Cameroon’s diverse landscapes—from coastal mangroves and lowland rainforests to highland plateaus—make it a hotspot for both native biodiversity and species that arrive from elsewhere. Invasive organisms can alter ecosystems, harm crops, and create new public‑health challenges, so understanding what’s present is a first step toward control and prevention.
There are 23 Invasive Species in Cameroon, ranging from the Asian tiger mosquito to the Whitefly (cassava/tomato pest). The list below covers that full range and is presented with clear data columns so you can scan distribution and status quickly: Scientific name,Status (Cameroon),Regions found (Cameroon). For each entry you’ll find below.
How do these invasive species impact agriculture and human health in Cameroon?
Many of the species on the list damage staple crops (reducing yields and increasing pesticide use) or act as disease vectors—Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito), for example, spreads dengue risk—while others displace native plants and animals, undermining ecosystem services that communities rely on.
What practical actions can local communities and authorities take to reduce harm?
Early detection, regular surveillance, public reporting systems, community education, and targeted control measures (integrated pest management, habitat cleanup, quarantine for high‑risk imports) are most effective; coordination with research institutions helps prioritize resources by species impact and region.
Invasive Species in Cameroon
| Common name | Scientific name | Status (Cameroon) | Regions found (Cameroon) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siam weed | Chromolaena odorata | Invasive | Littoral, South, Southwest, Centre, West |
| Lantana | Lantana camara | Invasive | Widespread (lowlands and uplands) |
| Parthenium | Parthenium hysterophorus | Invasive | Northern, Adamawa, Centre and other reported localities |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Invasive | Major waterways: Wouri, Sanaga, coastal and inland wetlands |
| Giant African snail | Achatina fulica | Established invasive | Littoral, Southwest, Centre, West |
| Floating water-fern | Salvinia molesta | Invasive | Wetlands and slow-moving rivers in southwest and littoral zones |
| Water lettuce | Pistia stratiotes | Established invasive | Wetlands and slow-moving waters in southern regions |
| Billygoat-weed | Ageratum conyzoides | Established invasive | Widespread in disturbed sites, farmlands and roadsides |
| Mikania vine | Mikania micrantha | Invasive | Reported in southern and western forest edges |
| Mesquite | Prosopis juliflora | Invasive | Far North, North, Adamawa regions |
| Asian tiger mosquito | Aedes albopictus | Established invasive | Urban and peri-urban areas (Littoral, Centre, Douala, Yaoundé) |
| Fall armyworm | Spodoptera frugiperda | Invasive | Widespread across maize-growing regions nationwide |
| Tomato leafminer | Tuta absoluta | Invasive | Tomato-growing areas (Littoral, Centre, West) |
| Whitefly (cassava/tomato pest) | Bemisia tabaci species complex | Established pest/invasive | Widespread in cassava and vegetable production areas |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | Established invasive | Urban, peri-urban and rural across Cameroon |
| Brown rat | Rattus norvegicus | Established invasive | Urban centers and port areas nationwide |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Established invasive | Widespread in buildings, farms and stores |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | Established invasive | Urban, peri-urban and rural settlements nationwide |
| Feral dog | Canis familiaris | Established invasive | Rural and peri-urban areas nationwide |
| Giant salvinia control target | Salvinia molesta | Invasive | Southern wetlands and floodplain systems |
| Cassava mealybug species | Phenacoccus manihoti | Established invasive | Cassava-growing areas (Centre, South, West) |
| Water fern (native replacement note) | Azolla spp. | Established, sometimes invasive | Ponds and rice paddies in southern regions |
| Golden apple snail | Pomacea canaliculata | Established invasive | Rice-growing lowlands reported locally |
Images and Descriptions

Siam weed
Fast-growing shrub from the Americas that forms dense stands in disturbed forests and farmland. Outcompetes native plants, hinders forest regeneration, increases fire risk, and reduces crop yields; introduced via ornamental and accidental spread.

Lantana
Showy shrub from tropical Americas, now a widespread weed in Cameroon. Forms impenetrable thickets, toxic to livestock, reduces native plant diversity, and invades roadsides and fallows; introduced as an ornamental and spreads by birds.

Parthenium
Aggressive American annual weed causing severe crop yield losses, pasture degradation and allergic dermatitis in people. Spreads rapidly by wind-blown seeds, colonizes disturbed soils, and is a growing management concern for farmers.

Water hyacinth
Free-floating aquatic plant from South America that forms dense mats, blocking navigation, reducing oxygen, harming fisheries and native biodiversity; introduced via ornamental trade and spread by watercraft and floods.

Giant African snail
Large land snail native to East Africa but invasive regionally; feeds on crops and garden plants, transmits plant pathogens and nuisance to households; spreads via human transport of soil and plants.

Floating water-fern
Rapidly spreading floating fern that forms thick mats, shading submerged plants, lowering oxygen and impairing fishing, irrigation and transport; often introduced with ornamental aquatic plants.

Water lettuce
Free-floating aquatic plant that clogs waterways, reduces light and oxygen, and harms fisheries; spreads via vegetative fragments and human-mediated movement.

Billygoat-weed
Annual herb from the Americas common in fallows and cultivated fields. Competes with crops, can host crop viruses and pests, and reduces yields; spreads by abundant windborne seed.

Mikania vine
Fast-climbing vine from the Americas that smothers seedlings and native vegetation, hindering forest regeneration and plantations; spreads rapidly vegetatively and by seed, problematic along disturbed forest margins.

Mesquite
Drought-tolerant shrub/tree from the Americas introduced for dryland value; forms dense, thorny stands that displace native savanna, reduce grazing, lower groundwater and impede livestock movement.
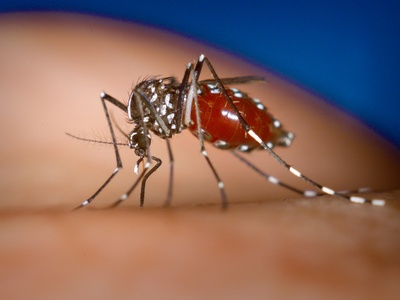
Asian tiger mosquito
Mosquito native to Asia that arrived via used tires/containers. Vector of dengue, chikungunya and Zika; competes with native mosquitoes and thrives in urban breeding sites, complicating public-health control.

Fall armyworm
Lepidopteran pest from the Americas that invaded Africa in 2016. Causes major maize yield losses, attacks sorghum and other crops, prompting emergency control programs and pesticide and integrated pest-management responses.

Tomato leafminer
Small moth from South America that devastates tomato crops by mining leaves and fruits. Rapid spread in Africa, causes heavy yield losses and increases pesticide use; introduced via trade in seedlings/fruit.

Whitefly (cassava/tomato pest)
A cryptic global whitefly complex that vectors plant viruses and causes direct feeding damage. Major pest of cassava, tomato and cotton; invasive shifts in biotypes intensify crop losses and management challenges.

Black rat
Commensal rodent introduced historically via ships and trade. Damages stored food and crops, preys on native fauna, and transmits zoonotic diseases; widespread in ports, markets and dwellings.

Brown rat
Large commensal rodent introduced by shipping; causes crop and foodstore losses, infrastructure damage, and spreads disease—important target for sanitation and control programs.

House mouse
Small, cosmopolitan rodent associated with humans that consumes and contaminates stored food, spreads pathogens and can damage equipment; introduced with human settlement and trade.

Feral cat
Domesticated cat turned feral preying on birds, reptiles and small mammals, contributing to native species declines. Widespread near human habitation; management relevance for biodiversity conservation and public health.

Feral dog
Free-ranging domestic dogs attack livestock and wildlife, spread rabies and other diseases, and cause human–wildlife conflicts. Control and vaccination are key management measures.

Giant salvinia control target
(See Salvinia molesta above) Rapid colonizer of slow waters forming mats that reduce fisheries, irrigation and local livelihoods; manual, mechanical and biological (weevil) controls used elsewhere and considered in Cameroon.

Cassava mealybug species
Invasive mealybug species attacking cassava, causing plant stunting and yield loss; arrived with planting material and trade, prompting integrated pest and resistant-variety approaches.

Water fern (native replacement note)
Small free-floating fern introduced with rice cultivation and aquaculture; can form dense mats reducing oxygen and interfering with aquatic systems, occasionally becoming a nuisance weed.

Golden apple snail
Freshwater snail from South America that feeds on young rice seedlings and aquatic plants, damaging crops and altering wetland ecology; spread via intentional and accidental introductions.





