Jamaica’s islands and coastal waters support diverse habitats, from mangroves and wetlands to upland forests, but those same routes of trade and travel have also introduced non-native organisms that alter ecosystems and affect livelihoods. Knowing which species are present helps prioritize control, protect agriculture, and reduce health risks.
There are 27 Invasive Species in Jamaica, ranging from Aedes aegypti to Water hyacinth. For each entry you’ll find below the fields Scientific name,Origin (native range),Jamaican distribution, listed below.
How do these invasive species affect Jamaica’s ecosystems?
Impacts vary by organism: some compete with native plants and animals, others change habitat structure (for example, Water hyacinth choking waterways), and some are disease vectors or agricultural pests (Aedes aegypti spreads human disease). Collectively they can reduce biodiversity, harm fisheries and crops, and increase management costs.
What practical steps can residents take to help limit their spread?
Simple actions matter: avoid releasing non-native pets or plants, clean boats and equipment between waterways, remove standing water to limit mosquitoes, report unusual species to local authorities, and support community removal or monitoring programs to reduce establishment and spread.
Invasive Species in Jamaica
| Name | Scientific name | Origin (native range) | Jamaican distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lantana | Lantana camara | Central and South America | Widespread in disturbed lowlands, roadsides across parishes |
| Water hyacinth | Eichhornia crassipes | Amazon basin, South America | Rivers, ponds and wetlands islandwide |
| Australian pine | Casuarina equisetifolia | Australia, SE Asia | Coastal beaches and dunes, especially western and southern coasts |
| Small Indian mongoose | Herpestes javanicus (Urva auropunctata) | South Asia | Widespread in rural and forested areas across Jamaica |
| Cane toad | Rhinella marina | Central and South America | Widespread in lowland and agricultural areas |
| Lionfish | Pterois volitans/miles | Indo‑Pacific | Coastal reefs and seagrass beds around Jamaica |
| Nile tilapia | Oreochromis niloticus | Africa | Freshwater lakes, rivers and farm ponds islandwide |
| Giant African land snail | Achatina fulica | East Africa | Gardens, agricultural lands in multiple parishes |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | Old World (Africa/Asia) | Urban and rural areas across Jamaica |
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | Eurasia | Ports, urban and peri‑urban areas across island |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Eurasia | Urban, agricultural and storage areas across Jamaica |
| Feral cat | Felis catus | Domesticated (Eurasian origins) | Urban, rural and wildland edges islandwide |
| Feral pig | Sus scrofa | Eurasia | Woodlands, agricultural and upland areas |
| Feral goat | Capra hircus | Domesticated (origins in Middle East/Central Asia) | Hills, dry zones and agricultural margins, especially St. Elizabeth and Clarendon |
| Rock pigeon | Columba livia | Eurasia | Urban centers (Kingston, Montego Bay) and ports |
| House sparrow | Passer domesticus | Eurasia | Towns and urban areas across Jamaica |
| Common myna | Acridotheres tristis | South Asia | Urban and suburban areas, reported in Kingston and other towns |
| Green iguana | Iguana iguana | Central and South America | Coastal and lowland areas with established populations |
| Coffee berry borer | Hypothenemus hampei | Central Africa | Coffee‑growing regions, Blue Mountains, Portland, St. Andrew |
| Aedes aegypti | Aedes aegypti | Africa | Nationwide urban and peri‑urban areas |
| Aedes albopictus | Aedes albopictus | Asia | Found in parts of Jamaica, especially vegetated and peri‑urban zones |
| Coffee rust dispersal pests (example) | Hemileia vastatrix (pathogen) | Likely Africa origin | Affects coffee farms in coffee regions |
| Brazilian pepper | Schinus terebinthifolius | South America | Coastal and disturbed inland sites |
| African tulip tree | Spathodea campanulata | West Africa | Ornamental and disturbed sites in multiple parishes |
| Tilapia (Mozambique tilapia) | Oreochromis mossambicus | Southeast Africa | Freshwater systems and farm ponds |
| Miconia | Miconia spp. | Neotropics (Central/South America) | Localized reports; invasive potential in montane forests |
| Citrus greening (HLB) | Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (pathogen) | Asia | Affects citrus groves in Jamaica |
Images and Descriptions

Lantana
A shrubby flowering plant that forms dense thickets, shading out native vegetation and reducing grazing land. Lantana is toxic to livestock and complicates restoration; management requires mechanical removal and persistent herbicide or biological control efforts.

Water hyacinth
Floating aquatic plant that forms dense mats, blocking waterways, harming fisheries, and increasing mosquito habitat. Rapid reproduction clogs irrigation and transport; control relies on mechanical removal, biological agents and integrated water management.

Australian pine
Coastal tree that stabilizes dunes but outcompetes native vegetation, alters sand movement and reduces beachfront habitat. Its dense litter inhibits native seedling growth; removal and replanting with native coastal species are common control measures.

Small Indian mongoose
Introduced to control rodents in plantations, the mongoose preys on native birds, reptiles and amphibians, driving declines in ground‑nesting species. Control is difficult; impacts remain a major conservation concern for native fauna.

Cane toad
Large toad introduced for pest control that secretes toxins harmful to pets and native predators. It competes with native amphibians and alters food webs; management focuses on exclusion from sensitive sites and community removal efforts.

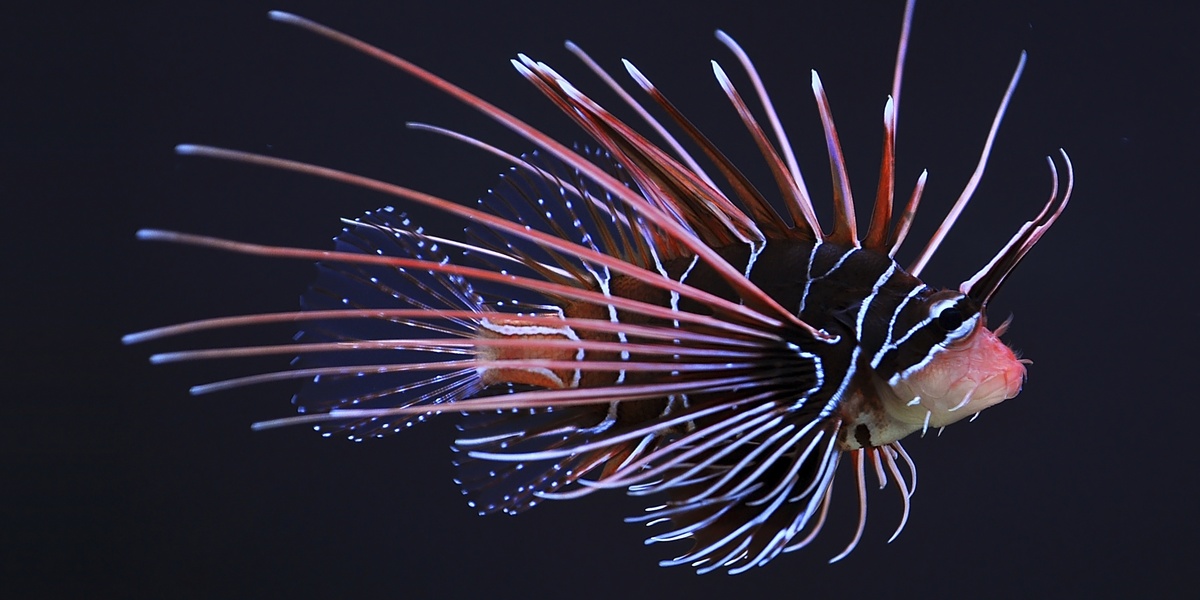
Lionfish
Colorful predatory fish consuming native reef fish and juveniles, reducing biodiversity and reef resilience. Rapid spread across Caribbean; fisheries and targeted culling, along with awareness and market development, are primary management strategies.

Nile tilapia
Introduced aquaculture fish that outcompetes native fishes, alters aquatic vegetation and can reduce water quality. Widely farmed and feral populations established; management involves containment, fishing pressure and prevention of further escapes.

Giant African land snail
Large herbivorous snail that damages crops and garden plants, vectors plant pathogens and poses human health risks. Rapid reproduction makes control challenging; measures include manual collection, barriers, molluscicides and public reporting.

Black rat
Arboreal rodent that raides crops, preys on eggs and nestlings, and transmits disease. Major pest in agriculture and conservation, especially for ground‑nesting birds; integrated pest management uses traps, baiting and habitat sanitation.

Norway rat
Ground‑dwelling rodent that damages infrastructure, contaminates food and spreads pathogens. Common in seaports and settlements; control combines sanitation, trapping and rodenticides with biosecurity at ports to limit spread.

House mouse
Small commensal rodent that spoils stored food, transmits disease and supports introduced predators. Control relies on improved storage, exclusion and trapping; significant economic impact in food storage and processing.

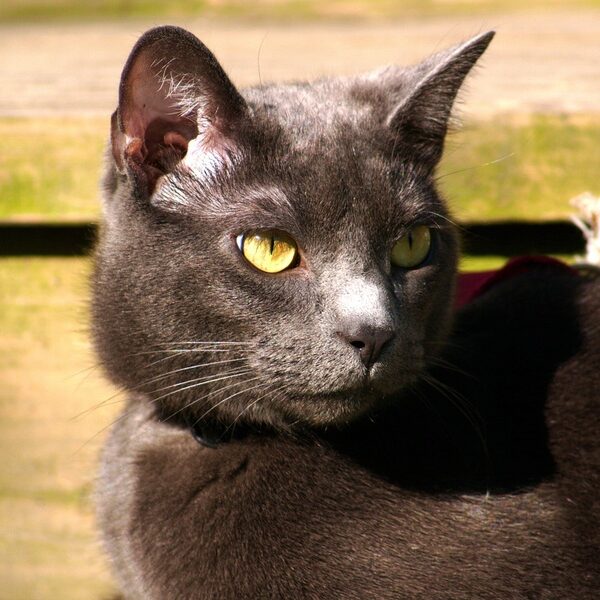
Feral cat
Free‑roaming cats prey heavily on native birds, reptiles and small mammals, contributing to declines and disease transmission. Management includes responsible pet ownership, trap‑neuter‑release debates, and targeted removal in sensitive conservation areas.

Feral pig
Omnivorous feral pigs root soils, damage crops, spread invasive plants and disturb native habitats. They carry diseases affecting livestock and wildlife; control combines fencing, trapping, hunting and biosecurity measures.

Feral goat
Goats browse native vegetation, causing erosion and preventing forest regeneration. They impact watersheds and biodiversity; management uses fencing, controlled culling and community grazing plans.

Rock pigeon
Introduced urban bird that fouls buildings, spreads disease and competes with native birds. Control includes exclusion, public hygiene, population management and building modifications to reduce roosting.

House sparrow
Small introduced bird that competes for nest sites and can impact native cavity‑nesting species. Common in settlements; management focuses on habitat modification and limiting supplemental feeding.

Common myna
Aggressive passerine that competes for nest sites, displaces native birds and can damage fruit crops. Control programs often combine trapping, public education and nest site management.

Green iguana
Large herbivorous lizard often introduced via pet trade; it can damage crops, alter vegetation and hybridize/compete with native Cyclura in some islands. Management includes trapping, public engagement and preventing releases.

Coffee berry borer
Tiny beetle that bores into coffee beans, drastically reducing yields and quality. One of the most damaging coffee pests; management uses integrated pest management, trapping and rigorous inspection protocols.
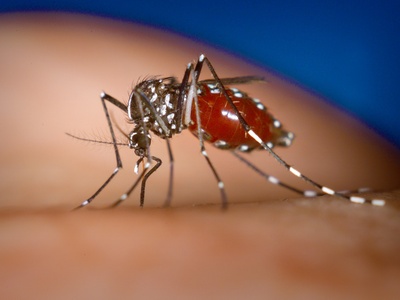
Aedes aegypti
Mosquito vector of dengue, Zika and chikungunya. Thrives in human environments, breeds in artificial containers, and poses significant public‑health challenges. Control focuses on source reduction, larvicides, community engagement and surveillance.
Aedes albopictus
Invasive mosquito vector that can transmit arboviruses and competes with Aedes aegypti. Its spread increases vector control complexity; management emphasizes monitoring, habitat removal and targeted insecticidal measures.

Coffee rust dispersal pests (example)
Fungal pathogen of coffee introduced historically; causes defoliation and yield loss, driving management practices like resistant varieties and fungicide programs. (Note: included as significant invasive pathogen impacting Jamaican agriculture.)

Brazilian pepper
Evergreen shrub/tree that forms dense stands, displacing native plants and altering habitats. Produces abundant seed spread by birds; control includes mechanical removal, herbicides and restoration with native species.

African tulip tree
Showy fast‑growing tree used ornamentally that invades forest edges and disturbed lands, outcompeting natives and altering light regimes. Mechanical removal and replacement planting recommended in restoration.

Tilapia (Mozambique tilapia)
Introduced for aquaculture, this tilapia species can hybridize with others, alter food webs, and degrade freshwater habitats by overgrazing vegetation. Management emphasizes containment, harvest and prevention of escapes.
Miconia
Fast‑growing tree species known to form dense monospecific stands, causing erosion and biodiversity loss where established. Early detection, rapid response and mechanical/herbicide control are essential to prevent spread.

Citrus greening (HLB)
Bacterial disease vectored by psyllids causing severe citrus decline and big economic losses. Management focuses on vector control, removal of infected trees and strict nursery practices to limit spread.





