In marshes, swamps and pond margins, plants form the backbone of habitat structure and water filtration. Whether you’re walking a coastal saltmarsh or surveying an inland sedge meadow, a clear species list helps with identification, monitoring and practical management.
There are 44 wetland vegetation, ranging from American lotus to Yellow iris. For each entry you’ll find below the columns Scientific name,Growth form & habitat,Typical height (cm) so you can compare identification features, preferred environments and expected stature — see the full list you’ll find below.
How can I use this list to identify plants in the field?
Use the Scientific name to confirm identifications, check Growth form & habitat to narrow where a species is likely to occur, and compare observed stems or leaves to Typical height (cm). Take photos of key features (flowers, leaves, seedheads) and note water depth and substrate; combine the list with a regional field guide for best results.
Which species on the list should I watch as potential invasives or management targets?
Some common wetland ornamentals and colonizers (for example, Yellow iris in many regions) can spread aggressively; consult your local invasive species list first. Management approaches vary by species and site condition but often include monitoring, targeted removal, and follow-up to prevent reestablishment.
Wetland Vegetation
| Name (common) | Scientific name | Growth form & habitat | Typical height (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cattail | Typha latifolia | Emergent; freshwater marsh edges, ditches, ponds | 100-300 |
| Common reed | Phragmites australis | Emergent; brackish and freshwater marshes, tidal flats | 200-400 |
| Bulrush | Schoenoplectus tabernaemontani | Emergent; shallow water margins, marshes, ponds | 75-250 |
| Soft rush | Juncus effusus | Emergent; wet meadows, ditches, marsh margins | 50-120 |
| Tussock sedge | Carex stricta | Emergent; freshwater marshes, wet meadows, stream edges | 30-100 |
| Marsh marigold | Caltha palustris | Emergent; spring-flooded marshes, streambanks, wet meadows | 15-50 |
| Pickerelweed | Pontederia cordata | Emergent; shallow ponds, marsh edges, slow streams | 30-100 |
| White water lily | Nymphaea odorata | Floating-leaved; ponds, lakes, slow rivers | 10-60 |
| Duckweed | Lemna minor | Free-floating; still waters, ponds, slow backwaters | 0.1-0.5 |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Free-floating; freshwater lakes, slow rivers, tropical wetlands | 10-50 |
| Water smartweed | Persicaria amphibia | Emergent/submerged; ponds, marshes, stream margins | 20-100 |
| Common arrowhead | Sagittaria latifolia | Emergent; marshes, shallow pond bottoms, ditches | 20-70 |
| Eurasian watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum | Submerged; lakes, ponds, slow streams | 5-150 |
| Pondweed | Potamogeton perfoliatus | Submerged/emergent; ponds, lakes, slow rivers | 10-200 |
| Eelgrass | Zostera marina | Submerged marine; tidal flats, estuaries, shallow coastal bays | 10-100 |
| Smooth cordgrass | Spartina alterniflora | Emergent; intertidal salt marshes, tidal creeks | 50-200 |
| Red mangrove | Rhizophora mangle | Woody; tropical tidal mangrove fringe | 200-1,000 |
| Black mangrove | Avicennia germinans | Woody; tropical/subtropical tidal flats, salt marsh margins | 200-700 |
| Buttonbush | Cephalanthus occidentalis | Woody shrub; freshwater swamps, pond margins, floodplains | 150-400 |
| Black willow | Salix nigra | Woody; streambanks, floodplains, wet woods | 500-1,200 |
| Black alder | Alnus glutinosa | Woody; riparian zones, wet woodlands, swamp edges | 500-1,200 |
| Sphagnum moss | Sphagnum palustre | Moss; peat bogs, acidic pools, hummocks | 0.5-10 |
| Cotton grass | Eriophorum angustifolium | Emergent; peat bogs, wet heaths | 20-80 |
| Purple loosestrife | Lythrum salicaria | Emergent; wetlands, marshes, ditches, river edges | 50-150 |
| Bur-reed | Sparganium eurycarpum | Emergent; shallow water, pond margins, marshes | 30-120 |
| Water plantain | Alisma plantago-aquatica | Emergent; ponds, ditches, slow rivers | 20-100 |
| Water horsetail | Equisetum fluviatile | Emergent; marshes, ditches, wet meadows | 30-120 |
| Yellow iris | Iris pseudacorus | Emergent; pond margins, ditches, wetlands | 50-100 |
| Skunk cabbage | Symplocarpus foetidus | Emergent; wet woods, swampy ground, spring seepages | 30-120 |
| Leatherleaf | Chamaedaphne calyculata | Woody shrub; acidic bogs, peatlands, hummocks | 20-100 |
| Bog laurel | Kalmia polifolia | Woody shrub; bogs, peatlands, cold wetlands | 10-50 |
| Seaside goldenrod | Solidago sempervirens | Emergent; coastal dunes, salt marsh edges | 30-150 |
| Switchgrass | Panicum virgatum | Emergent; wet prairies, marsh edges, ditches | 50-200 |
| Bogbean | Menyanthes trifoliata | Emergent/floating; bog pools, shallow marshes | 10-50 |
| Bladderwort | Utricularia vulgaris | Submerged/free-floating; ponds, marshes, slow waters | 1-50 |
| Watercress | Nasturtium officinale | Submerged/emergent; springs, streams, slow-flowing waters | 10-60 |
| Spike rush | Eleocharis palustris | Emergent; marshes, pond edges, mudflats | 10-70 |
| Marsh fern | Thelypteris palustris | Emergent; wet woodlands, marsh edges, floodplain forests | 30-90 |
| Glasswort (pickleweed) | Salicornia europaea | Succulent halophyte; salt marshes, mudflats, saline flats | 5-50 |
| American lotus | Nelumbo lutea | Floating-leaved; shallow ponds, marshes, slow rivers | 30-200 |
| Spatterdock | Nuphar lutea | Floating-leaved; ponds, slow rivers, marshes | 20-100 |
| Rice-cutgrass | Leersia oryzoides | Emergent; marshes, wet meadows, pond edges | 50-150 |
| Swamp milkweed | Asclepias incarnata | Emergent; wet meadows, marsh edges, ditches | 50-150 |
| Golden club | Orontium aquaticum | Emergent/floating; acidic bog ponds, swamps | 20-70 |
Images and Descriptions

Cattail
Tall, dense marsh perennial with cigar-shaped brown flower spikes and long straplike leaves. Easily identified by distinctive seed heads and erect leaves. Provides wildlife cover, nests, and sediment stabilisation; some Typha taxa spread where water regimes change.

Common reed
Robust grass forming tall reedbeds with feathery tan plumes. Native and invasive lineages exist; invasive types form dense monocultures that displace natives and alter hydrology. Look for hairy ligules, dense stands, and tall, rigid stems.

Bulrush
Stout, round stems with tufted brown flower clusters near stem tips. Grows in shallow water or mud forming dense stands used by birds and fish. Stems are hollow; often mistaken for other rushes but terminal inflorescences are diagnostic.

Soft rush
Clump-forming rush with smooth, cylindrical green stems and inconspicuous brown flowers. Tolerates saturated, poorly drained soils and forms tussocks. Often confused with sedges or grasses; stems are leafless and round, producing small clusters of seed capsules.

Tussock sedge
Forms dense tussocks of narrow, rough-edged leaves with brown seed spikes. Common in marshes and wet meadows, creating hummocks used by amphibians and insects. Clumping habit and saddle-shaped perigynia help identify sedges from grasses.

Marsh marigold
Early spring bloomer with bright yellow buttercup-like flowers and glossy rounded leaves. Favors cold, seasonally flooded soils. Easy to spot when flowering; historically used medicinally but leaves are mildly toxic raw.

Pickerelweed
Perennial with heart-shaped leaves and erect spikes of blue-violet flowers in summer. Roots in shallow mud; leaves may float or rise above water. Attracts pollinators and waterfowl; common in North American freshwater wetlands.

White water lily
Large rounded floating leaves with fragrant white flowers that open on the water surface. Pads shade water, reduce algae and provide habitat for aquatic life. Distinctive star-shaped flowers and central yellow stamens aid identification.
Duckweed
Tiny round to oblong floating fronds often forming green mats. Rapidly colonizes nutrient-rich waters; useful for nutrient removal but can reduce light and oxygen. Identified by single rootlet per frond and very small size.

Water hyacinth
Showy floating plant with glossy leaves and violet flower spikes; notorious invasive forming dense mats that block waterways. Bulbous petioles and feathery roots are diagnostic. Major ecological and management problem in warm climates.

Water smartweed
Variable aquatic perennial with submerged or emergent stems, lance-shaped leaves, and spikes of pink flowers. Can root in mud or float. Identified by clasping leaf bases, sheathing stipules (ocrea), and alternate leaves.

Common arrowhead
Recognizable by arrowhead-shaped leaves and white three-petaled flowers. Produces edible tubers historically used by Native peoples. Roots in muddy substrates; easy to identify by distinctive leaf shape and marsh habitat.

Eurasian watermilfoil
Feathery, finely divided underwater leaves arranged in whorls create dense underwater canopies. Eurasian watermilfoil is invasive in many regions, forming surface mats and altering habitats. Identification by leaf division and branching habit.

Pondweed
Variable genus with submerged and floating leaves; P. perfoliatus has blade-like submerged leaves and clasping bases. Important food for waterfowl and fish. Species ID often requires close examination of leaf shape, arrangement, and fruits.

Eelgrass
Long ribbonlike leaves form underwater meadows crucial for fish nurseries and shoreline stability. Found in saline to brackish tidal zones; leaves often host epiphytes. Sensitive to turbidity and nutrient loading; unique marine wetland plant.

Smooth cordgrass
Dominant low marsh grass tolerant of daily tidal flooding and salinity. Builds sediment and supports marsh fauna. Identifiable by long narrow leaves and lower elevation tidal zone. Introduced strains can be invasive outside native range.

Red mangrove
Salt-tolerant tree with prominent prop roots and thick leathery leaves; grows at water’s edge in tropical zones. Root network creates crucial nursery habitat and stabilizes shorelines. Distinctive prop roots and viviparous seedlings aid ID.

Black mangrove
Tree with pneumatophores (air roots) and grey-green leaves often with salt excretion. Occupies higher intertidal zones and tolerates saline, compacted soils. Important for coastal stabilization and salt marsh zonation.

Buttonbush
Multi-stemmed shrub with spherical clusters of white tubular flowers that attract pollinators. Prefers standing water and saturated soils. Provides nectar and nesting habitat; seeds and foliage used by wildlife though toxic to livestock.

Black willow
Fast-growing riparian tree with lanceolate leaves and flexible branches. Sprouts readily from cuttings and stabilizes eroding banks. Early-season catkins feed pollinators; bark and branch habit help ID willows along waterways.

Black alder
Deciduous tree with serrated leaves and small cone-like fruiting bodies. Forms nitrogen-fixing root nodules that enrich wet soils; common along streams and in wet woodlands. Catkins in spring and dark bark aid recognition.

Sphagnum moss
Peat-forming moss creating spongy carpets that hold vast water quantities and acidify bogs. Pale green to red cushions form hummocks and hollows. Crucial for carbon storage and unique bog plant communities; easy to spot by texture.

Cotton grass
Grasslike perennial with narrow leaves and distinctive white cottony seed heads in summer. Thrives in acidic, waterlogged bogs and tundra, creating fluffy seed displays. Important for peatland ecology and visible in open bog landscapes.

Purple loosestrife
Tall perennial with spikes of magenta flowers and opposite leaves; highly invasive in many regions, forming dense stands that displace native wetland flora. Square stems and showy flower spikes make it easy to identify in disturbed wetlands.

Bur-reed
Rhizomatous plant with round or straplike leaves and distinctive spherical spiky seed heads. Roots in mud and offers cover and food for waterfowl. Spherical fruits readily separate it from other emergents.

Water plantain
Rosette of lance-shaped leaves with branching stalks bearing small white to pink flowers. Grows in shallow water or muddy banks and may be eaten historically in some areas. Leaves often held above or at water surface.

Water horsetail
Jointed, hollow green stems with rough texture and small reduced leaves. Prefers shallow water or saturated soils and spreads via rhizomes. Ancient nonflowering plant; identification by segmented stem and lack of broad leaves.

Yellow iris
Large showy plant with swordlike leaves and bright yellow flowers arising from rhizomes in shallow water. Invasive in many regions where it forms dense stands. Identification is simple by flower color and erect broad leaves.

Skunk cabbage
Early spring perennial with mottled hood-like spathe and a spadix, later producing huge odorous leaves. Generates heat to melt surrounding snow. Strong skunky smell when crushed; distinctive in wet forested wetlands.

Leatherleaf
Low evergreen shrub with leathery narrow leaves and drooping clusters of small white bell-shaped flowers. Thrives on peat hummocks in bogs, often with sphagnum. Forms dense mats that structure bog microhabitats.

Bog laurel
Low evergreen shrub with glossy leaves and pink, star-like clustered flowers in spring. Restricted to acidic peat bogs and wet heaths; leaves and tissues are toxic. Attractive but limited to specialized bog habitats.

Seaside goldenrod
Salt-tolerant goldenrod with dense clusters of yellow flowers late summer into fall. Stabilizes coastal soils and attracts pollinators; leaves often thick and somewhat succulent near tips. Common on upper salt marsh edges and dunes.

Switchgrass
Clump-forming perennial grass with tall airy seed panicles and coarse leaves. Tolerant of wet soils and periodic flooding; used for erosion control and wildlife cover. Foliage turns golden in autumn and stems persist.

Bogbean
Rhizomatous plant with glossy trifoliate leaves and upright clusters of white to pinkish fragrant flowers. Common in acidic pools and peaty marshes; roots in peat and forms small floating mats. Noted for its showy spring blooms.
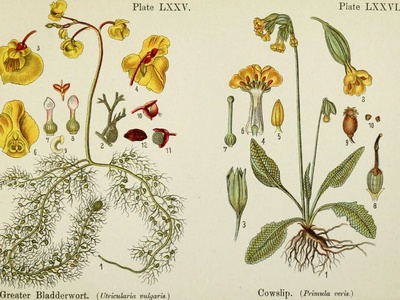
Bladderwort
Leafless or finely divided underwater foliage bearing tiny bladder traps for small aquatic animals; produces showy yellow snapdragon-like flowers above water. Carnivorous aquatic indicating nutrient-poor to moderate waters and unique feeding strategy.

Watercress
Fast-growing aquatic herb with pinnate, peppery-flavored leaves and small white flowers. Roots in flowing water or saturated banks and forms dense mats. Edible when harvested safely; identifiable by pinnate leaves and spicy taste.

Spike rush
Slender, grasslike stems topped by small brownish spikelets; leaves are reduced so stems perform photosynthesis. Forms dense colonies in shallow water and mud, useful for shore stabilisation and providing cover for small wildlife.

Marsh fern
Delicate-looking fern with arching pinnate fronds and toothed leaflets. Prefers shady, wet soils and seasonally flooded habitats. Identified by triangular frond outline and habitat specificity to marshy or flooded woodlands.

Glasswort (pickleweed)
Low, jointed succulent stems forming mats in high-salinity mudflats; often orange-red in autumn. Tolerates salt inundation and is a pioneer on saline substrates. Easily recognised by fleshy, segmented stems and lack of distinct leaves.

American lotus
Large circular leaves and showy pale pink flowers with distinctive round seedpods held well above water. Grows from rhizomes in mud and provides abundant wildlife habitat. Leaves are typically upright and distinct from water lilies.

Spatterdock
Large heart-shaped floating leaves with cup-shaped yellow flowers often held partially submerged. Grows near shore in stagnant to slow waters and provides cover for fish and amphibians. Fruit and flower form help differentiate from Nymphaea.

Rice-cutgrass
Coarse grass with sharp-edged leaves that can cut skin; produces open panicles and forms dense stands in shallow marshes and along shores. Important nesting cover and bank stabiliser; blades rough and characteristic when handled.

Swamp milkweed
Perennial with clusters of pink to mauve fragrant flowers that attract monarchs and other pollinators. Prefers wet soils and forms upright clumps. Milky sap and opposite leaves help identify milkweeds; ecologically valuable for butterflies.

Golden club
Unique aquatic with a single golden cone-like flower (spadix) and floating to emergent leaves. Native to eastern North America in boggy ponds and swamps. Flower lacks showy petals but is unmistakable by its golden spadix and simple leaves.





