Slovenia’s mix of Alpine peaks, karst plateaus, rivers and a short Adriatic coast creates diverse habitats where both native and non-native species can thrive. Human activity, trade and changing climates have opened pathways for organisms that can alter ecosystems, fisheries and local biodiversity.
There are 35 Invasive Species in Slovenia, ranging from American mink to Zebra/Asian jellyfish not applicable. Each entry below is organized with Scientific name,Status,Distribution (Slovenia) so you can quickly see taxonomy, current status and where it has been recorded — you’ll find below.
How do invasive species typically impact Slovenia’s ecosystems?
Invasive plants and animals can outcompete native species, change food webs, damage habitats (for example by altering riverbeds or shorelines), and harm agriculture or fisheries; impacts vary by species and location, so check the listed Distribution (Slovenia) and Status to gauge local risk.
What should I do if I spot a suspected invasive species?
Document it with photos, exact location and date, avoid moving the organism, and report observations to local environmental authorities or a conservation NGO; timely reports help authorities confirm records and prioritize management.
Invasive Species in Slovenia
| Name | Scientific name | Status | Distribution (Slovenia) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common ragweed | Ambrosia artemisiifolia | Invasive, regulated | Lowlands, arable land, roadsides, NE Slovenia common |
| Himalayan balsam | Impatiens glandulifera | Invasive, established | Riverbanks, floodplains across Slovenia |
| Japanese knotweed complex | Fallopia japonica/Reynoutria spp. | Invasive, regulated | Urban areas, river corridors, disturbed soils |
| Giant hogweed | Heracleum mantegazzianum | Invasive, regulated | Riverbanks, meadows, lowland disturbed sites |
| Canadian goldenrod | Solidago canadensis | Invasive, widespread | Meadows, field margins, roadsides |
| Giant goldenrod | Solidago gigantea | Invasive, widespread | Wet meadows, river margins, lowlands |
| Tree‑of‑heaven | Ailanthus altissima | Invasive, established | Urban areas, roadsides, river corridors |
| Black locust | Robinia pseudoacacia | Invasive, established | Dry slopes, forest edges, former farmland |
| Black cherry | Prunus serotina | Invasive, established | Forests, forest edges, upland and lowland |
| False indigo | Amorpha fruticosa | Invasive, regulated | River floodplains, wetlands, lowland rivers |
| Butterfly bush | Buddleja davidii | Invasive, established | Disturbed sites, railways, urban wastelands |
| Garden lupin | Lupinus polyphyllus | Invasive, established | Roadsides, mountain meadows, disturbed alpine sites |
| Water primrose (water primrose group) | Ludwigia grandiflora/L. peploides | Invasive, established | Ponds, slow rivers, wetlands |
| Canadian waterweed | Elodea canadensis | Invasive, established | Lakes, ponds, slow rivers nationwide |
| Nuttall’s waterweed | Elodea nuttallii | Invasive, established | Lakes and lowland rivers |
| Parrot’s feather | Myriophyllum aquaticum | Invasive, present | Ponds, canals near settlements |
| Floating fern | Azolla filiculoides | Invasive, established | Slow waters, ponds and ditches |
| Asian tiger mosquito | Aedes albopictus | Invasive, established | Urban areas, lowland containers and wetlands |
| Brown marmorated stink bug | Halyomorpha halys | Invasive, established | Orchards, gardens, urban buildings |
| Spotted wing drosophila | Drosophila suzukii | Invasive, established | Soft fruit plantations, gardens, hedgerows |
| Harlequin ladybird | Harmonia axyridis | Invasive, established | Urban gardens, orchards, forests |
| Red swamp crayfish | Procambarus clarkii | Invasive, established | Ponds, slow rivers, wetlands |
| Signal crayfish | Pacifastacus leniusculus | Invasive, established | Rivers and lakes |
| Zebra mussel | Dreissena polymorpha | Invasive, established | Rivers, reservoirs, lakes |
| Asian clam | Corbicula fluminea | Invasive, present | River stretches and reservoirs |
| Stone moroko (topmouth gudgeon) | Pseudorasbora parva | Invasive, established | Ponds, lowland rivers |
| Pumpkinseed sunfish | Lepomis gibbosus | Invasive, established | Lakes, ponds, slow rivers |
| Gibel carp | Carassius gibelio | Invasive, established | Standing waters, lowland lakes and ponds |
| Round goby | Neogobius melanostomus | Invasive, present | Lower river reaches, larger waterways |
| Raccoon | Procyon lotor | Invasive, established | Wetlands, forests, urban fringes |
| Raccoon dog | Nyctereutes procyonoides | Invasive, present | Forests and agricultural lands |
| Muskrat | Ondatra zibethicus | Invasive, established | Wetlands, riverbanks, floodplains |
| American mink | Neogale vison | Invasive, established | Rivers, wetlands, lakeshores |
| Brown trout invasives note (non‑native stocking) | Oncorhynchus mykiss (rainbow trout) | Established, managed | Cold streams and stocked ponds |
| Zebra/Asian jellyfish not applicable | — | — | — |
Images and Descriptions

Common ragweed
Highly allergenic annual that forms dense stands in fields and roadside margins. Produces huge seed banks, worsens hay fever and reduces crop yields. Control by early mowing/weed removal and seed‑bank management; report large outbreaks to local authorities.

Himalayan balsam
Fast‑growing riparian annual that outcompetes native riverbank plants and causes erosion when pulled out. Spreads by explosive seed pods and river transport. Control by hand‑pulling before seed set, cutting and repeated monitoring along waterways.

Japanese knotweed complex
Robust perennial with extensive rhizomes that damage infrastructure and outcompete natives. Very costly to remove; requires persistent herbicide and root removal over years. Report sightings; eradication is slow and often professional.

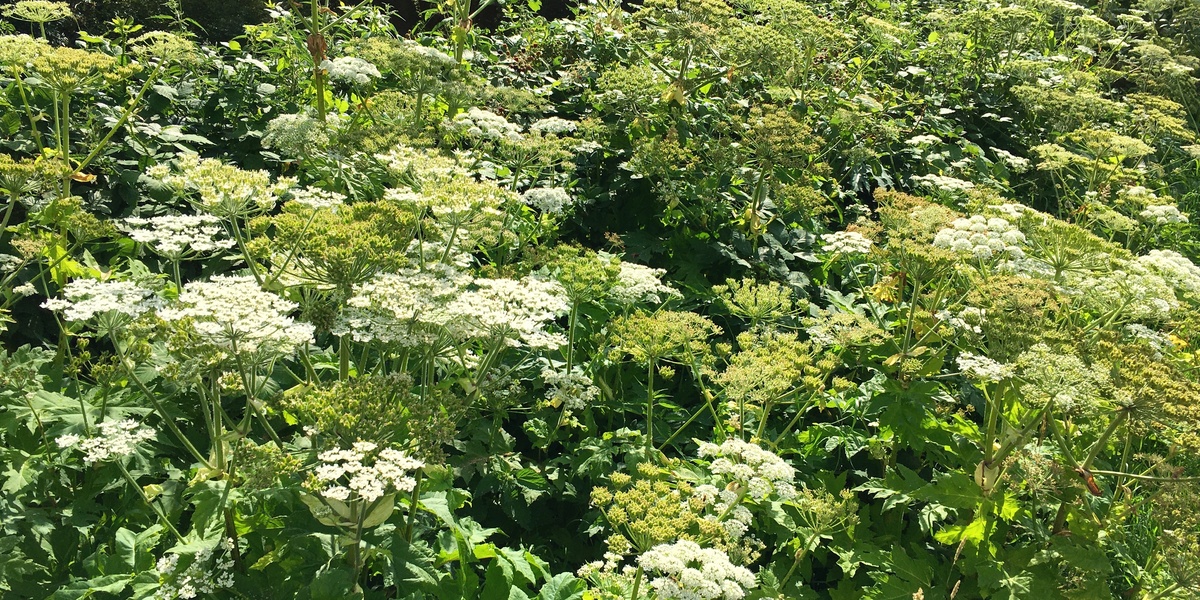
Giant hogweed
Large phototoxic plant causing severe burns and ecological displacement of native flora. Seeds spread along waterways and roads. Wear protection when handling; report populations and follow local eradication programmes.

Canadian goldenrod
Perennial that forms dense stands, reducing plant diversity and altering habitats. Spreads by rhizomes and seed. Control via mowing before seed set, grazing, or targeted herbicide; early detection is important to prevent spread.

Giant goldenrod
Similar impacts to S. canadensis: dense colonies reduce native wildflowers and meadow biodiversity. Management includes mowing, digging of roots, and long‑term monitoring to prevent reinvasion.

Tree‑of‑heaven
Fast‑growing tree that colonises disturbed sites, producing many wind‑dispersed seeds and toxic root compounds. Damages pavements and natural regeneration. Control via cutting plus basal/stump herbicide or ring‑barking and follow‑up treatments.

Black locust
Introduced nitrogen‑fixing tree that converts ecosystems, forms dense stands and suppresses native trees. Valuable timber but invasive; controlled by cutting, herbicide on stumps and preventing seed spread.

Black cherry
Rapidly spreading tree that shades out native seedlings and alters forest composition. Produces abundant seeds eaten by birds. Control by cutting followed by herbicide treatment and removing saplings.

False indigo
Shrubby legume that forms dense stands in floodplains, reducing native wetland plants and altering flood dynamics. Seeds spread via water. Management includes cutting, excavation, and herbicide, often as part of river restoration.

Butterfly bush
Popular ornamental that self‑seeds prolifically and forms dense stands on disturbed ground, crowding natives. Control by removing seedheads, digging seedlings and selective herbicide on persistent shrubs.

Garden lupin
Showy ornamental that escapes into mountain and roadside habitats, forming dense stands that alter soil nitrogen and displace native alpine flora. Remove before seeding and restore invaded patches with natives.

Water primrose (water primrose group)
Floating/emergent plants that form dense mats, blocking waterways and smothering native aquatic vegetation. Difficult mechanical control; combine cutting, draining and herbicide; prevent spread between water bodies.

Canadian waterweed
Submerged pondweed that rapidly colonises still waters, clogging intakes and altering oxygen regimes. Spreads by fragments. Control via mechanical removal, shading, and careful biosecurity to avoid transfer on equipment.

Nuttall’s waterweed
Another invasive submerged species that forms dense beds and outcompetes natives. Spreads easily by fragments; management similar to E. canadensis with emphasis on preventing spread.

Parrot’s feather
Attractive aquatic plant that forms dense floating mats and displaces native species; hard to eradicate. Remove whole plants, dry and dispose safely; prevent aquarium releases.

Floating fern
Tiny floating fern that can form thick carpets, reducing light and oxygen and altering nutrient cycling. Spreads by water and equipment. Manual removal and preventing spread are primary control methods.
Asian tiger mosquito
Aggressive day‑biting mosquito that breeds in artificial containers and can transmit diseases. Public health concern; control by removing standing water, larvicides and surveillance; report new infestations to health authorities.

Brown marmorated stink bug
Crop pest that damages fruit and invades homes in autumn. Difficult to control once established; integrated pest management, netting and trapping help reduce impacts in orchards.

Spotted wing drosophila
Female lays eggs in ripe fruit causing crop loss and rot. Rapid breeder requiring coordinated management: monitoring traps, prompt harvest, netting and targeted insecticides when needed.

Harlequin ladybird
Introduced as biocontrol, now outcompetes native ladybirds and invades homes. Dense aggregations and impacts on other insects; control limited to exclusion from buildings and reporting large colonies.

Red swamp crayfish
Aggressive crayfish that burrows, eats vegetation and fauna, spreads disease and alters banks. Hard to eradicate; containment, trapping and preventing transport between waters are used.

Signal crayfish
Introduced for aquaculture; carries crayfish plague and outcompetes native crayfish. Management focuses on preventing transfers, trapping and protecting unaffected water bodies.

Zebra mussel
Bivalve that attaches to hard surfaces, clogging pipes and altering food webs. Extremely prolific; prevention via boat cleaning, monitoring and physical/chemical control where feasible.

Asian clam
Fast‑breeding clam that alters sediment and filtration regimes, fouling infrastructure. Spread via boats and sediments; control is difficult, emphasise biosecurity and monitoring.

Stone moroko (topmouth gudgeon)
Small fish that competes with native juveniles and can carry parasites. Easily transported between water bodies. Prevent spread by not moving fish and draining/cleaning equipment.

Pumpkinseed sunfish
Introduced recreational fish that preys on invertebrates and fish eggs, altering community structure. Control by targeted removal, angling and drainage of small ponds.

Gibel carp
Highly adaptable carp that can dominate ponds, hybridise with other carps and alter aquatic vegetation. Management via fishing, draining ponds and preventing transfers.
Round goby
Bottom‑dwelling fish that competes with native species and alters benthic communities. Spread via ballast water and canals; monitor and restrict translocation of live fish.

Raccoon
Introduced mammal that raids nests and crops, spreads parasites and adapts to urban environments. Control via trapping under licence, nest protection and public reporting of sightings.

Raccoon dog
Escaped/introduced canid that predates ground‑nesting birds and amphibians; potential vector of disease. Managed through hunting and monitoring under wildlife regulations.

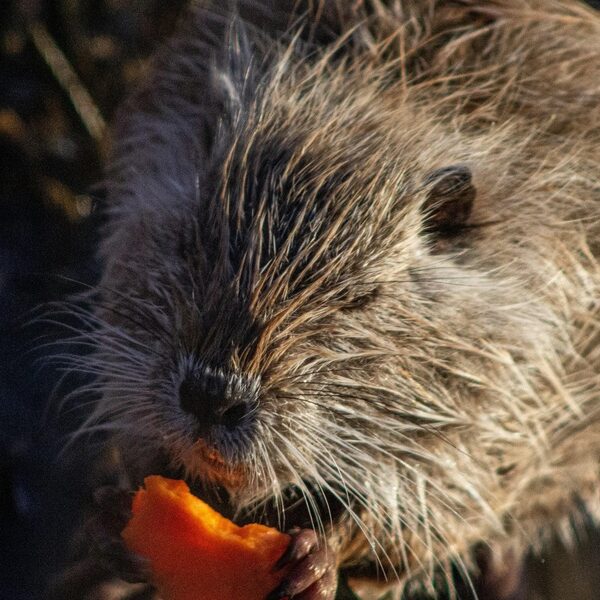
Muskrat
Burrowing rodent that causes bank erosion, damages crops and alters wetland vegetation. Control by trapping, habitat modification and water level management where possible.

American mink
Fur‑farm escapee that preys on waterbirds and small mammals, causing declines in vulnerable species. Control via trapping programs and protecting nesting sites.

Brown trout invasives note (non‑native stocking)
Widely stocked non‑native trout can compete/interbreed with native salmonids and spread disease. Management focuses on regulated stocking, habitat protection and preventing escapes from farms.

Zebra/Asian jellyfish not applicable
—





