for the future of climate-resilient coffee farming.

African Peach
A small tree or shrub whose fruit, bark, and roots are a veritable pharmacy in traditional medicine, used especially for fever and malaria. It produces a spherical, fleshy fruit that resembles a peach and is eaten by humans and animals.

Velvet Tamarind
This tall tree produces small, grape-sized fruits with a black, velvety shell. Inside is a sweet-sour, orange-colored pulp that is eaten as a snack. The pulp is rich in vitamin C, and the dense, hard wood is used for construction.

Camwood
A shrub or small tree from which a brilliant, red, insoluble dye is obtained from the heartwood. The powdered wood is used as a cosmetic for the skin and hair, as well as for dyeing cloth. It is an important cultural and economic plant.

Jiga
Known as the Violet Tree, this small tree produces beautiful, fragrant, violet-colored flowers. The roots are highly poisonous but are a powerful component in traditional medicine when used correctly, particularly for treating pain and inflammation. Its scent is very distinctive.

African Canarium
A large forest tree that produces an edible, olive-like fruit with oily, purple-black skin. The resin from the bark is fragrant and used as an incense and for caulking canoes. The hard seeds contain an edible oil, and the timber is used locally.

Water-lettuce
A free-floating aquatic plant that forms rosettes of leaves resembling a small head of lettuce. It provides habitat for fish and invertebrates but can become invasive, covering water surfaces. It is used in traditional medicine to treat skin conditions.

African Dragon’s Blood Tree
A branching, tree-like plant with clusters of strap-like leaves at the ends of its branches. When the bark is cut, it exudes a red resin, known as “dragon’s blood,” which is used as a dye and in traditional medicine.

Sausage Tree
This tree is unmistakable due to its large, sausage-shaped fruits that hang from long, rope-like stalks. The fruits are inedible for humans but are used in traditional medicine. The beautiful, dark red, bell-shaped flowers open at night to attract bat pollinators.

African Star Apple
A large forest tree that bears a round, yellowish fruit. When cut, the pulp has a star-shaped pattern. The fruit is sweet and is a popular snack. The tree’s bark and leaves are used in traditional medicine for their healing properties.

Fara
A spiny, multi-stemmed shrub or small tree with distinctive green bark and long, feathery leaves. It is extremely drought-tolerant and often grows in harsh environments. While native to the Americas, it is considered pre-historically naturalized and native to the Old World as well.

African Fan-weed
A large, woody climbing plant (liana) that can reach the tops of tall trees. It is characterized by its large, fan-shaped clusters of cream-colored, fragrant flowers. The strong, flexible stems are used as rope in construction and for tying bundles.

Casamance Tam-tam
A deciduous tree that produces an edible, velvety, apricot-like fruit. The wood is hard and is used for making drums (tam-tams), tool handles, and furniture. It is a valuable species for both its food and material resources in local communities.

Sudan Teak
A small, slender tree adapted to arid conditions. It has a bright yellow flower and produces a distinctive circular, winged fruit. The wood is hard and termite-resistant, and it is an important source of fodder for livestock, especially for camels.

Water Cabbage
A beautiful aquatic plant with large, round floating leaves and fragrant, white or pinkish flowers that open at night. The seeds and rhizomes are edible. It is an important part of freshwater ecosystems, providing food and shelter for wildlife.

Senegal Date Palm
A clustering palm that forms dense thickets, with several stems leaning out from a central clump. It produces small, edible but thin-fleshed dates. The leaves are used for weaving mats and baskets, and the sap can be tapped for palm wine.

Blackwood
This small, spiny tree yields one of the world’s most valuable timbers: African blackwood. The heartwood is extremely dense, fine-grained, and dark, making it ideal for musical instruments like clarinets and oboes. It is a slow-growing and highly threatened species.

Senegal Indigo
A shrubby plant that is a traditional source of blue indigo dye. The leaves are harvested, fermented, and processed to create the pigment used to color textiles. It was a historically important cash crop before the advent of synthetic dyes.

Wild Melon
This is the wild ancestor of the cultivated watermelon. Native to the arid regions of Africa, its fruits are typically smaller and have a more bitter or bland flesh. The seeds are nutritious and are a key source of food and oil in drylands.

African Foxglove
A slender, herbaceous plant with pink, foxglove-like flowers. The leaves are slimy and used as a vegetable to thicken soups and sauces, similar to okra. The seeds are rich in oil. It is both a wild and semi-domesticated food plant.
African Olive
The wild relative of the cultivated olive tree. It produces small, purple-black fruits that are edible but not as fleshy as commercial olives. The wood is extremely hard and durable. Its presence in Senegal marks the southern edge of its range.

Bird Plum
A medium-sized tree that produces a sweet, date-like fruit that is popular with birds and people. The fruit can be eaten fresh or stored and is a good source of energy. The tree is drought-resistant and provides valuable fodder for animals.

Wild Abutilon
A small shrub with velvety, heart-shaped leaves and yellow-orange flowers. The plant’s stems contain a strong fiber that can be used for making ropes and cords. It is a hardy plant often seen along roadsides and in fallow fields.

Gao Tree
A close relative of the African Birch, this tree is adapted to extremely arid conditions. It is a valuable and rare species in Senegal, representing a unique part of the country’s biodiversity. Its wood is dense and used for charcoal.

Sickle Bush
A spiny shrub or small tree easily identified by its distinctive bicolored flower spikes (pink and yellow) and its coiled, sickle-shaped seed pods. It can form dense, impenetrable thickets and is an important source of fodder and high-quality firewood.

Jumping Seed Tree
This tree is known for its seeds, which can be infested by moth larvae that cause them to “jump.” The tree produces a milky latex that is poisonous but has uses in traditional medicine. The wood is light and used for general-purpose work.

Wild Medlar
A small, multi-stemmed tree or shrub that produces a round, glossy fruit that is sweet and apple-flavored when fully ripe. It is a popular wild fruit, eaten fresh. The plant is hardy and has various uses in traditional medicine.

Tallow Tree
A tall forest tree whose seeds yield a yellow, edible fat known as “Kanya butter,” which is similar to shea butter. It is used for cooking and lighting. The tree’s large, showy red flowers are also a notable feature.

Devil’s Thorn
A prostrate herb known for its hard, spiny fruit that can pierce feet and tires. Despite being a nuisance, it is a powerful medicinal plant in many cultures, used to enhance vitality and treat various ailments. It is very drought-tolerant.

Marlberry
A small, evergreen shrub found in the humid undergrowth of forests. It produces clusters of small, red or black berries. While mainly an ornamental plant in other regions, it is a native component of Senegal’s forest flora.

African Cucumber
A climbing vine with tendrils and lobed leaves. It produces a warty, orange-red fruit that bursts open to reveal seeds covered in a bright red, sweet pulp. The leaves and young fruits are used as a vegetable and in traditional medicine.

Red Stinkwood
A rare tree in Senegal, found at higher elevations. The bark is a major source for a medicinal extract used to treat prostate disorders. High demand has led to over-harvesting, making it an endangered species across its African range.

Bush Banana
A small shrub or liana with aromatic leaves and distinctively lumpy, finger-like yellow or red fruits. The sweet, aromatic pulp of the fruit is edible. The roots and leaves are widely used in traditional medicine, especially for fevers.

Cat’s Whiskers
A shrub recognized by its dense, ball-shaped clusters of white, fragrant flowers with long, protruding stamens that resemble a cat’s whiskers. It is a common and attractive plant in the undergrowth of wetter areas and has medicinal uses.





