Mexico’s landscapes — from Baja deserts and Sierra Madre peaks to tropical lowlands — create a mosaic of habitats that support a wide variety of mammals. Whether you’re a wildlife watcher or compiling species data, this diversity shows up across ecosystems and elevations.
There are 59 Mammals of Mexico, ranging from the American badger to the White-tailed deer; for each species the entries are organized with Scientific name,IUCN status,Range (Mexico), and you’ll find below.
How can I use the IUCN status in the list to understand conservation priorities?
The IUCN status gives a quick snapshot of each species’ global risk level (e.g., Least Concern to Endangered); use it alongside the Range (Mexico) column to spot species with limited or fragmented Mexican ranges that may need local conservation attention even if their global status seems lower risk.
Are the ranges listed precise enough to plan field visits or surveys?
Ranges indicate general Mexican distribution (states, regions, or habitat types) to help narrow search areas, but for fieldwork you should consult detailed range maps or local experts to account for seasonal movements, elevation limits, and recent range shifts.
Mammals of Mexico
| Name | Scientific name | IUCN status | Range (Mexico) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jaguar | Panthera onca | Near Threatened | Southern Mexico: Chiapas,Campeche,Quintana Roo,Veracruz,Oaxaca |
| Puma | Puma concolor | Least Concern | Mountains and deserts from Sonora to Chiapas |
| Ocelot | Leopardus pardalis | Least Concern | Southern forests and Yucatán Peninsula |
| Margay | Leopardus wiedii | Near Threatened | Tropical forests in Chiapas,Oaxaca,Yucatán Peninsula |
| Bobcat | Lynx rufus | Least Concern | Northern and central Mexico highlands and deserts |
| Coyote | Canis latrans | Least Concern | Widespread across Mexico |
| Gray wolf | Canis lupus | Least Concern | Reintroduced populations in Sonora and Chihuahua (northern Mexico) |
| Jaguarundi | Herpailurus yagouaroundi | Least Concern | Lowland scrub and forests across southern states |
| White-tailed deer | Odocoileus virginianus | Least Concern | Widespread across Mexico |
| Mule deer | Odocoileus hemionus | Least Concern | Northwestern and highland regions: Sonora,Chihuahua,Durango |
| Pronghorn | Antilocapra americana | Near Threatened | Northern Mexico: Sonora,Chihuahua,Coahuila |
| Collared peccary | Pecari tajacu | Least Concern | Widespread in forests and scrublands |
| Baird’s tapir | Tapirus bairdii | Endangered | Southern Mexico: Chiapas and parts of Oaxaca |
| West Indian manatee | Trichechus manatus | Vulnerable | Coastal Caribbean and Gulf: Quintana Roo,Yucatán |
| Vaquita | Phocoena sinus | Critically Endangered | Upper Gulf of California (northern Baja California,Sonora) |
| Humpback whale | Megaptera novaeangliae | Least Concern | Migratory along both Pacific and Gulf coasts,notably Baja |
| Blue whale | Balaenoptera musculus | Endangered | Offshore Pacific and Gulf of California feeding grounds |
| Bottlenose dolphin | Tursiops truncatus | Least Concern | Coastal waters across Pacific and Gulf coasts |
| Sperm whale | Physeter macrocephalus | Vulnerable | Deep offshore Pacific and Gulf waters |
| California sea lion | Zalophus californianus | Least Concern | Pacific coast and Gulf of California |
| Guadalupe fur seal | Arctocephalus townsendi | Vulnerable | Breeding on islands off Baja California |
| Mexican free-tailed bat | Tadarida brasiliensis | Least Concern | Widespread; large colonies in northern and central Mexico |
| Lesser long-nosed bat | Leptonycteris yerbabuenae | Endangered | Sonoran Desert to central Mexico migrations |
| Greater long-nosed bat | Leptonycteris nivalis | Endangered | Mountain corridors and central Mexican ranges |
| Common vampire bat | Desmodus rotundus | Least Concern | Southern Mexico: Chiapas,Yucatán and Veracruz regions |
| Nine-banded armadillo | Dasypus novemcinctus | Least Concern | Eastern and southern Mexico,expanding north |
| Mexican volcano rabbit | Romerolagus diazi | Endangered | High-altitude pine-fir slopes near Mexico City,Puebla,Hidalgo |
| Eastern cottontail | Sylvilagus floridanus | Least Concern | Widespread in fields,woods and disturbed areas |
| Black-tailed jackrabbit | Lepus californicus | Least Concern | Deserts and scrub of northern and central Mexico |
| Antelope jackrabbit | Lepus alleni | Near Threatened | Sonoran Desert, mainly Sonora state |
| North American beaver | Castor canadensis | Least Concern | Rivers and highland lakes in northern and central Mexico |
| American badger | Taxidea taxus | Least Concern | Grasslands and deserts of northern Mexico |
| Raccoon | Procyon lotor | Least Concern | Forests and wetlands nationwide |
| White-nosed coati | Nasua narica | Least Concern | Forests from northern to southern Mexico |
| Kinkajou | Potos flavus | Least Concern | Tropical forests in southern Mexico: Chiapas,Oaxaca |
| Tayra | Eira barbara | Least Concern | Lowland forests of southern Mexico |
| Geoffroy’s spider monkey | Ateles geoffroyi | Endangered | Southern lowland forests: Chiapas,Veracruz (fragmented) |
| Mexican gray squirrel | Sciurus aureogaster | Least Concern | Central and southern Mexico: Veracruz,Oaxaca,Chiapas regions |
| Central American agouti | Dasyprocta punctata | Least Concern | Southern lowland forests: Chiapas,Oaxaca |
| Hoary bat | Lasiurus cinereus | Least Concern | Widespread migratory species across Mexico |
| Big brown bat | Eptesicus fuscus | Least Concern | Widespread across Mexico in varied habitats |
| Gray fox | Urocyon cinereoargenteus | Least Concern | Woodlands, scrub, and mountains across Mexico |
| Striped skunk | Mephitis mephitis | Least Concern | Northern and central Mexico habitats |
| Spotted skunk | Spilogale angustifrons | Least Concern | Northern and central Mexico in varied habitats |
| Nutria (Coypu) | Myocastor coypus | Least Concern | Introduced, established in wetlands of northern/central Mexico |
| Pantropical spotted dolphin | Stenella attenuata | Least Concern | Offshore Pacific waters of Mexico |
| Spinner dolphin | Stenella longirostris | Least Concern | Tropical Pacific and Gulf waters near Mexico |
| Mexican long-tongued bat | Choeronycteris mexicana | Near Threatened | Arid and semi-arid regions from Sonora to Oaxaca |
| Harbor seal | Phoca vitulina | Least Concern | Pacific coast and Gulf of California shorelines |
| White-lipped peccary | Tayassu pecari | Vulnerable | Southern lowland forests: Chiapas (limited) and border areas |
| Black howler | Alouatta pigra | Endangered | Yucatán Peninsula and adjacent lowlands (Yucatán, Campeche, Quintana Roo, southern Chiapas) |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | Least Concern | Widespread in human settlements across Mexico (introduced) |
| Brown rat | Rattus norvegicus | Least Concern | Widespread in urban, port, and agricultural areas (introduced) |
| Long-tailed weasel | Neogale frenata | Least Concern | Widespread across Mexico except driest deserts |
| Hispid cotton rat | Sigmodon hispidus | Least Concern | Grasslands and wetlands across much of Mexico |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | Least Concern | Coastal and urban areas across Mexico (introduced) |
| Elk | Cervus canadensis | Least Concern | Reintroduced populations in northern states: Sonora,Chihuahua,Coahuila |
| Water opossum | Chironectes minimus | Least Concern | Riparian lowlands of southern Mexico: Chiapas |
| Virginia opossum | Didelphis virginiana | Least Concern | Northern and central Mexico woodlands and edges |
Images and Descriptions

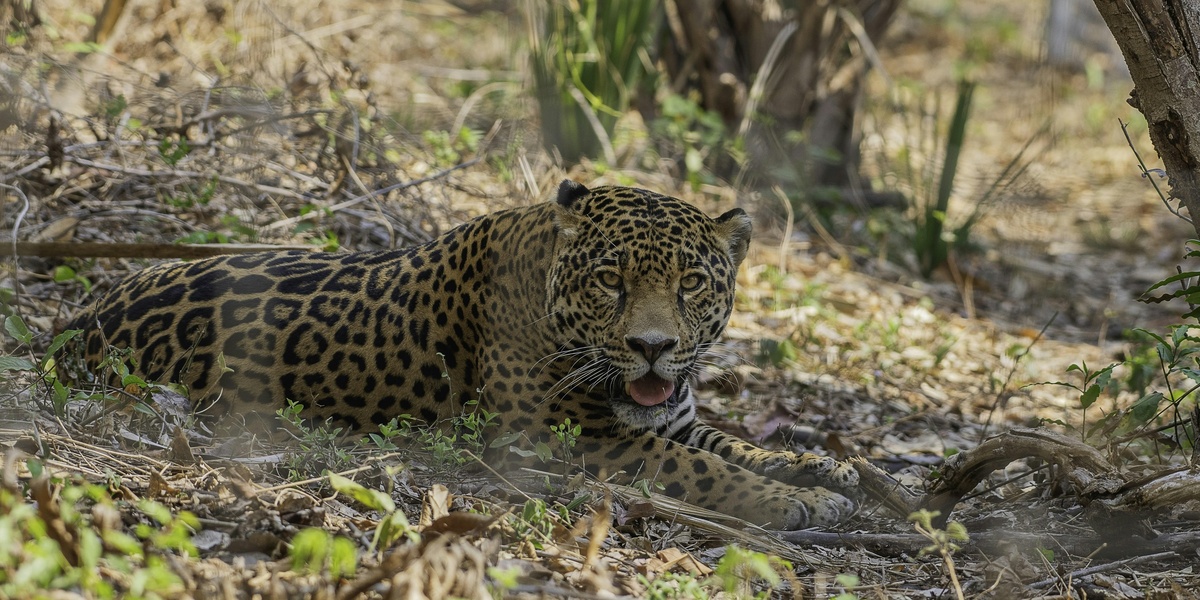
Jaguar
Powerful, spotted big cat of Mexico’s tropical forests and wetlands. Often secretive, jaguars hunt deer and peccaries; their presence indicates healthy ecosystems. Threats include habitat loss and poaching; look for them in protected reserves in southern states.

Puma
Large adaptable predator found from arid north to southern mountains. Solitary and stealthy, pumas prey on deer and small mammals. They survive near human landscapes but face habitat fragmentation and conflict with ranchers.

Ocelot
Medium-sized spotted cat of dense forest and brush. Nocturnal and arboreal, ocelots eat rodents, birds, and small mammals. They are prized historically for fur and now protected; best spotted in southern protected areas.

Margay
Small, nocturnal tree-climbing cat with large eyes and flexible ankles. Margays hunt birds and monkeys in the canopy. Threatened by deforestation and pet trade, they are a rare sight for wildlife watchers.

Bobcat
Robust, short-tailed wildcat common in varied habitats from deserts to forests. Crepuscular and adaptable, bobcats eat rabbits and rodents. They tolerate fragmented landscapes but avoid heavily urbanized areas.

Coyote
Versatile medium-sized canid found from deserts to cities. Coyotes are omnivores and clever scavengers, often adapting to urban environments. Their flexible diet and behavior make them one of Mexico’s most widespread carnivores.

Gray wolf
Iconic large canid historically widespread; Mexican recovery focuses on reintroduced wolves in the north. Wolves hunt elk and deer in packs; conservation balances recovery with livestock protection.

Jaguarundi
Low-slung, weasel-like wild cat with uniform coat color. Jaguarundis are daytime hunters of birds, reptiles, and small mammals in scrub and riparian habitats. Often overlooked due to secretive habits.

White-tailed deer
Familiar deer with bushy tail used as a signal. Found in forests, scrub, and farmland, they are an important game species and prey for large predators. Populations vary regionally with hunting pressure.

Mule deer
Large deer of open country and mountains with mule-like ears. Mule deer thrive in semi-arid highlands and are valued by hunters. Habitat loss and fragmentation affect some local populations.

Pronghorn
Fast, antelope-like ungulate of open plains and deserts. Pronghorns are North America’s speed specialists, relying on sight and endurance to escape predators. Populations reduced by fencing and habitat loss.

Collared peccary
Sturdy, pig-like ungulate traveling in small herds. Peccaries are social, feeding on fruits, roots, and cacti. Common across many habitats, they are important seed dispersers in tropical and dry forests.

Baird’s tapir
Large browsing mammal of lowland rainforests and wetlands. Baird’s tapir is Mexico’s largest terrestrial mammal, important for seed dispersal. Severely threatened by deforestation and hunting, found in remote southern reserves.

West Indian manatee
Gentle, slow-moving marine herbivore in warm coastal lagoons and rivers. Manatees graze on seagrass and mangroves and are vulnerable to boat strikes and habitat loss along the Yucatán and Gulf coasts.

Vaquita
Small, critically endangered porpoise endemic to the northern Gulf of California. Vaquita populations are tiny due to bycatch in illegal gillnets; conservationists regard them as one of the world’s most threatened marine mammals.

Humpback whale
Acrobatic baleen whale famed for breaching and songs. Humpbacks migrate through Mexican waters to feed or breed; whale-watching around Baja California is popular during migrations.

Blue whale
The world’s largest animal visits Mexican offshore waters to feed on krill. Blue whales are globally endangered; sightings in productive Gulf and Pacific waters attract research and ecotourism.

Bottlenose dolphin
Robust, sociable dolphin commonly seen near shore. Bottlenose dolphins form pods and are often observed bow-riding; they thrive in coastal waters but face pollution and fisheries interactions.
Sperm whale
Massive-headed deep-diving whale that feeds on squid in deep waters off Mexico. Sperm whales surface to breathe and produce strong social sounds; they face historic whaling pressures and modern entanglement risks.

California sea lion
Noisy, social pinniped seen on rocky shores and islands. Males have loud territorial displays; sea lions forage in coastal waters and haul out on islands, often near human activity.

Guadalupe fur seal
Once nearly extirpated, this fur seal now breeds on remote Baja islands. Small colonies are recovering but remain vulnerable to disturbance and climate effects.

Mexican free-tailed bat
Famous for enormous maternity colonies bursting from caves at dusk. This insectivorous bat roosts in huge numbers (sometimes millions), playing a key role in pest control.

Lesser long-nosed bat
Nectar-feeding bat that pollinates agave and cactus flowers. Migratory and vital to desert ecosystems, it faces threats from habitat loss and agave harvesting.

Greater long-nosed bat
Large nectar-feeding bat that migrates long distances following flowering agaves and cacti. Essential pollinator facing declines from habitat fragmentation and loss of native plants.

Common vampire bat
Blood-feeding bat that mainly targets livestock and wildlife at night. Social and roosting in caves or buildings, vampire bats impact ranchers and are studied for disease ecology.

Nine-banded armadillo
Small armored mammal that digs for insects and grubs. Armadillos are solitary and have unique reproductive quirks; their range is expanding with changing climates.

Mexican volcano rabbit
Tiny, endemic rabbit living among grasses on cool volcanic slopes. Restricted to high-elevation mounts near Mexico City, it is threatened by habitat loss and fire.

Eastern cottontail
Common rabbit with a white tail, adaptable to many habitats including farmland and urban edges. Widespread and often seen at dawn and dusk feeding on grasses and shrubs.

Black-tailed jackrabbit
Large desert hare with long ears and powerful hindlegs. Crepuscular and fast, black-tailed jackrabbits are a common prey species for raptors and carnivores.

Antelope jackrabbit
Large, desert-adapted hare with long ears and salt-and-pepper fur. Specialized to Sonoran habitats, it is vulnerable to habitat conversion and localized declines.

North American beaver
Large semi-aquatic rodent building dams and lodges that reshape waterways. Beavers create wetlands benefiting biodiversity; Mexican populations persist in forested river valleys and highlands.

American badger
Stocky, fossorial predator that digs for small mammals. Badgers are solitary, active at night and dawn, and are important small-mammal population regulators in arid zones.

Raccoon
Masked, adaptable omnivore frequently found near water and human settlements. Raccoons forage for fruits, crustaceans, and refuse; they thrive in diverse habitats including urban areas.

White-nosed coati
Social, long-tailed procyonid seen in groups; diurnal and curious. Coatis forage for insects, fruits, and eggs, often in forest canopy and along trails in protected areas.

Kinkajou
Arboreal, nocturnal rainforest mammal with a prehensile tail and long tongue for nectar. Kinkajous are playful tree-dwellers that feed on fruit and flowers, rarely seen due to secretive habits.

Tayra
Sleek, diurnal mustelid that hunts rodents, birds, and fruit in forest canopies and on the ground. Tayras are curious and agile omnivores found in intact tropical forests.

Geoffroy’s spider monkey
Large, long-limbed arboreal primate using brachiation to move through canopy. Spider monkeys feed on fruit and are sensitive to deforestation and hunting, making them conservation priorities.

Mexican gray squirrel
Bushy-tailed tree squirrel that forages on seeds, fruits, and nuts. Common in woodlands and gardens, they are active both day and early evening and are familiar to residents.

Central American agouti
Medium-sized rodent that disperses seeds in tropical forests. Agoutis are diurnal and important for forest regeneration; they are often seen near fruiting trees.

Hoary bat
Solitary, tree-roosting insectivore that migrates through Mexico. Hoary bats are swift aerial hunters active at dusk and night, recognizable by frosted fur.

Big brown bat
Robust insectivorous bat that roosts in buildings, bridges, and caves. Big brown bats help control pest insects and are common near human settlements.

Gray fox
Small, nimble canid that can climb trees to escape predators. Gray foxes hunt small mammals and birds; they are adaptable but often shy around people.

Striped skunk
Familiar black-and-white mammal using a powerful spray for defense. Striped skunks eat insects, small vertebrates, and plant matter and often live near farms and rural settlements.

Spotted skunk
Small, nimble skunk species that performs handstands when threatened. Spotted skunks prey on insects and rodents; they are nocturnal and elusive.

Nutria (Coypu)
Large semi-aquatic rodent introduced for fur farming and now present in wetlands. Nutria burrow and feed on aquatic plants, sometimes causing habitat damage and conflict with conservation goals.

Pantropical spotted dolphin
Graceful, fast-swimming dolphin common in open ocean. Often forms large schools and is seen in offshore waters; vulnerable to bycatch in some fisheries.

Spinner dolphin
Slender, acrobatic dolphin known for spinning leaps. Spinner dolphins frequent shallow bays and offshore waters and are a common target for marine ecotourism.

Mexican long-tongued bat
Medium-sized nectar-feeding bat that visits agaves and flowers with a long tongue. Important pollinator but sensitive to roost disturbance and habitat loss.

Harbor seal
Small, spotted pinniped hauling out on rocky shores and beaches. Harbor seals feed on fish nearshore and are occasionally seen in Gulf and Baja inlets and estuaries.

White-lipped peccary
Social, herd-forming pig-like ungulate roaming tropical forests. White-lipped peccaries shape forest ecology but face steep declines from hunting and habitat loss in fragmented southern habitats.

Black howler
Loud-calling howler monkey of tropical forests, important seed disperser. Black howlers live in family groups and are vulnerable to habitat fragmentation and hunting.

House mouse
Small commensal rodent living in buildings and farms. House mice thrive around people, reproduce quickly, and are ubiquitous in urban and rural environments throughout Mexico.

Brown rat
Large, adaptable rodent commonly found in cities, sewers, and farms. Brown rats forage omnivorously and are a familiar urban wildlife species with global distribution.

Long-tailed weasel
Small, elongated predator feeding on rodents and rabbits. Long-tailed weasels are agile hunters in grasslands and woodlands and are often active at dusk and night.

Hispid cotton rat
Stout, coarse-furred rodent common in grassy areas and marsh edges. Important prey for many predators, cotton rats are prolific breeders and influence grassland dynamics.

Black rat
Agile climber among commensal rodents, commonly found in older structures and ports. Black rats eat seeds, fruit, and scraps and are widespread in warmer coastal regions.

Elk
Large cervid once widespread, now reintroduced in parts of northern Mexico. Elk favor open woodlands and grasslands and are a charismatic species for conservation and hunting management.

Water opossum
Also called yapok, a semi-aquatic marsupial that forages in streams for crustaceans and fish. The water opossum is unique among marsupials for its aquatic habits and webbed feet.

Virginia opossum
Adaptable marsupial that forages widely including near humans. Opossums eat insects, fruit, and carrion; they are North America’s only marsupial and common in varied habitats.





