Micronesia’s islands span coral atolls and volcanic peaks with tightly knit ecosystems that evolved in isolation. That makes native plants and animals especially vulnerable when non-native species arrive, and impacts can cascade quickly across small islands.
There are 26 Invasive Species in Micronesia, ranging from Aedes aegypti to Tropical fire ant; for each species the list below shows Scientific name,Native range,Islands affected to help you assess impacts and distribution — you’ll find below.
Which invasive species cause the most immediate harm to people and wildlife?
Mosquitoes like Aedes aegypti pose direct public-health risks by spreading dengue and other diseases, while species such as the Tropical fire ant disrupt ground-nesting birds, agriculture and native invertebrates; rats, invasive plants and freshwater predators can likewise drive rapid declines depending on the island. Prioritizing species depends on local ecology, human health risks and feasibility of control.
How can residents and visitors reduce the chance of introducing or spreading invasive species?
Follow basic biosecurity: clean boats, gear and footwear, avoid moving soil or firewood, inspect and quarantine plants or animals, and report unusual sightings to local authorities. Community monitoring, early reporting and cooperating with eradication efforts make prevention and rapid response far more effective.
Invasive Species in Micronesia
| Name | Scientific name | Native range | Islands affected |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brown tree snake | Boiga irregularis | Southeast Asia (New Guinea, Solomon Is.) | Guam |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | South Asia/commensal cosmopolitan origin | Widespread across Micronesia (Guam,CNMI,Palau,FSM,RMI) |
| Polynesian rat | Rattus exulans | Southeast Asia/Polynesia | Widespread across Micronesia (island-by-island) |
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | Northern Asia/Europe (commensal) | Major ports and islands across Micronesia |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Global (commensal) | Widespread across Micronesia |
| Feral pig | Sus scrofa | Eurasia (domesticated origin) | Many islands in Micronesia (Guam,CNMI,Palau,FSM) |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | Domesticated origin (global) | Widespread across Micronesia |
| Feral dog | Canis lupus familiaris | Domesticated origin (global) | Widespread across Micronesia |
| Philippine deer | Rusa marianna | Philippines | Guam,Northern Mariana Islands (some islands) |
| Coconut rhinoceros beetle | Oryctes rhinoceros | South/Southeast Asia | Guam,Northern Mariana Islands,Palau,other Micronesian detections |
| Giant African snail | Achatina fulica | East Africa | Guam,CNMI,Palau,FSM |
| Aedes aegypti | Aedes aegypti | Africa (globalized tropics) | Widespread across Micronesia (Guam,CNMI,Palau,FSM,RMI) |
| Aedes albopictus | Aedes albopictus | Southeast Asia | Widespread across Micronesia |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | Culex quinquefasciatus | Tropical/subtropical global | Widespread across Micronesia |
| Tilapia | Oreochromis spp. | Africa (introduced worldwide) | Freshwater habitats across Micronesia (FSM,Palau,Guam) |
| Leucaena | Leucaena leucocephala | Mexico/Central America | Widespread across Micronesia |
| Siam weed | Chromolaena odorata | Central/South America | Palau,Guam,FSM,and other islands |
| Mile-a-minute vine | Mikania micrantha | Central/South America | Pohnpei,Palau,other FSM sites |
| Australian pine | Casuarina equisetifolia | Australia/Asia | Coastal areas across Micronesia (Guam,Palau,FSM) |
| Common guava | Psidium guajava | Central/South America | Widespread across Micronesia |
| Koster’s curse | Clidemia hirta | Neotropics (Americas) | Guam,Palau,FSM (select islands) |
| Lantana | Lantana camara | Tropical Americas | Guam,Palau,FSM |
| Cogon grass | Imperata cylindrica | Southeast Asia/Africa | Guam and other disturbed sites |
| Rat lungworm | Angiostrongylus cantonensis | Southeast Asia | Guam,CNMI,detected in other Micronesian islands |
| Common myna | Acridotheres tristis | South Asia | Palau,Guam,other Micronesian islands |
| Tropical fire ant | Solenopsis geminata | Central/South America/Neotropics | Guam,CNMI,other Micronesian locations |
Images and Descriptions

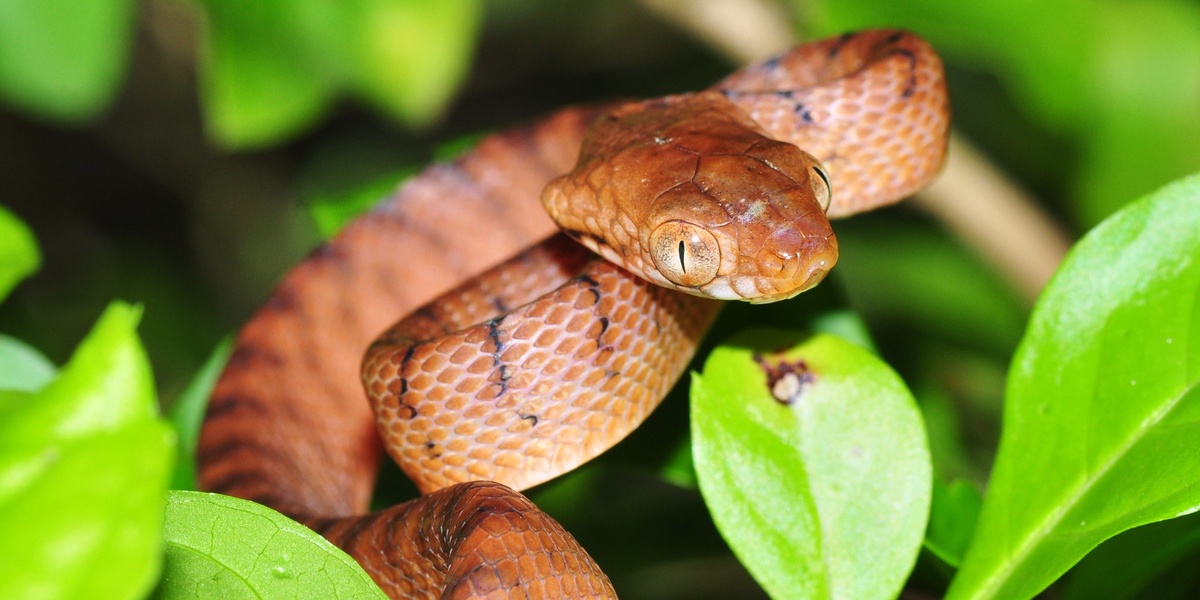
Brown tree snake
A nocturnal arboreal snake that arrived after WWII and devastated Guam’s native birds, lizards, and bats. Ongoing surveillance, baiting and transport checks aim to prevent spread to other Micronesian islands; eradication on Guam remains unattained.

Black rat
A common ship-borne rodent that predates eggs and small vertebrates, spreads disease and crops damage. Control programs (trapping/poison) are used on islands and for seabird nesting restoration; complete eradication is challenging on larger islands.

Polynesian rat
An early human-associated rat that has driven seabird and land bird declines and damaged crops. Often targeted in island restoration and seabird nesting protection; eradication is feasible on small islands but difficult on inhabited ones.

Norway rat
A burrowing, robust rat that damages infrastructure, food stores and native fauna. Common in urban/port areas; biosecurity and integrated control reduce local impacts but reintroductions via shipping remain a threat.

House mouse
Small but prolific pest on islands; consumes seeds, competes with native fauna and can impede bird nesting success. Control typically focuses on high-value conservation sites with trapping and rodenticides.

Feral pig
Introduced pigs root soils, destroy vegetation and archaeological sites, spread invasive plants, and alter watershed processes. Hunting, fencing and trapping are used for control; pigs are culturally and economically important, complicating management.

Feral cat
Feral cats prey on native birds, reptiles and invertebrates, contributing to extinctions and declines. Management includes trapping, sterilization and removal in conservation zones; public outreach is needed to reduce free-roaming populations.

Feral dog
Free-roaming dogs disturb wildlife, hunt native species, and pose public health risks. Control combines vaccination, leash laws, sterilization campaigns and removal in sensitive habitats to protect ground-nesting birds and livestock.

Philippine deer
Introduced deer browse native vegetation, alter forest structure and facilitate invasive plants. Hunting is used to reduce numbers; local managers consider population control important for forest recovery and agriculture protection.

Coconut rhinoceros beetle
A large scarab beetle that bores into coconut and oil palms, killing palms and lowering copra yields. Quarantine, trapping, biocontrol and research on new resistant beetle strains are active management priorities after recent outbreaks.

Giant African snail
A voracious land snail that destroys crops, garden plants and carries rat lungworm. Intensive hand-collection, baiting and public reporting are used in eradication and suppression efforts, but reintroductions via trade persist.
Aedes aegypti
A mosquito that transmits dengue, Zika and chikungunya; thrives in human containers and urban areas. Vector control, source reduction and public health surveillance are routine to reduce disease outbreaks and human suffering.
Aedes albopictus
Also called the Asian tiger mosquito, it spreads arboviruses and competes with other mosquitoes. It colonizes rural and urban habitats; management focuses on removing larval sites and targeted spraying during outbreaks.

Culex quinquefasciatus
A night-biting mosquito that transmits filarial worms and can amplify arboviruses. Common in polluted water and storm drains; control emphasizes larval source reduction and community sanitation measures.

Tilapia
Introduced for aquaculture and food security, tilapia outcompete native fish, alter aquatic vegetation and degrade water quality. Management includes fishing, containment and preventing further introductions to protect freshwater biodiversity.

Leucaena
A fast-growing leguminous tree used for fodder and reforestation but forms dense monocultures that suppress native plants and alter soils. Control involves mechanical removal, herbicide and replanting with native species; still valued economically, complicating removals.

Siam weed
A highly invasive shrub that forms thick stands, reduces native biodiversity and hinders regeneration. Rapid control is difficult; managers use manual clearing, herbicides and biological control where possible.

Mile-a-minute vine
A fast-climbing vine that smothers trees and crops, reducing forest and agricultural productivity. Mechanical removal, herbicide application and community awareness are primary tools; early detection is critical to limit spread.

Australian pine
Forming dense coastal stands, Casuarina outcompetes native shoreline vegetation, changes sedimentation, and alters habitat. Removal and replacement with native coastal plants are used where coastal conservation or tourism values justify management.

Common guava
A planted fruit tree that naturalizes and invades forests, competing with natives and altering regeneration. While culturally and economically useful, it’s often targeted in restoration projects to recover native plant communities.

Koster’s curse
A shade-tolerant shrub that forms dense thickets, suppressing native understory and hindering forest regeneration. Managers use manual uprooting, herbicides and biological control trials in restoration areas.

Lantana
A thorny, flowering shrub that invades dry and disturbed habitats, reduces pasture value and poisons livestock. Control includes cutting, herbicides and sustained follow-up; its ornamental use has promoted spread.

Cogon grass
An aggressive perennial grass that forms flammable monocultures, increasing wildfire risk and choking out native plants. Management is costly and requires repeated herbicide, mowing and restoration with native species.

Rat lungworm
A parasitic nematode introduced with rats and snails that causes human eosinophilic meningitis. Public-health education, snail control and rodent management are key to reducing human cases; it complicates food safety and health services.

Common myna
An aggressive introduced bird that outcompetes native birds for nesting sites and spreads weeds. Control (trapping and public awareness) aims to protect native avifauna; eradication is difficult on populated islands.

Tropical fire ant
A stinging ant that inflicts painful bites, harms ground‑nesting wildlife, and disrupts agriculture and human activity. Control focuses on colony baiting and quarantine measures; infestations are persistent in disturbed habitats.





