The Dominican Republic’s variety of climates—coastal mangroves, mountain forests and urban centers—makes it a hotspot for both native biodiversity and incoming species. Some nonnative organisms arrive accidentally through trade or travel, others spread after being introduced for landscaping or pest control, and the effects can show up in health, agriculture and wild ecosystems.
There are 28 Invasive Species in the Dominican Republic, ranging from Aedes aegypti to Wedelia. The list below is organized so you can scan each entry by Scientific name,Status,Distribution in DR, and you’ll find below concise notes on where each species is established and what managers are tracking.
How do these invasive species affect people and the environment in the Dominican Republic?
Impacts vary by species: mosquitoes like Aedes aegypti pose direct public‑health risks through dengue, Zika and chikungunya; invasive plants such as Wedelia can outcompete native flora, reduce pasture quality and alter habitats; aquatic invaders change water chemistry and fisheries. Together they raise costs for healthcare, agriculture and conservation while complicating ecosystem recovery.
What practical steps can residents and visitors take to reduce spread?
Small actions help: eliminate standing water, clean boats and gear, avoid planting nonnative ornamentals, declare agricultural products at borders, and report sightings to local authorities or conservation hotlines. Early reporting and community cleanup efforts are often the most effective ways to limit establishment and spread.
Invasive Species in the Dominican Republic
| Name | Scientific name | Status | Distribution in DR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lionfish | Pterois volitans | Established; severe reef predator | Coastal reefs and seagrass beds around the entire island |
| Nile tilapia | Oreochromis niloticus | Established; ecosystem and fisheries impact | Freshwater lakes, reservoirs, rivers, farm ponds islandwide |
| Peacock bass | Cichla ocellaris | Established; top predator altering lakes | Reservoirs, rivers and inland lakes, introduced for sport fishing |
| Mosquitofish | Gambusia affinis | Established; competes with native species | Freshwater ponds, ditches, irrigation canals, wetlands |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Established; clogs waterways, disrupts fisheries | Rivers, canals, ponds and wetlands across the country |
| Sun coral | Tubastraea coccinea | Established; biofouling and reef competitor | Rocky shores, artificial structures, offshore reefs and wrecks |
| Mediterranean fruit fly | Ceratitis capitata | Established; serious agricultural pest | Orchards, fruit farms, urban fruit trees islandwide |
| Red imported fire ant | Solenopsis invicta | Established; human and ecological impacts | Urban, agricultural and disturbed habitats islandwide |
| Aedes aegypti | Aedes aegypti | Established; human disease vector | Urban and peri-urban areas, breeding in containers islandwide |
| Aedes albopictus | Aedes albopictus | Established; disease vector and competitor | Urban, peri-urban, forest edges across island |
| Giant African snail | Achatina fulica | Established; crop pest and public health concern | Gardens, farms, roadsides and urban green areas |
| Small Asian mongoose | Herpestes javanicus | Established; major predator of native fauna | Rural, agricultural, coastal and disturbed habitats islandwide |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | Established; predation and disease vector | Forests, urban areas, farms, ports islandwide |
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | Established; pest and contaminant | Urban areas, seaports, farms and sewers islandwide |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Established; stored-product pest and disease vector | Homes, granaries, urban and rural buildings islandwide |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | Established; severe native predator | Urban, rural, agricultural and protected areas islandwide |
| Feral pig | Sus scrofa | Established; ecosystem disturbance and agricultural damage | Forests, wetlands, agricultural lands islandwide |
| Rock pigeon | Columba livia | Established; urban pest and disease vector | Cities, ports, markets and towns islandwide |
| House sparrow | Passer domesticus | Established; competitor in urban areas | Towns, villages, agricultural buildings islandwide |
| Tropical house gecko | Hemidactylus mabouia | Established; competitor with native reptiles | Buildings, urban areas, gardens, disturbed sites islandwide |
| Common house gecko | Hemidactylus frenatus | Established; invasive, competes with natives | Urban, coastal and disturbed habitats across island |
| Australian pine | Casuarina equisetifolia | Established; displaces native coastal vegetation | Beaches, dunes, coastal scrub and disturbed shoreline areas |
| Lantana | Lantana camara | Established; forms dense, toxic thickets | Roadsides, pastures, disturbed forests and coastal scrub |
| Siam weed | Chromolaena odorata | Established; highly invasive shrub | Disturbed forests, roadsides, secondary growth and plantations |
| Brazilian pepper | Schinus terebinthifolius | Established; invasive shrub/tree in wetlands | Mangroves, coastal scrub, wetlands and riparian zones |
| Leucaena | Leucaena leucocephala | Established; invasive nitrogen-fixer in dry areas | Pasture edges, coastal lowlands, disturbed sites and degraded forests |
| Wedelia | Sphagneticola trilobata | Established; smothers native groundcover | Gardens, roadsides, coastal areas and disturbed sites |
| Golden apple snail | Pomacea canaliculata | Established; herbivorous crop pest | Rice paddies, wetlands, irrigation canals and freshwater bodies |
Images and Descriptions

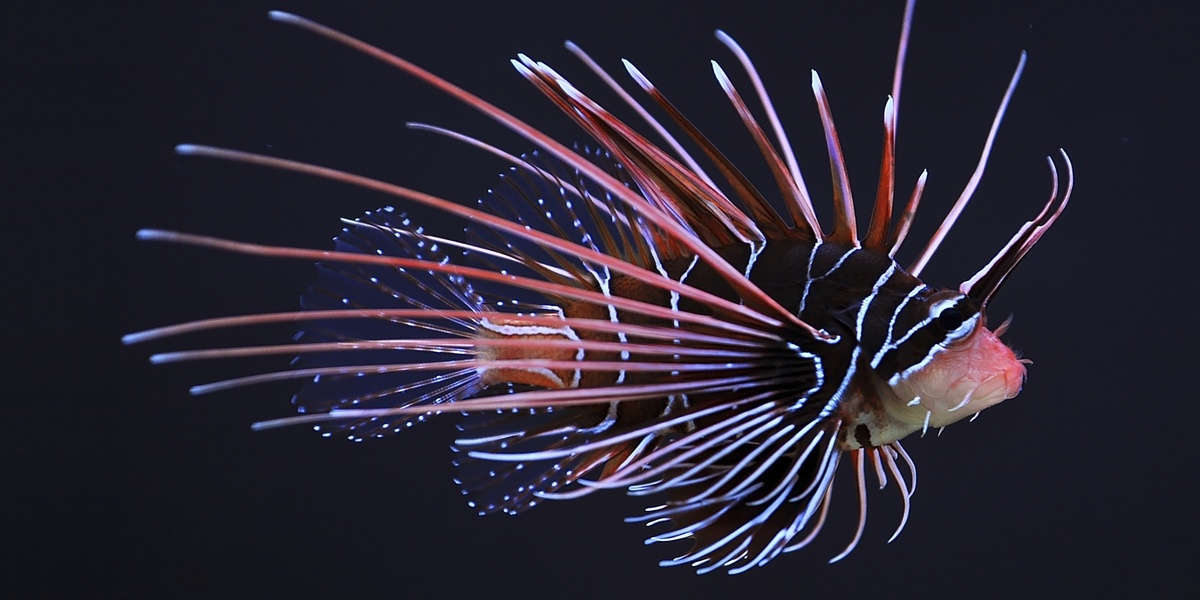
Lionfish
Venomous Indo-Pacific predator now abundant on Dominican reefs. Eats juvenile fish and crustaceans, reduces reef biodiversity and fisheries; spread via aquarium releases. Managed by removals, spearfishing derbies and market promotion.

Nile tilapia
Introduced for aquaculture, tilapia outcompete and prey on native fish and alter habitats. They hybridize and change food webs; managed by harvest, containment, and aquaculture biosecurity.

Peacock bass
South American predatory cichlid introduced for angling. Drastically reduces native fish populations and changes food chains; management focuses on containment and angler awareness.
Mosquitofish
Introduced for mosquito control, now widespread. Eats native larvae and small fishes, harms amphibians; control is difficult once established, prevention emphasized.

Water hyacinth
Floating South American plant forms dense mats that block navigation, harm fisheries, increase disease risk and reduce oxygen; control via mechanical removal and local use initiatives.

Sun coral
Indo-Pacific coral that colonizes hard substrates, smothering native corals and altering reef communities. Likely spread on ship hulls; management uses targeted removal and monitoring.
Mediterranean fruit fly
Highly polyphagous fruit fly attacking many crops and backyard fruit. Causes economic losses and quarantine restrictions; managed by baiting, sterile insect techniques and export controls.

Red imported fire ant
Aggressive South American ant that inflicts painful stings, damages crops and wildlife, and alters soil ecology. Spread via soil and plant movement; control uses baits, barriers and sanitation.

Aedes aegypti
Introduced mosquito vector for dengue, Zika and chikungunya. Thrives in human environments; managed by removing standing water, insecticide campaigns, community education and surveillance.

Aedes albopictus
Asian tiger mosquito spreads dengue and other viruses; competes with native mosquitoes and A. aegypti. Control focuses on habitat cleanup, larvicides and monitoring.

Giant African snail
Large snail that feeds on many crops and ornamentals and can carry parasites harmful to humans. Often introduced via plant trade; control by hand collection, baiting and quarantine.

Small Asian mongoose
Introduced historically to control rodents; now preys on native birds, reptiles and small mammals, contributing to declines. Control uses trapping and exclusion in sensitive areas.

Black rat
Arboreal rat introduced centuries ago; preys on bird eggs and reptiles, damages crops, spreads disease. Management includes trapping, baiting, and biosecurity at ports.

Norway rat
Commensal rodent causing structural damage, food contamination and predation on ground-nesting fauna. Managed with traps, baits, sanitation and exclusion.

House mouse
Small commensal rodent that damages stored food, spreads pathogens and undermines biosecurity. Management through exclusion, traps and improved storage practices.

Feral cat
Domestic cat populations that hunt birds, reptiles and small mammals, significantly impacting native fauna. Management includes neuter-and-release, removal around protected sites, and public education.

Feral pig
Introduced domestic/wild pigs root soil, destroy vegetation, spread parasites and damage crops. Control via hunting, trapping and fencing in priority conservation areas.

Rock pigeon
Domesticated pigeon now feral in urban areas; fouling, disease transmission and competition with native birds. Management includes roost exclusion, nest removal and public waste control.

House sparrow
Old World passerine introduced with colonization; competes with native birds for nest sites and resources. Urban management focuses on habitat modification and exclusion.

Tropical house gecko
West African gecko that colonizes human structures, preying on insects and competing with native geckos. Spread via shipping and trade; control limited to exclusion and habitat modification.

Common house gecko
Southeast Asian gecko that thrives in human environments, outcompeting some native lizards. Often spreads through transport of goods; management is by reducing roosting opportunities.

Australian pine
Fast-growing coastal tree that stabilizes dunes but reduces native plant diversity and alters soil chemistry. Introduced for shade and windbreaks; removed mechanically and via herbicide in restoration zones.

Lantana
Ornamental shrub that invades and forms impenetrable thickets, impeding regeneration and poisoning livestock. Spread via birds and gardens; control with cutting, herbicide and biological agents where applicable.

Siam weed
Fast-growing Asian shrub that invades disturbed habitats, suppresses native seedlings and increases fire risk. Spread by wind-dispersed seeds; controlled by manual removal, herbicide, and restoring native cover.

Brazilian pepper
South American tree that forms dense stands in coastal and wet habitats, displacing native plants and altering hydrology. Managed by mechanical removal, herbicide and monitoring.

Leucaena
Fast-growing tropical legume used for forage and reforestation that invades open habitats, outcompeting natives and changing soil chemistry. Control through cutting, grazing management and restoration planting.

Wedelia
Groundcover from tropical Americas/Asia that spreads rapidly, outcompetes native herbaceous plants and alters understory composition. Often introduced as ornamental groundcover; removal and replacement with natives recommended.

Golden apple snail
Large South American snail that consumes aquatic vegetation and crops, causing significant damage to rice and wetland plants. Spread via aquarium and food trade; control by trapping and barriers.





