Denmark’s mix of islands, coastline, farmland and forest supports a surprising variety of mammals, from small coastal rodents to large forest species. Seasonal migrations and human land use make the country’s mammal fauna dynamic and interesting to follow.
There are 49 Mammals of Denmark, ranging from American mink to Wild boar. For each species you’ll see the columns Scientific name,Status,Size (weight kg; length cm); details you’ll find below.
Which species on the list are non-native or introduced to Denmark?
A few species are introduced or escaped from captivity, the most notable being the American mink (originally from fur farms) which has impacted native wildlife; others have been translocated or expanded their range naturally. The list’s Status column highlights whether a species is native, introduced, re-established or vagrant, so check that field first.
How can I use the table to help identify mammals I see in the field?
Use the Size (weight kg; length cm) together with habitat notes and the Scientific name to narrow possibilities; weight and length give quick size cues, status indicates how likely a sighting is (common vs. rare), and comparing multiple columns makes identification and follow-up research straightforward.
Mammals of Denmark
| Common name | Scientific name | Status | Size (weight kg; length cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red fox | Vulpes vulpes | Native | 5–8 kg; 60–90 cm |
| European badger | Meles meles | Native | 7–12 kg; 60–90 cm |
| Eurasian otter | Lutra lutra | Native | 7–12 kg; 80–110 cm |
| Eurasian beaver | Castor fiber | Native | 16–30 kg; 70–100 cm |
| European hedgehog | Erinaceus europaeus | Native | 0.6–1.2 kg; 20–30 cm |
| European mole | Talpa europaea | Native | 0.06–0.1 kg; 11–16 cm |
| Red squirrel | Sciurus vulgaris | Native | 0.2–0.5 kg; 18–25 cm |
| European rabbit | Oryctolagus cuniculus | Introduced | 1–2.5 kg; 30–45 cm |
| Brown hare | Lepus europaeus | Native | 3–5 kg; 50–70 cm |
| Roe deer | Capreolus capreolus | Native | 15–30 kg; 90–135 cm |
| Red deer | Cervus elaphus | Native | 100–250 kg; 170–250 cm |
| Fallow deer | Dama dama | Introduced | 30–80 kg; 120–150 cm |
| Wild boar | Sus scrofa | Native | 50–150 kg; 120–200 cm |
| Moose | Alces alces | Vagrant | 200–600 kg; 180–250 cm |
| Stoat | Mustela erminea | Native | 0.1–0.4 kg; 17–32 cm |
| Least weasel | Mustela nivalis | Native | 0.02–0.1 kg; 11–20 cm |
| European polecat | Mustela putorius | Native | 0.7–1.6 kg; 35–50 cm |
| Pine marten | Martes martes | Native | 0.8–2.0 kg; 40–55 cm |
| Stone marten | Martes foina | Native | 0.7–1.8 kg; 35–50 cm |
| American mink | Neogale vison | Introduced | 0.6–1.2 kg; 30–50 cm |
| Brown rat | Rattus norvegicus | Introduced | 0.2–0.5 kg; 20–30 cm |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Introduced | 0.015–0.03 kg; 6–10 cm |
| Common vole | Microtus arvalis | Native | 0.02–0.08 kg; 9–12 cm |
| Field vole | Microtus agrestis | Native | 0.02–0.06 kg; 9–13 cm |
| Bank vole | Myodes glareolus | Native | 0.02–0.06 kg; 10–15 cm |
| Water vole | Arvicola amphibius | Native | 0.1–0.3 kg; 15–22 cm |
| Common shrew | Sorex araneus | Native | 0.005–0.02 kg; 5–10 cm |
| Pygmy shrew | Sorex minutus | Native | 0.003–0.007 kg; 4–6 cm |
| Greater white-toothed shrew | Crocidura russula | Native | 0.01–0.02 kg; 7–10 cm |
| Water shrew | Neomys fodiens | Native | 0.02–0.05 kg; 8–12 cm |
| Harbour porpoise | Phocoena phocoena | Native | 40–60 kg; 130–170 cm |
| Harbour seal | Phoca vitulina | Native | 60–120 kg; 120–170 cm |
| Grey seal | Halichoerus grypus | Native | 160–300 kg; 200–300 cm |
| Minke whale | Balaenoptera acutorostrata | Vagrant | 5,000–8,000 kg; 700–1,000 cm |
| Fin whale | Balaenoptera physalus | Vagrant | 15,000–25,000 kg; 1500–2700 cm |
| Sperm whale | Physeter macrocephalus | Vagrant | 35,000–57,000 kg; 900–1,200 cm |
| Orca | Orcinus orca | Vagrant | 3,000–6,000 kg; 600–900 cm |
| Common dolphin | Delphinus delphis | Vagrant | 80–150 kg; 180–260 cm |
| White-beaked dolphin | Lagenorhynchus albirostris | Vagrant | 150–220 kg; 200–250 cm |
| Daubenton’s bat | Myotis daubentonii | Native | 0.007–0.015 kg; 4–6 cm |
| Common pipistrelle | Pipistrellus pipistrellus | Native | 0.004–0.008 kg; 3–5 cm |
| Soprano pipistrelle | Pipistrellus pygmaeus | Native | 0.004–0.008 kg; 3–5 cm |
| Nathusius’ pipistrelle | Pipistrellus nathusii | Native | 0.006–0.012 kg; 4–6 cm |
| Noctule | Nyctalus noctula | Native | 0.02–0.04 kg; 6–9 cm |
| Brown long-eared bat | Plecotus auritus | Native | 0.006–0.013 kg; 4–6 cm |
| Natterer’s bat | Myotis nattereri | Native | 0.006–0.012 kg; 4–6 cm |
| Leisler’s bat | Nyctalus leisleri | Native | 0.02–0.04 kg; 6–9 cm |
| Parti-coloured bat | Vespertilio murinus | Vagrant | 0.02–0.03 kg; 6–8 cm |
| Serotine | Eptesicus serotinus | Native | 0.02–0.06 kg; 6–9 cm |
Images and Descriptions

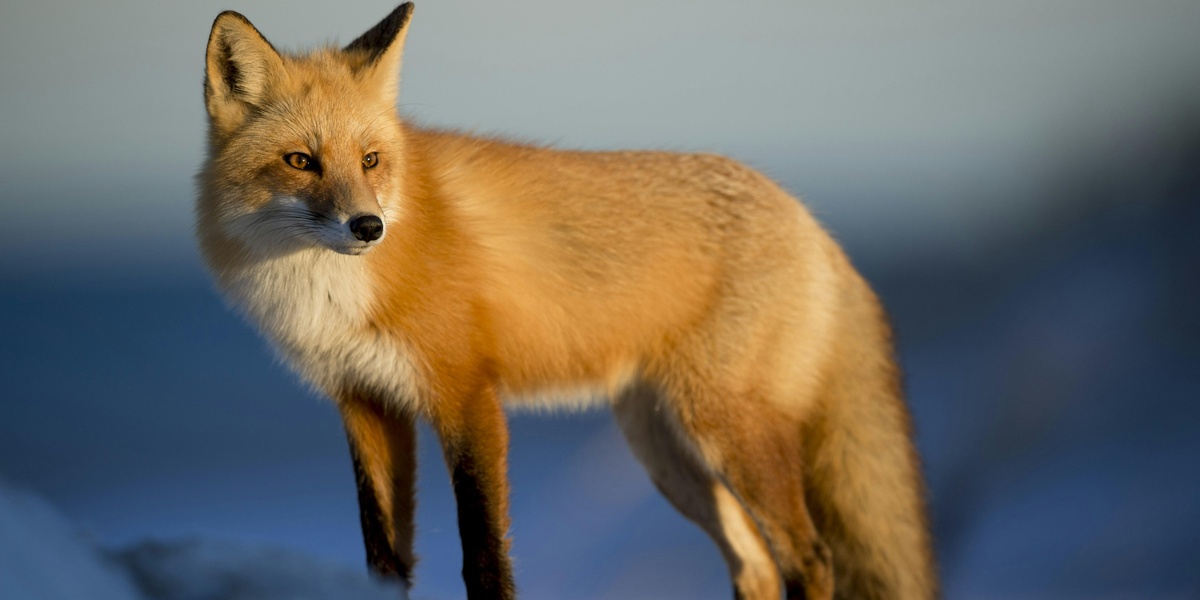
Red fox
Widespread across Denmark in farmland, forests and near towns. Clever, adaptable predator often seen at dusk and dawn; scatters dens and feeds on rodents, birds and human food waste, making it Denmark’s familiar wild canid.

European badger
Common in woodlands and hedgerows across Jutland and Zealand. Social, burrowing mammal living in setts; primarily nocturnal omnivore notable for its strong claws and role in controlling small mammals and insects.

Eurasian otter
Found along Denmark’s coasts, estuaries and larger rivers. Semi-aquatic predator that eats fish and crustaceans; populations have recovered following pollution control and legal protection, now seen more often near shorelines.

Eurasian beaver
Reintroduced and now established in rivers and wetlands across Denmark. Industrious ecosystem engineer that builds dams and lodges, creating valuable wetland habitats and attracting birdlife; increasingly common in suitable freshwater areas.

European hedgehog
Familiar garden visitor across Denmark’s towns and countryside. Nocturnal insect-eater that hibernates in winter; faces decline from road traffic and habitat loss, so gardeners often create hedgehog-friendly spaces.

European mole
Widespread in lawns, meadows and farmland throughout Denmark. Subterranean insectivore that creates distinctive molehills and tunnels; rarely seen above ground but common signposts of healthy soil in parks and fields.

Red squirrel
Found in woodland patches and parks, especially in larger forested areas. Diurnal tree-dweller that caches seeds and cones; reddish coat and ear tufts make it a much-loved woodland resident.

European rabbit
Introduced and established in dunes, grasslands and parks, especially on coastal islands. Burrowing, social herbivore that can form large colonies; valued for conservation grazing but sometimes considered an agricultural pest.

Brown hare
Common in open farmland and heathland across Denmark. Fast, long-legged mammal visible at twilight; known for its solitary lifestyle, long ears and the spectacular “boxing” behavior in spring.

Roe deer
Widespread in woodland edges, hedgerows and farmland. Small deer commonly seen at dawn and dusk; browsers that adapt well to human-modified landscapes and are a familiar sight on rural roadsides.

Red deer
Occurs in larger forested areas and reserves in Jutland and Zealand. Large, stately deer with impressive antlers on stags; historically managed for hunting, populations have expanded in recent decades.

Fallow deer
Introduced, now present in parks and woodlands, often in managed populations. Distinctive spotted coats and palmate antlers on males; commonly seen in estate woodlands and some wild populations.

Wild boar
Present in forests and scrubby areas across Denmark with growing numbers. Omnivorous and nocturnal, boar root for food and can cause crop damage; populations have expanded following protection and habitat changes.

Moose
Occasional visitor from Sweden, mostly in northern Jutland and island coastlines. Massive, solitary browsers rarely establish long-term populations; notable when seen because of their size and rarity in Denmark.

Stoat
Found in woodland edges, farmland and wetlands across Denmark. Agile small carnivore that hunts rodents and birds; undergoes seasonal coat change in northern areas (brown to white in winter).

Least weasel
Tiny, widespread predator of small rodents in fields and gardens. Extremely agile and fierce for its size, the least weasel helps control vole and mouse populations and is active day and night.

European polecat
Occurs across farmland and woodland; adaptable and mostly nocturnal. Historically persecuted, polecats have recovered and sometimes hybridise with feral domestic cats in edge habitats.

Pine marten
Lives in mature woodlands and forested areas in Denmark. Arboreal, solitary predator feeding on small mammals, birds and fruit; elusive but increasing in parts of the country.

Stone marten
Common around villages, farms and towns; often uses buildings for dens. Opportunistic omnivore that thrives near humans, known for raiding poultry and nesting boxes.

American mink
Escaped or released from fur farms and now established along coasts, rivers and wetlands. Semi-aquatic predator affecting native waterbird and small mammal populations; target of control in some areas.

Brown rat
Very common in urban, port and agricultural areas across Denmark. Successful commensal species associated with humans; scavenges food and can spread disease if not managed.

House mouse
Widespread in buildings, farms and fields. Small, adaptable commensal rodent that breeds year-round indoors; common but largely unnoticed except where it becomes a pest.

Common vole
Abundant in grasslands, meadows and field margins across Denmark. Important prey for raptors and mustelids, the vole’s population cycles influence predator numbers and farmland ecology.

Field vole
Widespread in grassy and marshy habitats, especially in northern and central Denmark. Short-lived and highly productive, field voles are key food for owls, foxes and stoats.

Bank vole
Common in woodlands, hedges and gardens across Denmark. Seed-eating rodent that nests among ground vegetation; often more abundant in wooded patches and supports many predators.

Water vole
Found along slow rivers, ditches and wetlands though locally reduced. Herbivorous burrower that creates steep bank burrows; habitat loss and mink predation have impacted some populations.
Common shrew
Widespread in gardens, fields and woodlands. High-metabolism insectivore that feeds constantly; small but abundant, playing a significant role in controlling invertebrates.
Pygmy shrew
Tiny insect-eating shrew found in moist grassland and woodland. Highly active and secretive, it consumes large quantities of invertebrates relative to body size.

Greater white-toothed shrew
Occurs mainly in southern Denmark and coastal areas. Insectivore that has expanded its range in parts of northern Europe; often found in gardens, hedgerows and grassy habitats.

Water shrew
Semi-aquatic shrew found along streams and marshes. Excellent swimmer with water-repellent fur; feeds on aquatic invertebrates and small fish and is an indicator of healthy waterways.

Harbour porpoise
Small cetacean common in Danish coastal and offshore waters. Often seen singly or in small groups, porpoises are shy but abundant in the Baltic and North Sea, important for marine biodiversity.

Harbour seal
Seen on sandy shores and sheltered coasts throughout Denmark. Common seal that hauls out on sandbanks and rocks; feeds on fish and has recovered after hunting restrictions.

Grey seal
Larger seal found on Wadden Sea coasts and rocky shores. Breeds on offshore sandbanks and islands; powerful swimmer and an increasingly visible part of Denmark’s marine life.

Minke whale
Regular seasonal visitor to Danish waters, especially the North Sea. Small baleen whale seen during summer migrations; occasional strandings and sightings excite local whale-watchers and scientists.

Fin whale
Rare but recorded in Danish territorial waters. Second-largest whale species that passes through the North Sea; notable for their speed and occasional spectacular sightings offshore.

Sperm whale
Occasional deep-water visitor or stranded individual in Danish waters. Iconic deep-diving toothed whale, large and uncommon; strandings get considerable public and scientific attention.

Orca
Rare visitor to Danish seas, typically in groups. Apex predator occasionally seen offshore or during unusual marine events; charismatic and notable when observed by whale-watchers.

Common dolphin
Occasionally recorded in the North Sea off Denmark, especially in warmer years. Fast, sociable dolphin that sometimes forms large pods and attracts attention from coastal observers.

White-beaked dolphin
Seen in offshore North Sea waters and occasionally closer to Danish coasts. Robust dolphin of colder waters; sporadic sightings are exciting for marine mammal enthusiasts.

Daubenton’s bat
Common near rivers, lakes and wetlands across Denmark. Hunts low over water for insects, using clicks and calls; often roosts in bridges and buildings as well as trees.
Common pipistrelle
Very common around buildings, parks and woodland edges. Tiny evening flier that eats midges and mosquitoes; often encounters in towns and cities make it the most familiar bat.
Soprano pipistrelle
Closely related to the common pipistrelle but prefers wetland and coastal habitats. Regular in Denmark, especially near reedbeds and waterways where it feeds on small aquatic insects.
Nathusius’ pipistrelle
Migratory species recorded regularly in Denmark during migration seasons and breeding in some areas. Prefers woodlands and coastal stopover sites, notable for long-distance autumn and spring movements.

Noctule
Large tree-roosting bat found in parks and open woodlands. Early evening flier that hunts high flying insects; often among the first bats to appear at dusk.

Brown long-eared bat
Seen in woodland and rural buildings, notable for very large ears and slow, maneuverable flight. Hunts moths and gleaners that it catches from vegetation or surfaces.

Natterer’s bat
Found in woodlands and buildings; agile flier that gleans insects from vegetation and bark. Prefers sheltered habitats and roosts in tree holes and old buildings.

Leisler’s bat
Occasionally common in southern and coastal Denmark. Migratory and fast-flying, often uses tree and building roosts; seen at dusk hunting over open countryside and water.

Parti-coloured bat
Irregular migrant to Denmark, recorded most often in autumn. Striking two-toned fur and fast flight; sightings are notable because this species is mainly eastern in distribution.

Serotine
Generally found in southern Denmark and urban areas. Larger, slow-flying bat that hunts beetles and moths; roosts in buildings and attics and is active later at night.





